Question: 8. The US Government's announced this week that they will bring sanction on countries who buy oil from Iran. This decision is intended to bring
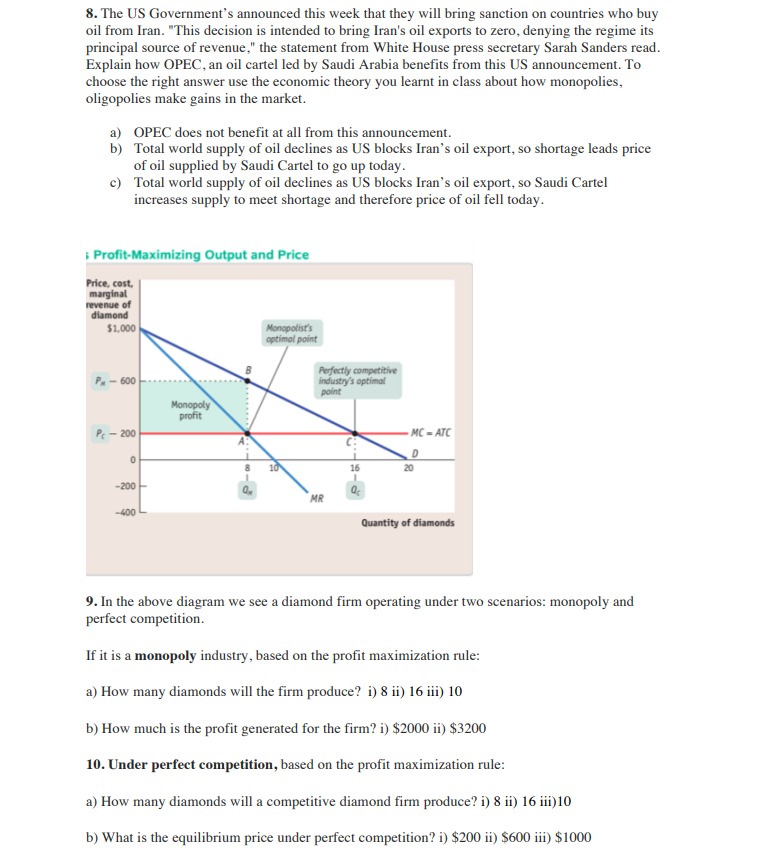

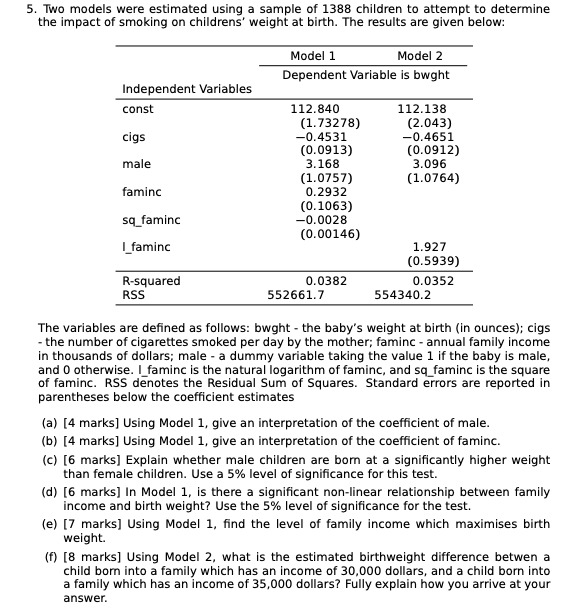

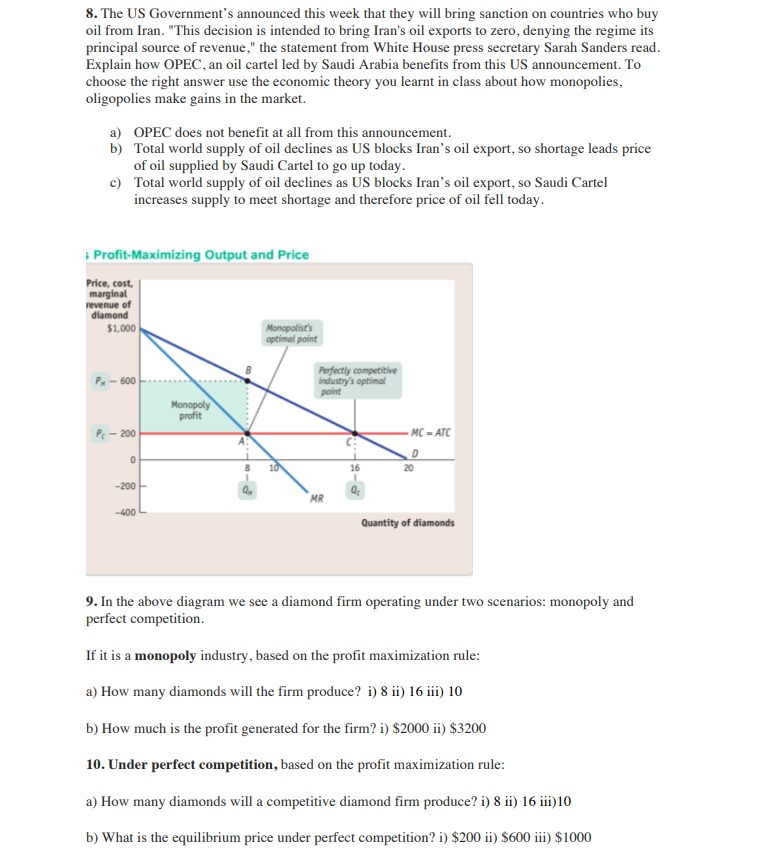

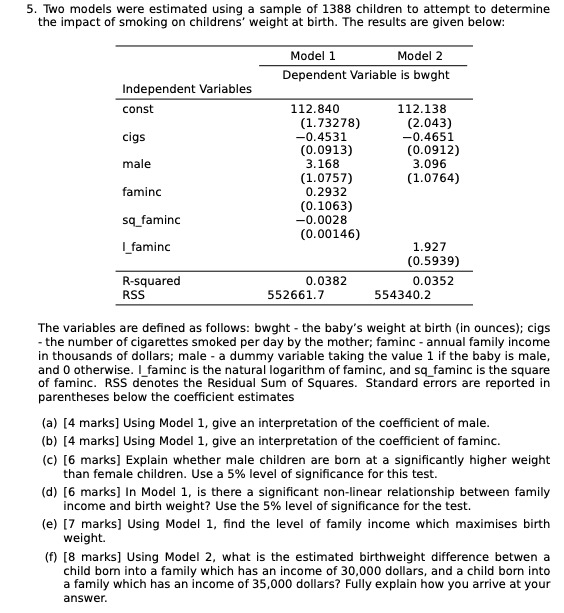

8. The US Government's announced this week that they will bring sanction on countries who buy oil from Iran. "This decision is intended to bring Iran's oil exports to zero, denying the regime its principal source of revenue," the statement from White House press secretary Sarah Sanders read. Explain how OPEC, an oil cartel led by Saudi Arabia benefits from this US announcement. To choose the right answer use the economic theory you learnt in class about how monopolies, oligopolies make gains in the market. a) OPEC does not benefit at all from this announcement. b) Total world supply of oil declines as US blocks Iran's oil export, so shortage leads price of oil supplied by Saudi Cartel to go up today. C) Total world supply of oil declines as US blocks Iran's oil export, so Saudi Cartel increases supply to meet shortage and therefore price of oil fell today. Profit-Maximizing Output and Price Price, cost, marginal revenue of diamond $1,000 Monopolist's optimal point Perfectly competitive PH - 600 industry's optimal point Monopoly profit Pr - 200 MC - ATC D 16 20 -200 MR -400 Quantity of diamonds 9. In the above diagram we see a diamond firm operating under two scenarios: monopoly and perfect competition. If it is a monopoly industry, based on the profit maximization rule: a) How many diamonds will the firm produce? i) 8 ii) 16 iii) 10 b) How much is the profit generated for the firm? i) $2000 ii) $3200 10. Under perfect competition, based on the profit maximization rule: a) How many diamonds will a competitive diamond firm produce? i) 8 ii) 16 iii)10 b) What is the equilibrium price under perfect competition? i) $200 ii) $600 iii) $1000[1] A perfectly competitive aluminum producer is currently producing a quantity where the market price is $0.67 per pound (i.e., 67 cents per pound), average total cost is $0.70, and average variable cost of $0.60 (which corresponds to the minimum point on the average variable cost curve). Would you recommend this firm expand output, contract output, or shut down in the short-run? Provide a graph to illustrate your answer. (2] Suppose the local crawfish market is perfectly competitive, with the following market demand and supply: Market Demand: QD = 6500 - 100P Market Supply: Qs = 1200P, where market quantity demanded (Qo) and market quantity supplied (Qs) are measured in pounds and price (P) is measured in dollars per pound. Assuming all firms have identical costs, suppose the typical firm in the market has the following short-run total cost (TC) and marginal cost (MC), with q being the quantity produced by the firm: Total Cost: TC = 722+ Marginal Cost: MC = 29 200 A. production? What is the price at which a firm is indifferent between producing in the short-run and shutting down B. Determine the market equilibrium price and quantity of crawfish, the output supplied by each firm, and the profit of each firm. How many firms must currently be in this market? C. Based on your answer to B, would you expect to see entry or exit in the long-run? How would this impact the price of crawfish over time, ceteris paribus? [3] A monopolist is operating in the short-run, facing a market demand given by the following: Q = 1000 - 2P, where Q is market quantity and P is market price. Suppose the firm's short-run total cost (TC) is: TC = 100-Q. Find the price and quantity that maximizes this firm's short-run profit. What is the level of profit? Determine the values of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and market welfare under monopoly. If the firm operated as if perfectly competitive (i.e., where P = MC), what would be the values of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and market welfare? What is the value of the deadweight loss in market welfare due to monopoly? [4] The market for lemonade in a town consists of two lemonade stands (i.e., firms), 1 and 2. An agricultural economist estimates the following demand for lemonade in this town: Q=300 - P, where Q is the market quantity and P is the market price. Total costs of the two firms are indicated below: TCI = 60Q1 TC2 = 40Q2 Acting as Cournot competitors, find and graph the reaction functions of each firm (indicating appropriate horizontal- and vertical-axis intercepts). Determine the Cournot equilibrium output of each producer, as well as the profit of each producer.5. Two models were estimated using a sample of 1388 children to attempt to determine the impact of smoking on childrens' weight at birth. The results are given below: Model 1 Model 2 Dependent Variable is bwght Independent Variables const 112.840 112.138 (1.73278) (2.043) cigs -0.4531 -0.4651 (0.0913) (0.0912) male 3.168 3.096 (1.0757) (1.0764) faminc 0.2932 (0.1063) sq_faminc -0.0028 (0.00146) L_faminc 1.927 (0.5939) R-squared 0.0382 0.0352 RSS 552661.7 554340.2 The variables are defined as follows: bwght - the baby's weight at birth (in ounces); cigs - the number of cigarettes smoked per day by the mother; faminc - annual family income in thousands of dollars; male - a dummy variable taking the value 1 if the baby is male, and 0 otherwise. I_faminc is the natural logarithm of faminc, and sq_faminc is the square of faminc. RSS denotes the Residual Sum of Squares. Standard errors are reported in parentheses below the coefficient estimates (a) [4 marks] Using Model 1, give an interpretation of the coefficient of male. (b) [4 marks] Using Model 1, give an interpretation of the coefficient of faminc. (c) [6 marks] Explain whether male children are born at a significantly higher weight than female children. Use a 5% level of significance for this test. (d) [6 marks] In Model 1, is there a significant non-linear relationship between family income and birth weight? Use the 5% level of significance for the test. (e) [7 marks] Using Model 1, find the level of family income which maximises birth weight. (f) [8 marks] Using Model 2, what is the estimated birthweight difference betwee child born into a family which has an income of 30,000 dollars, and a child born into a family which has an income of 35,000 dollars? Fully explain how you arrive at your answer.l) The market for wheat consists of 1000 identical farms, each with the total and marginal cost functions shown: TC = 9 + 0.2q2 where q is measured in bushels per year. The market demand curve for wheat is Q = 6,000 500P, where Q is measured in bushels and P is the price per bushel. a. Determine the short-run equilibrium price and quantity that would exist in the market. b. Calculate the prot maximizing quantity for the individual farm. Calculate a representative farm's short-run prot (loss) at that quantity. c. Assume that the short-run prot or loss is representative of the current long- run prospects in this market. You may further assume that there are no barriers to entry or exit in the market. Describe the expected long-run response to the conditions described in part b. (The TC function for the rm may be regarded as an economic cost function that captures all implicit and explicit costs.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


