
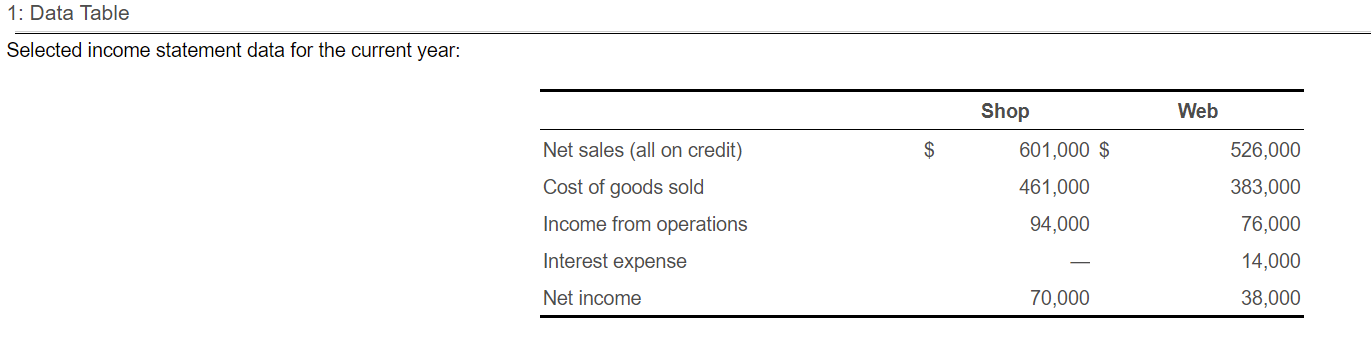
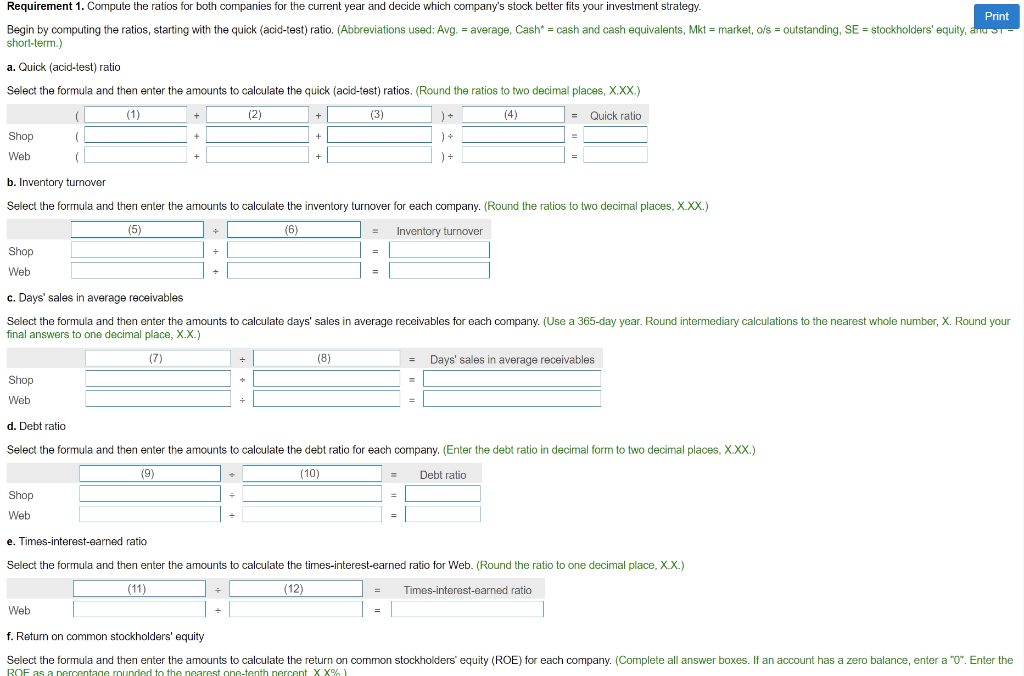
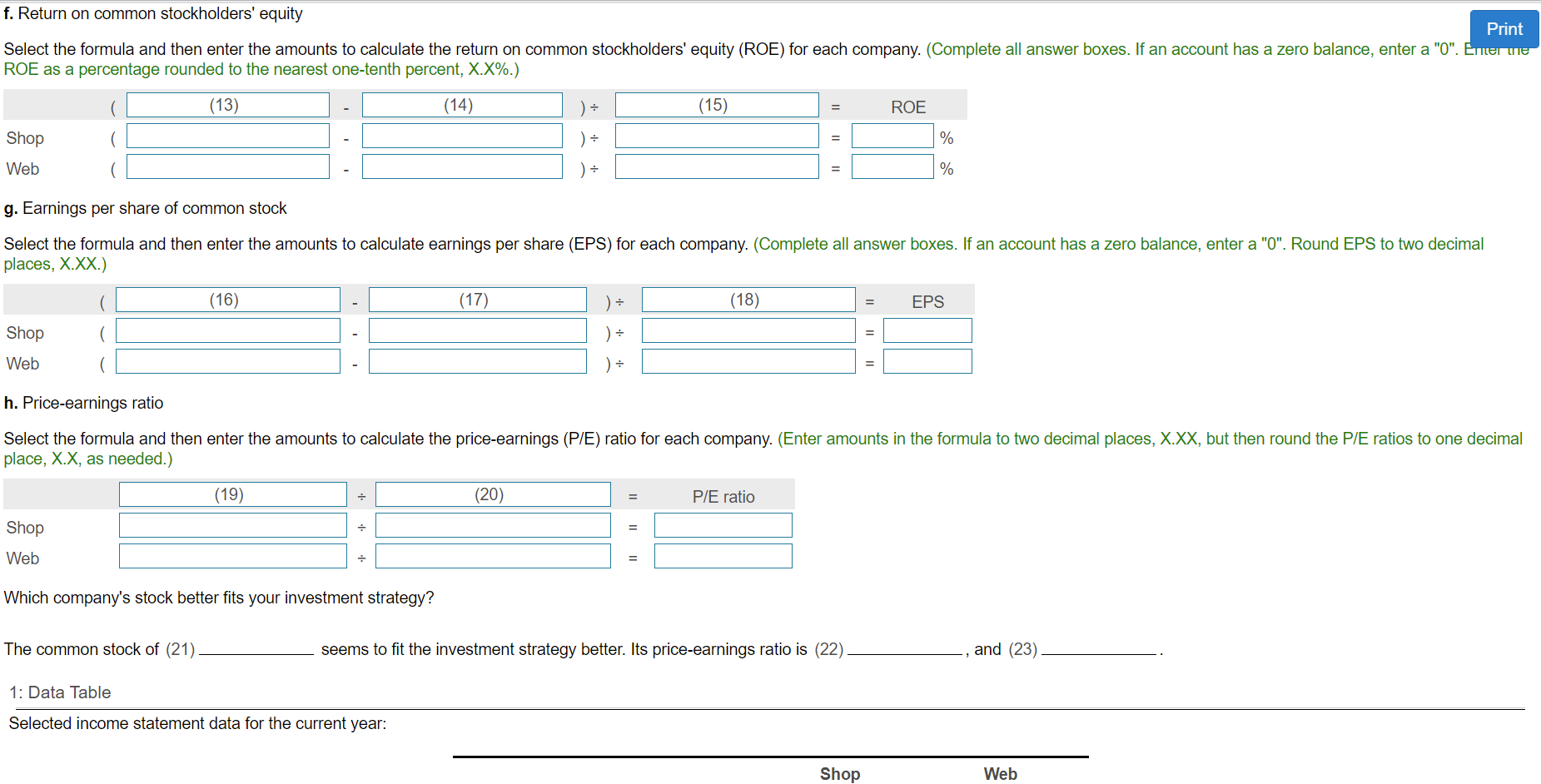
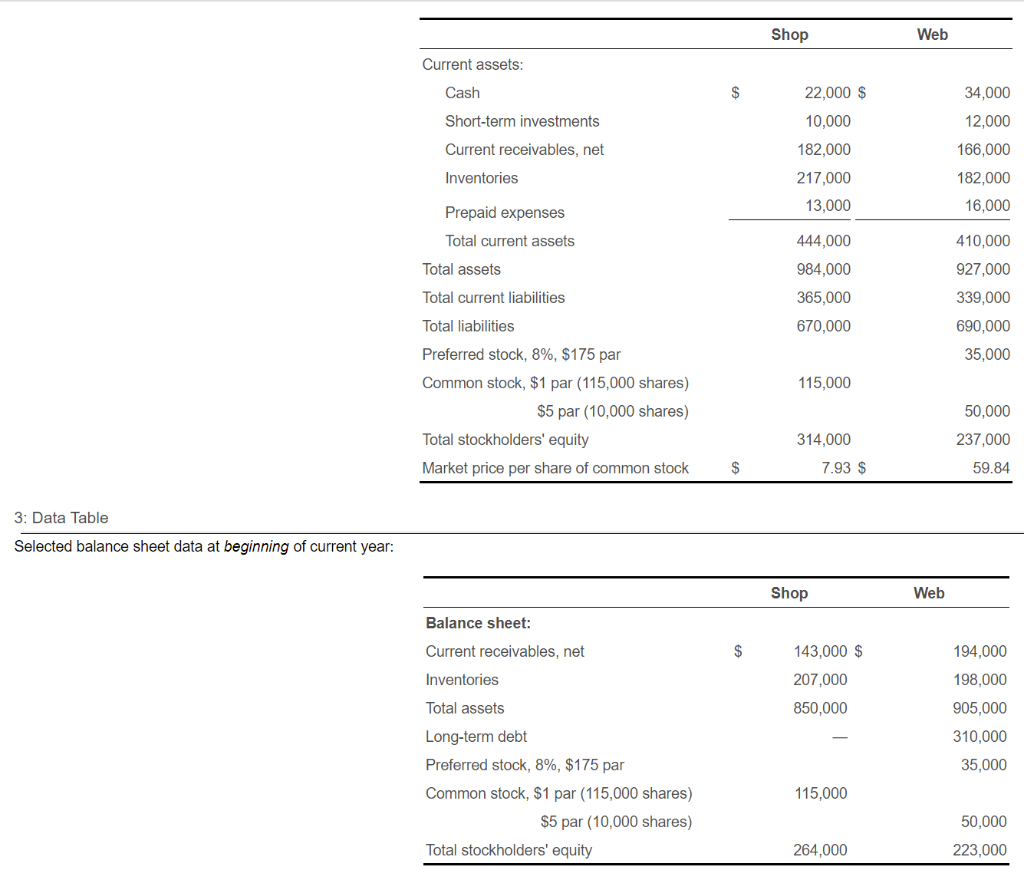
7. Assume that you are considering purchasing stock as an investment. You have narrowed the choice to either Shop Corporation stock or Web Company stock and have assembled the following data for the two companies. 1(Click the icon to view the income statement data.) 2 (Click the icon to view data at end of current year.) 3(Click the icon to view data at beginning of current year.) Your strategy is to invest in companies that have low price-earnings ratios but appear to be in good shape financially. Assume that you have analyzed all other factors and that your decision depends on the results of ratio analysis. Read the requirements4. Requirement 1. Compute the ratios for both companies for the current year and decide which company's stock better fits your investment strategy. Begin by computing the ratios, starting with the quick (acid-test) ratio. (Abbreviations used: Avg. = average, Cash* = cash and cash equivalents, Mkt = market, o/s = outstanding, SE = stockholders' equity, and ST = short-term.) 1: Data Table Selected income statement data for the current year: Web Shop 601,000 $ $ 526,000 Net sales (all on credit) Cost of goods sold Income from operations 461,000 94,000 383,000 76,000 14,000 Interest expense Net income 70,000 38,000 Requirement 1. Compute the ratios for both companies for the current year and decide which company's stock better fits your investment strategy. Print Begin by computing the ratios, starting with the quick (acid-test) ratio. (Abbreviations used: Avg. = average, Cash* = cash and cash equivalents, Mkt = market, o/s = outstanding, SE = stockholders' equity, anus- short-term.) a. Quick (acid-test) ratio Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the quick (acid-test) ratios. (Round the ratios to two decimal places, X.XX.) (1) (2) + (3) (4) = Quick ratio + )4 Shop Web ( ) + = b. Inventory tumover Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the inventory turnover for each company. (Round the ratios to two decimal places, X.XX.) (5) (6) Inventory turnover Shop Web c. Days' sales in average receivables Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate days' sales in average receivables for each company. (Use a 365-day year. Round intermediary calculations to the nearest whole number, X. Round your final answers to one decimal place, X.X.) (7) ( (8) Days' sales in average receivables Shop + Web + d. Debt ratio Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the debt ratio for each company. (Enter the debt ratio in decimal form to two decimal places, XXX.) (9) (10) Debt ratio Shop Web e. Times-interest-earned ratio Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the times-interest-earned ratio for Web. (Round the ratio to one decimal place, X.X.) (11) (12) Times-interest-earned ratio Web f. Return on common stockholders' equity Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the return on common stockholders' equity (ROE) for each company. (Complete all answer boxes. If an account has a zero balance, enter a "0". Enter the ROF as a percentage rounded to the nearest one-tenth percent XX%) f. Return on common stockholders' equity Print Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the return on common stockholders' equity (ROE) for each company. (Complete all answer boxes. If an account has a zero balance, enter a "0". Emer e ROE as a percentage rounded to the nearest one-tenth percent, X.X%.) (13) (14) ): (15) ROE Shop ) = = % Web % g. Earnings per share of common stock Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate earnings per share (EPS) for each company. (Complete all answer boxes. If an account has a zero balance, enter a "0". Round EPS to two decimal places, X.XX.) (16) (17) ): (18) EPS ( Shop Web h. Price-earnings ratio Select the formula and then enter the amounts to calculate the price-earnings (P/E) ratio for each company. (Enter amounts in the formula to two decimal places, X.XX, but then round the P/E ratios to one decimal place, X.X, as needed.) (19) (20) P/E ratio Shop . = Web = Which company's stock better fits your investment strategy? The common stock of (21) seems to fit the investment strategy better. Its price-earnings ratio is (22) and (23) 1: Data Table Selected income statement data for the current year: Shop Web Shop Web Current assets: Cash $ 22,000 $ 34,000 10,000 12,000 Short-term investments Current receivables, net Inventories 182,000 166,000 182,000 217,000 13,000 16,000 Prepaid expenses Total current assets 444,000 410,000 984,000 Total assets Total current liabilities 927,000 339,000 365,000 670,000 690,000 35,000 115,000 Total liabilities Preferred stock, 8%, $175 par Common stock, $1 par (115,000 shares) $5 par (10,000 shares) Total stockholders' equity Market price per share of common stock 314,000 50,000 237,000 59.84 $ 7.93 $ 3: Data Table Selected balance sheet data at beginning of current year: Shop Web Balance sheet: Current receivables, net $ 143,000 $ 194,000 Inventories 198,000 207,000 850,000 905,000 310,000 35,000 Total assets Long-term debt Preferred stock, 8%, $175 par Common stock, $1 par (115,000 shares) $5 par (10,000 shares) Total stockholders' equity 115,000 50,000 264,000 223,000











