Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
9-3. The velocity of an object as a function of time is shown in Fig. P9.3. The acceleration is constant during the first 4
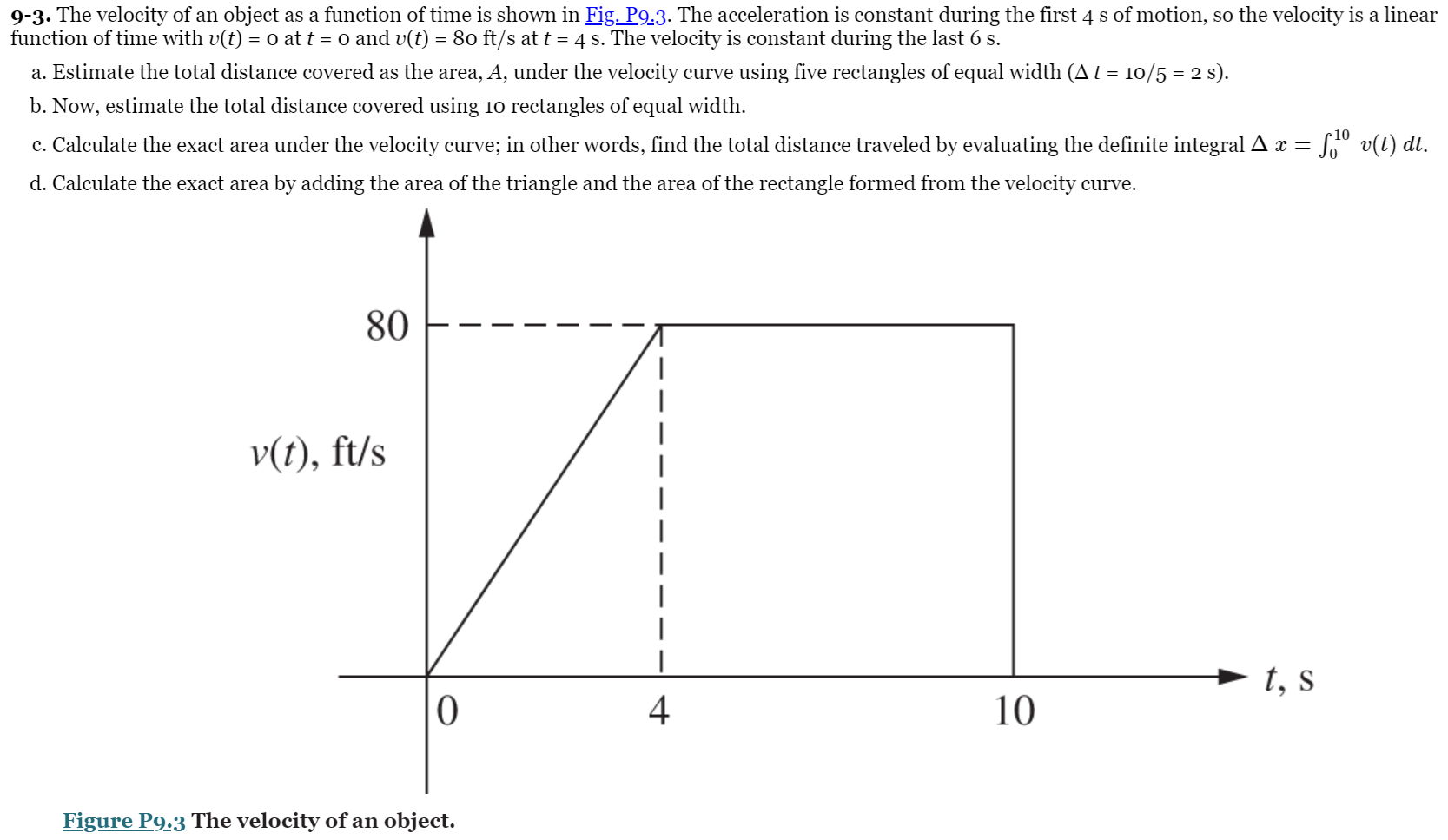
9-3. The velocity of an object as a function of time is shown in Fig. P9.3. The acceleration is constant during the first 4 s of motion, so the velocity is a linear function of time with v(t) = 0 at t = 0 and v(t) = 80 ft/s at t = 4 s. The velocity is constant during the last 6 s. a. Estimate the total distance covered as the area, A, under the velocity curve using five rectangles of equal width (A t = 10/5 = 2 s). b. Now, estimate the total distance covered using 10 rectangles of equal width. c. Calculate the exact area under the velocity curve; in other words, find the total distance traveled by evaluating the definite integral A x = d. Calculate the exact area by adding the area of the triangle and the area of the rectangle formed from the velocity curve. 10 = 1 v(t) dt. 80 v(t), ft/s t, s 0 4 10 Figure P9.3 The velocity of an object.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To solve this problem lets break it down step by step a Estimate the total distance covered using five rectangles of equal width t 105 2 s 1 Divide the time interval into five equal parts 0 2 2 4 4 6 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


