

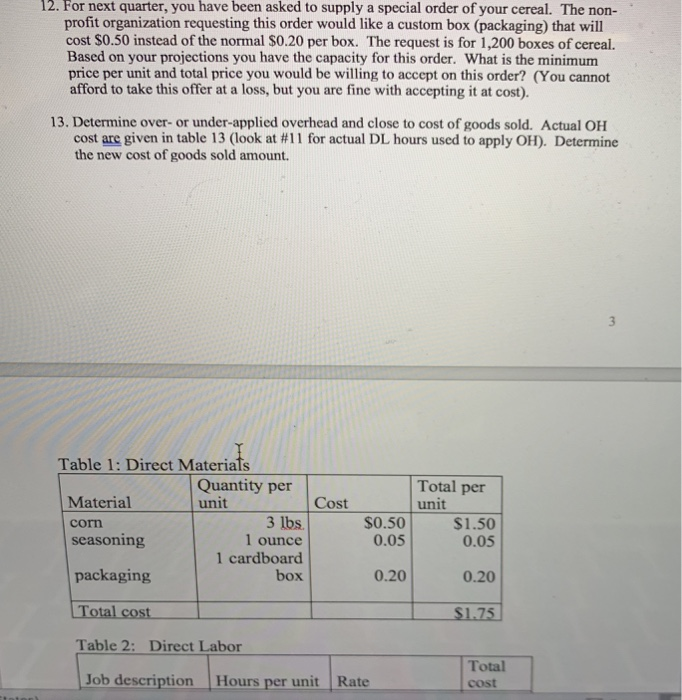
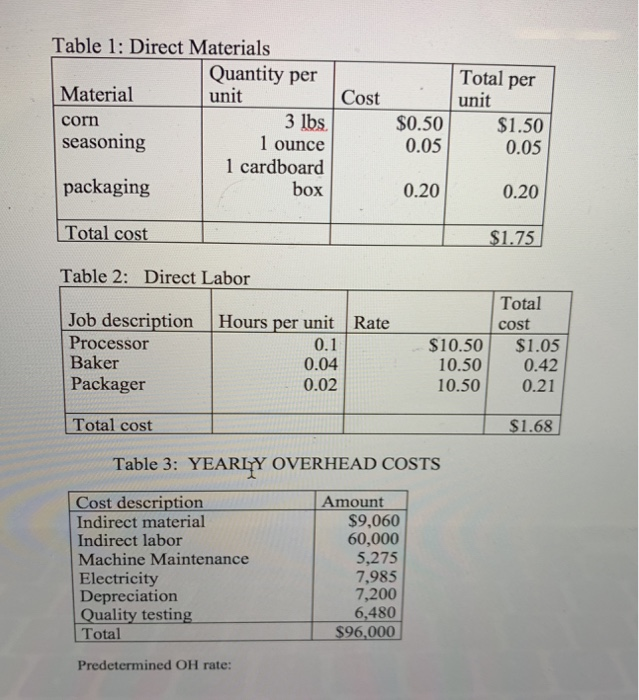
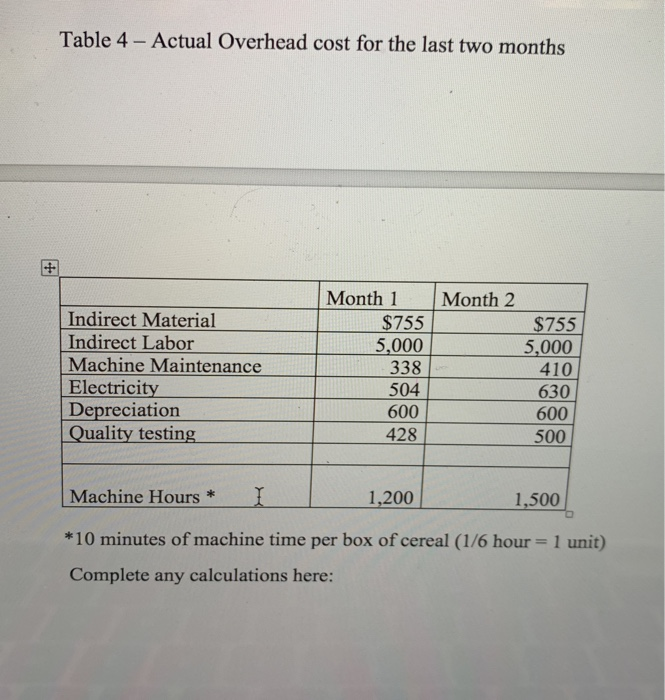
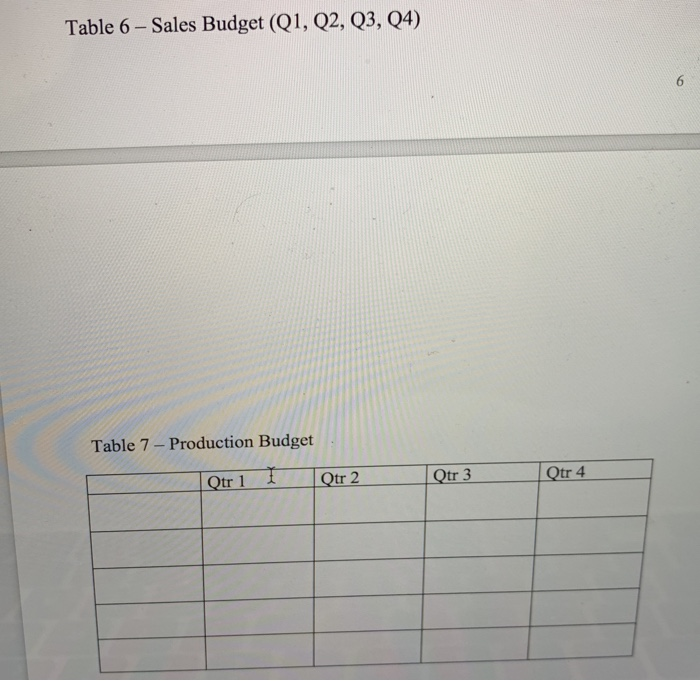
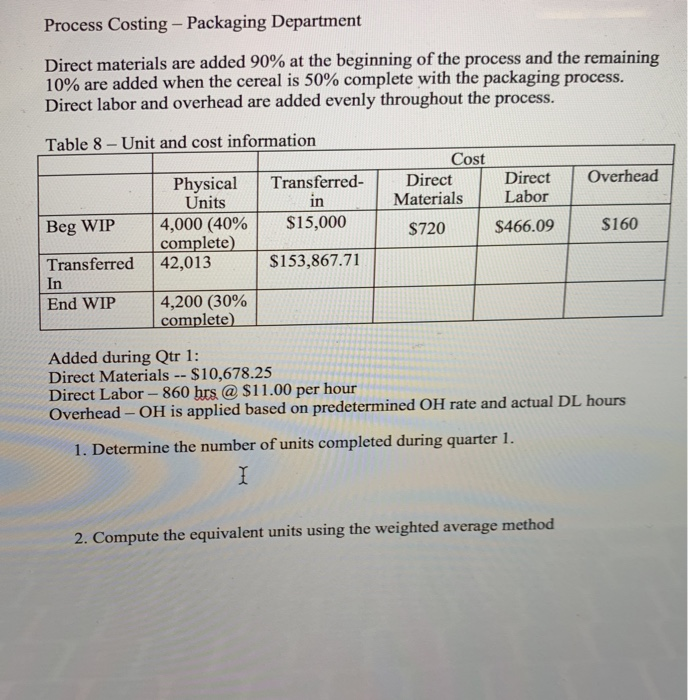

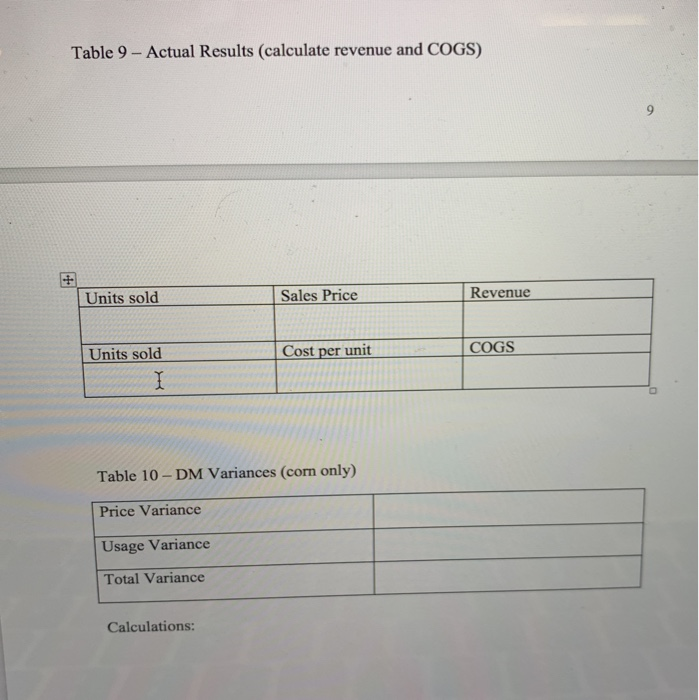
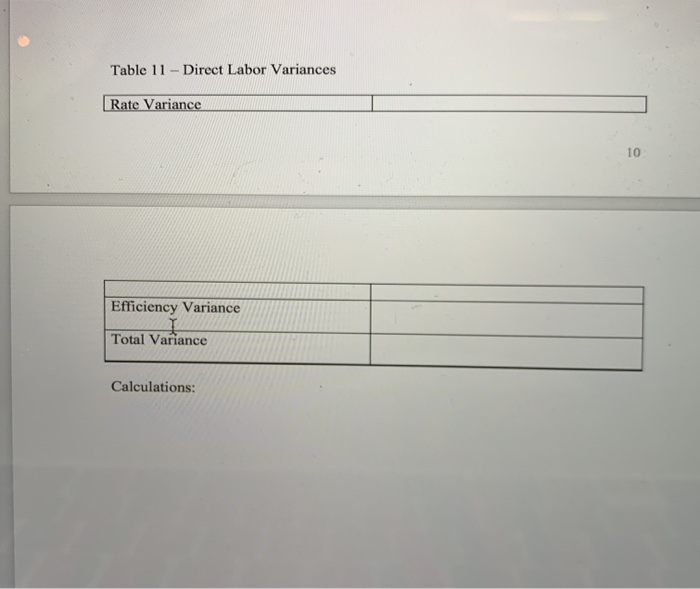
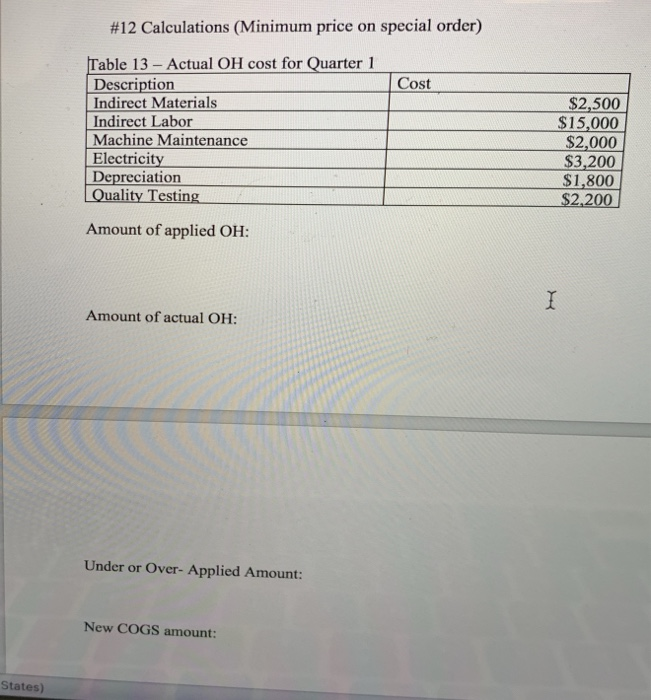
7. Budgeting: 2 Create a sales budget using the information for earning an average profit for the a. year. You will break the budget down into the four quarters for the year. (Sales tend to be consistent each quarter, you can only sale a whole unit so round-up if necessary) Use table 6 to complete the sales budget. b. Create a production budget for each quarter of the year (keep it in quarters; you do not need to break it down by rnonth). You desire to keep IO% of next quarter's sales in ending inventory. Sales for Qtr 1 the following year (year 2) are expected to be 30,000 boxes of cereal. There is not any beginning finished goods inventory for quarter one this year. Use table 7 to complete the production budget 8. Running quarter one Weighted-average process costing. Table 8 presents the information for the packaging department. Complete the questions under table 8. Actuals are in for quardr one. You sold 10% more units than you budgeted for (round to a whole unit), but price per unit was only $5.50. 9. a. Calculate revenue b. Compute the cost of goods sold (total and per unit) before adjusting for actual OH cost 10. Actual corn usage for quarter one was 146,232 pounds at a price of s0.49 per pound. Actual equivalent units of production (boxes of cereal) completed through the first process (where the corn is added) was 46,214. Calculate the direct materials vari for the corn (price, usage, and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable 11. Actual direct labor hours for the quarter were 7,660 at an average rate of $11.00 per hour For actual production, you expected to use 7,300 direct labor hours. Calculate the direct labor variances (rate, efficiency and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable Table 1: Direct Materials Quantity per unit Total per Material corm seasoning Cost unit 3 lbs. 1 ounce 1 cardboard box S0.50 $1.50 0.05 0.05 0.20 $1.75 packaging Total cost Table 2: Direct Labor 0.20 Total cost Job description Hours per unit Rate Processor Baker Packager 0.1 0.04 0.02 $10.50 $1.05 10.500.42 10.500.21 Total cost $1.68 Table 3: YEARLY OVERHEAD COSTS Cost description Indirect material Indirect labor Machine Maintenance Electricity Depreciation Quality testing Total Amount $9,060 60,000 5,275 7,985 7,200 6,480 S96,000 Predetermined OH rate Table 4- Actual Overhead cost for the last two months Month 1 Month 2 Indirect Material Indirect Labor Machine Maintenance $755 5,000 338 504 600 428 $755 5,000 410 630 600 500 Blentc Depreciation Quality testing Machine Hours * * 10 minutes of machine time per box of cereal (1/6 hour= 1 unit) Complete any calculations here: 1,200 1,500 Table 6-Sales Budget (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4) Table 7- Production Budget tr 1 Otr 2 Qtr 4 AaBbCcDdE AaBbCeDdi Aab EmphasisHeading 1 3. Compute the cost per equivalent unit using the weighted average method 4. Compute the cost of goods transferred to finished goods inventory 5. Compute the ending balance in WIP, Packaging 0 1 FS F6 F7 F8 F9 10 7. Budgeting: 2 Create a sales budget using the information for earning an average profit for the a. year. You will break the budget down into the four quarters for the year. (Sales tend to be consistent each quarter, you can only sale a whole unit so round-up if necessary) Use table 6 to complete the sales budget. b. Create a production budget for each quarter of the year (keep it in quarters; you do not need to break it down by rnonth). You desire to keep IO% of next quarter's sales in ending inventory. Sales for Qtr 1 the following year (year 2) are expected to be 30,000 boxes of cereal. There is not any beginning finished goods inventory for quarter one this year. Use table 7 to complete the production budget 8. Running quarter one Weighted-average process costing. Table 8 presents the information for the packaging department. Complete the questions under table 8. Actuals are in for quardr one. You sold 10% more units than you budgeted for (round to a whole unit), but price per unit was only $5.50. 9. a. Calculate revenue b. Compute the cost of goods sold (total and per unit) before adjusting for actual OH cost 10. Actual corn usage for quarter one was 146,232 pounds at a price of s0.49 per pound. Actual equivalent units of production (boxes of cereal) completed through the first process (where the corn is added) was 46,214. Calculate the direct materials vari for the corn (price, usage, and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable 11. Actual direct labor hours for the quarter were 7,660 at an average rate of $11.00 per hour For actual production, you expected to use 7,300 direct labor hours. Calculate the direct labor variances (rate, efficiency and total) and indicate if these variances are favorable or unfavorable Table 1: Direct Materials Quantity per unit Total per Material corm seasoning Cost unit 3 lbs. 1 ounce 1 cardboard box S0.50 $1.50 0.05 0.05 0.20 $1.75 packaging Total cost Table 2: Direct Labor 0.20 Total cost Job description Hours per unit Rate Processor Baker Packager 0.1 0.04 0.02 $10.50 $1.05 10.500.42 10.500.21 Total cost $1.68 Table 3: YEARLY OVERHEAD COSTS Cost description Indirect material Indirect labor Machine Maintenance Electricity Depreciation Quality testing Total Amount $9,060 60,000 5,275 7,985 7,200 6,480 S96,000 Predetermined OH rate Table 4- Actual Overhead cost for the last two months Month 1 Month 2 Indirect Material Indirect Labor Machine Maintenance $755 5,000 338 504 600 428 $755 5,000 410 630 600 500 Blentc Depreciation Quality testing Machine Hours * * 10 minutes of machine time per box of cereal (1/6 hour= 1 unit) Complete any calculations here: 1,200 1,500 Table 6-Sales Budget (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4) Table 7- Production Budget tr 1 Otr 2 Qtr 4 AaBbCcDdE AaBbCeDdi Aab EmphasisHeading 1 3. Compute the cost per equivalent unit using the weighted average method 4. Compute the cost of goods transferred to finished goods inventory 5. Compute the ending balance in WIP, Packaging 0 1 FS F6 F7 F8 F9 10


















