Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
According to the Lindeman criterion, a crystal melts when the RMS dis- placement of its atoms exceeds one-third of the average separation of the
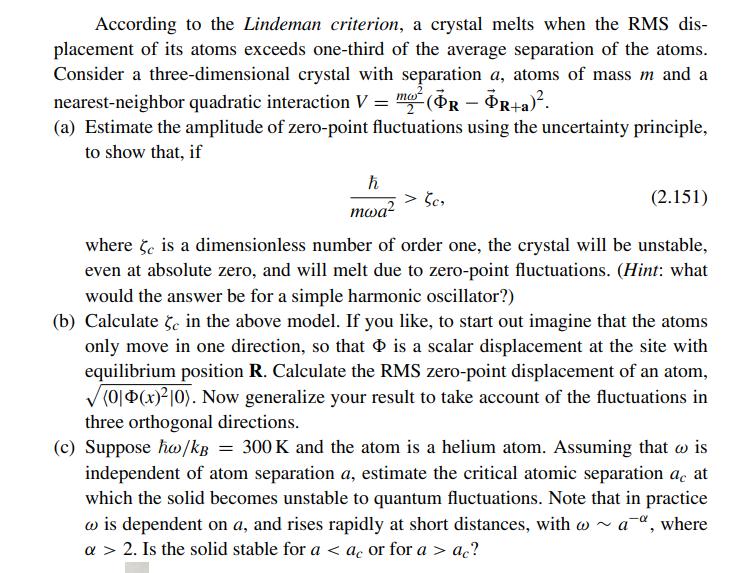
According to the Lindeman criterion, a crystal melts when the RMS dis- placement of its atoms exceeds one-third of the average separation of the atoms. Consider a three-dimensional crystal with separation a, atoms of mass m and a nearest-neighbor quadratic interaction V = ma (OR - PR+a). (a) Estimate the amplitude of zero-point fluctuations using the uncertainty principle, to show that, if mwa Scr where 5c is a dimensionless number of order one, the crystal will be unstable, even at absolute zero, and will melt due to zero-point fluctuations. (Hint: what would the answer be for a simple harmonic oscillator?) (b) Calculate e in the above model. If you like, to start out imagine that the atoms only move in one direction, so that is a scalar displacement at the site with equilibrium position R. Calculate the RMS zero-point displacement of an atom, (01(x)10). Now generalize your result to take account of the fluctuations in three orthogonal directions. (c) Suppose h/kB = 300K and the atom is a helium atom. Assuming that wis independent of atom separation a, estimate the critical atomic separation ac at which the solid becomes unstable to quantum fluctuations. Note that in practice w is dependent on a, and rises rapidly at short distances, with ~ a aa, where a> 2. Is the solid stable for a ac? (2.151)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.48 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


