Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
8. Purchasing-power parity Using data from The Economist's Big Mac Index for 2019, the following table shows the local currency price of a Big Mac
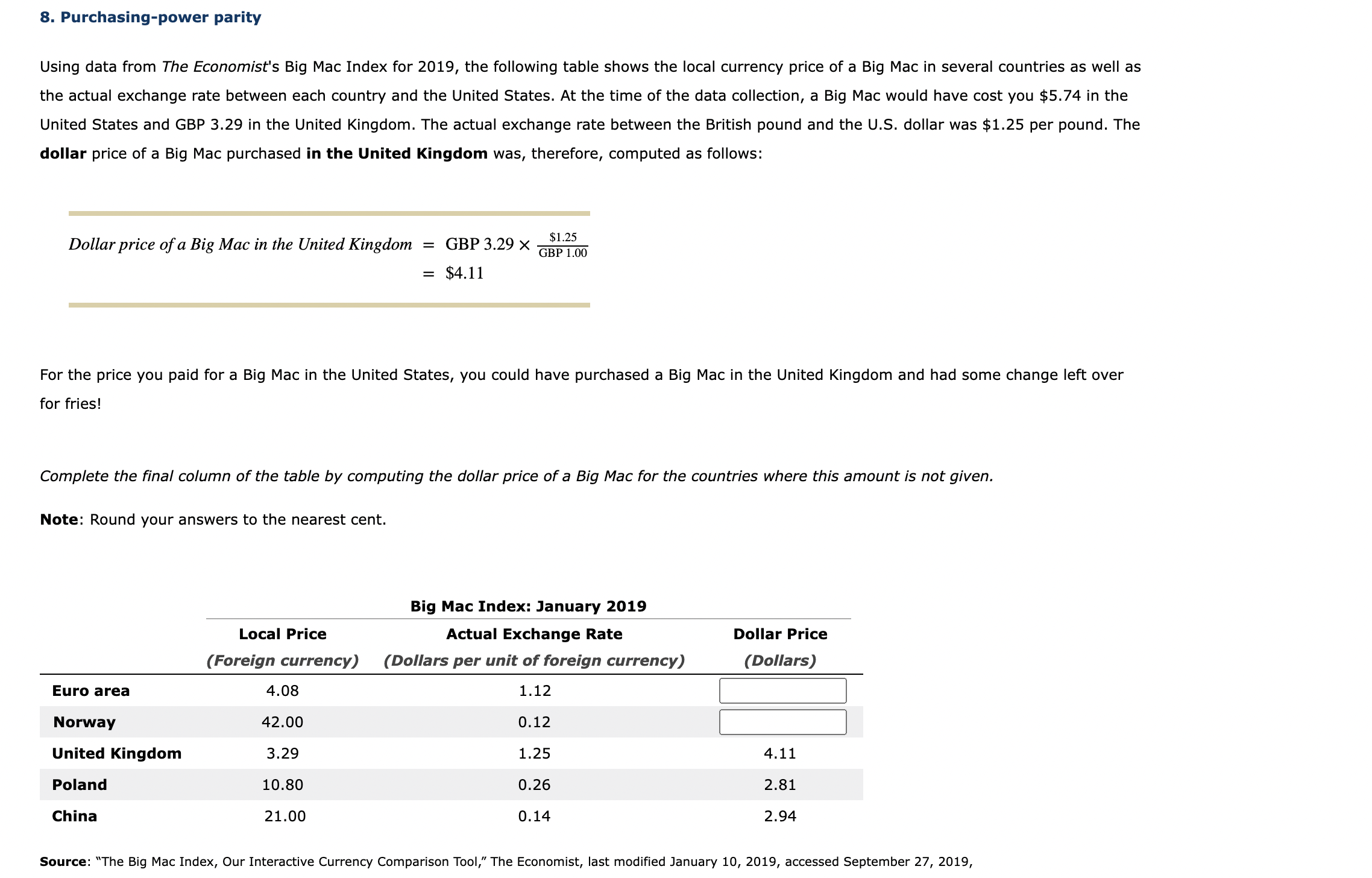
 8. Purchasing-power parity Using data from The Economist's Big Mac Index for 2019, the following table shows the local currency price of a Big Mac in several countries as well as the actual exchange rate between each country and the United States. At the time of the data collection, a Big Mac would have cost you $5.74 in the United States and GBP 3.29 in the United Kingdom. The actual exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar was $1.25 per pound. The dollar price of a Big Mac purchased in the United Kingdom was, therefore, computed as follows: DollarpriceofaBigMacintheUnitedKingdom=GBP3.29GBP1.00$1.25=$4.11 For the price you paid for a Big Mac in the United States, you could have purchased a Big Mac in the United Kingdom and had some change left over for fries! Complete the final column of the table by computing the dollar price of a Big Mac for the countries where this amount is not given. Note: Round your answers to the nearest cent. Source: "The Big Mac Index, Our Interactive Currency Comparison Tool," The Economist, last modified January 10, 2019, accessed September 27, 2019, https://www.economist.comews/2019/07/10/the-big-mac-index. Purchasing-power parity (PPP) theory states that exchange rates would need to equalize the prices of goods in any two countries. For the dollar price of a Big Mac to be the same in both countries, a U.S. citizen would need to be able to convert $5.74 into exactly GBP 3.29 . To find the exchange rate at which hamburger purchasing power is the same in both countries, divide the price in the United States by the price in the United Kingdom: PPPExchangeRate(U.S.DollarsperBritishpound)=GBP3.29$5.74=$1.74perpound The exchange rate that would have equalized the dollar price of a Big Mac in the United States and the Euro area (that is, the PPP exchange rate for Big Macs) is . This change would mean that the euro had against the dollar. If Big Macs were a durable good that could be costlessly transported between countries, which of the following would present an arbitrage opportunity? Check all that apply. Exporting Big Macs from Norway to China Exporting Big Macs from Norway to Poland Exporting Big Macs from the Euro area to the United States
8. Purchasing-power parity Using data from The Economist's Big Mac Index for 2019, the following table shows the local currency price of a Big Mac in several countries as well as the actual exchange rate between each country and the United States. At the time of the data collection, a Big Mac would have cost you $5.74 in the United States and GBP 3.29 in the United Kingdom. The actual exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar was $1.25 per pound. The dollar price of a Big Mac purchased in the United Kingdom was, therefore, computed as follows: DollarpriceofaBigMacintheUnitedKingdom=GBP3.29GBP1.00$1.25=$4.11 For the price you paid for a Big Mac in the United States, you could have purchased a Big Mac in the United Kingdom and had some change left over for fries! Complete the final column of the table by computing the dollar price of a Big Mac for the countries where this amount is not given. Note: Round your answers to the nearest cent. Source: "The Big Mac Index, Our Interactive Currency Comparison Tool," The Economist, last modified January 10, 2019, accessed September 27, 2019, https://www.economist.comews/2019/07/10/the-big-mac-index. Purchasing-power parity (PPP) theory states that exchange rates would need to equalize the prices of goods in any two countries. For the dollar price of a Big Mac to be the same in both countries, a U.S. citizen would need to be able to convert $5.74 into exactly GBP 3.29 . To find the exchange rate at which hamburger purchasing power is the same in both countries, divide the price in the United States by the price in the United Kingdom: PPPExchangeRate(U.S.DollarsperBritishpound)=GBP3.29$5.74=$1.74perpound The exchange rate that would have equalized the dollar price of a Big Mac in the United States and the Euro area (that is, the PPP exchange rate for Big Macs) is . This change would mean that the euro had against the dollar. If Big Macs were a durable good that could be costlessly transported between countries, which of the following would present an arbitrage opportunity? Check all that apply. Exporting Big Macs from Norway to China Exporting Big Macs from Norway to Poland Exporting Big Macs from the Euro area to the United States Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


