

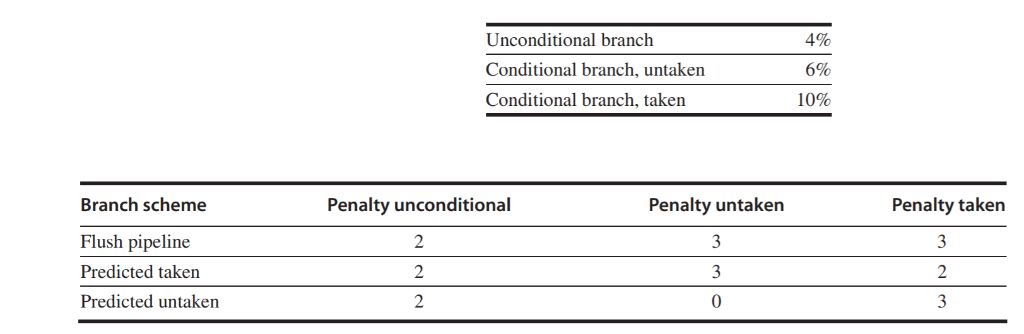
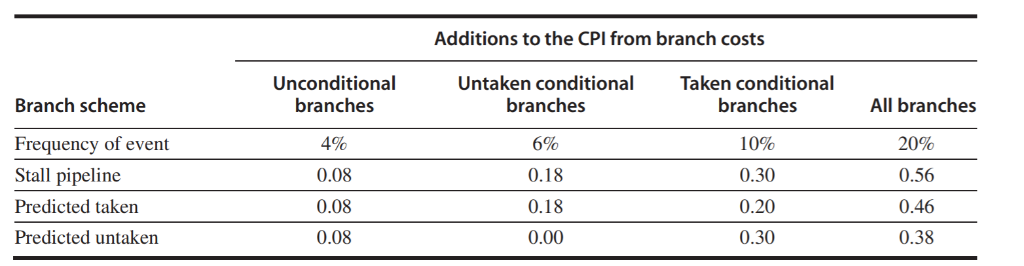
92. Referring to the example in page C-25 Rework the Question assuming it takes 5 cycles for the processor to compute and branch target address, but only takes 3 cycles for the processor to compute the branch condition. Find the effective addition to the CPI (Assume the frequency is the same the as the example.) For a deeper pipeline, such as that in a MIPS R4000, it takes at least three pipe- line stages before the branch-target address is known and an additional cycle before the branch condition is evaluated, assuming no stalls on the registers in the conditional comparison. A three-stage delay leads to the branch penalties for the three simplest prediction schemes listed in Figure C.15. Find the effective addition to the CPI arising from branches for this pipeline, assuming the following frequencies: Unconditional branch Conditional branch, untaken Conditional branch, taken 4% 5% 10% Branch scheme Flush pipeline Predicted taken Predicted untaken Penalty untaken Penalty unconditional 2 2 Penalty taken 2 0 Additions to the CPI from branch costs Unconditional branches 4% 0.08 0.08 0.08 Untaken conditional branches 6% 0.18 0.18 0.00 Taken conditional branches 10% 0.30 0.20 0.30 All branches 20% 0.56 0.46 0.38 Branch scheme requency of event Stall pipeline Predicted taken Predicted untaken 92. Referring to the example in page C-25 Rework the Question assuming it takes 5 cycles for the processor to compute and branch target address, but only takes 3 cycles for the processor to compute the branch condition. Find the effective addition to the CPI (Assume the frequency is the same the as the example.) For a deeper pipeline, such as that in a MIPS R4000, it takes at least three pipe- line stages before the branch-target address is known and an additional cycle before the branch condition is evaluated, assuming no stalls on the registers in the conditional comparison. A three-stage delay leads to the branch penalties for the three simplest prediction schemes listed in Figure C.15. Find the effective addition to the CPI arising from branches for this pipeline, assuming the following frequencies: Unconditional branch Conditional branch, untaken Conditional branch, taken 4% 5% 10% Branch scheme Flush pipeline Predicted taken Predicted untaken Penalty untaken Penalty unconditional 2 2 Penalty taken 2 0 Additions to the CPI from branch costs Unconditional branches 4% 0.08 0.08 0.08 Untaken conditional branches 6% 0.18 0.18 0.00 Taken conditional branches 10% 0.30 0.20 0.30 All branches 20% 0.56 0.46 0.38 Branch scheme requency of event Stall pipeline Predicted taken Predicted untaken










