Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A 1.4 x 1021 kg moon orbits a distant planet in a circular orbit of radius 1.5 108 m. It experiences a 1.1 x
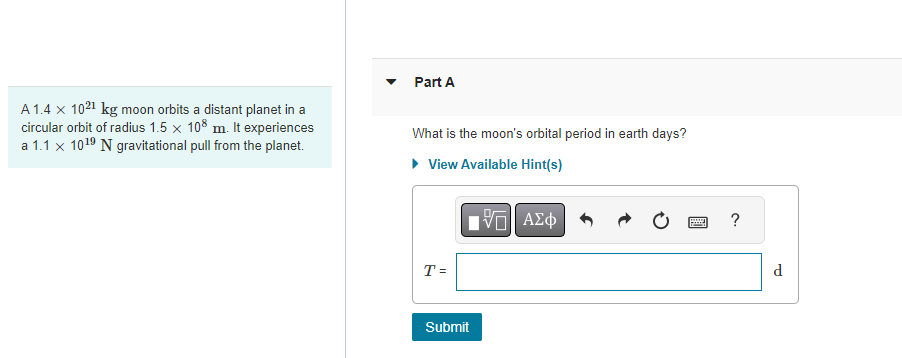
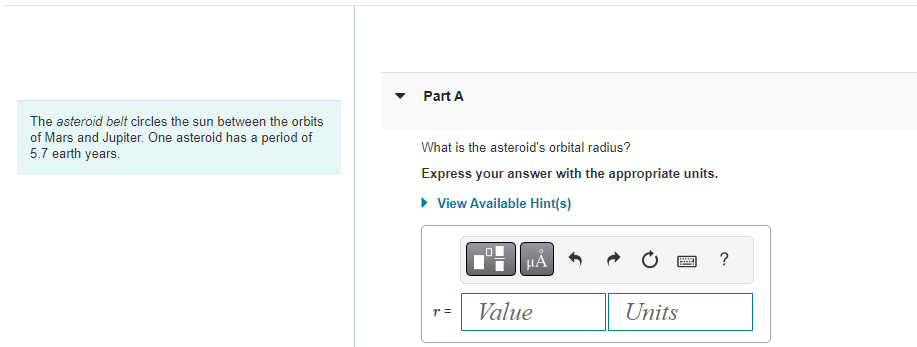
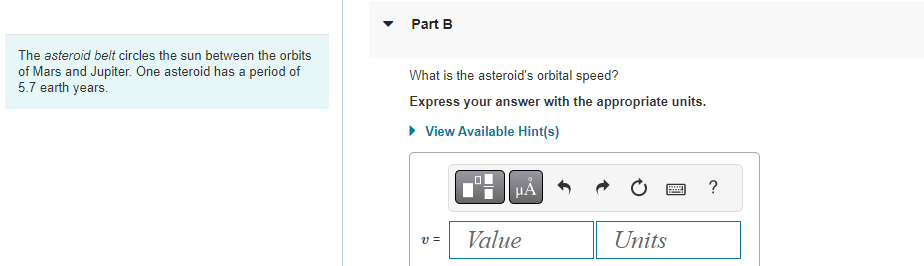
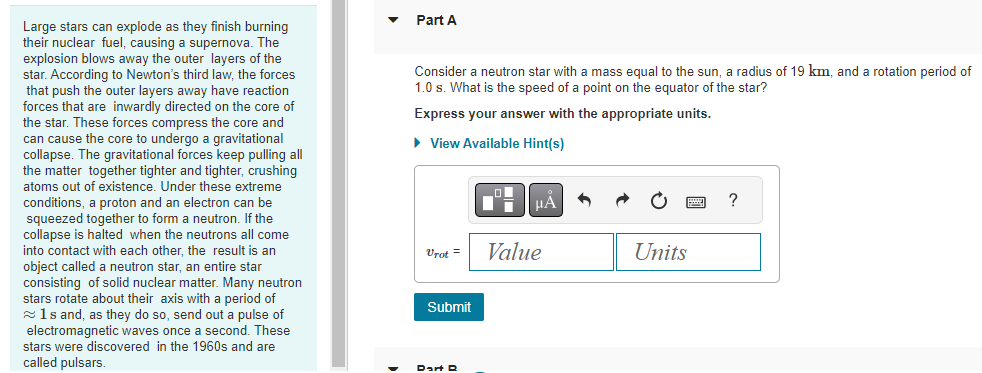
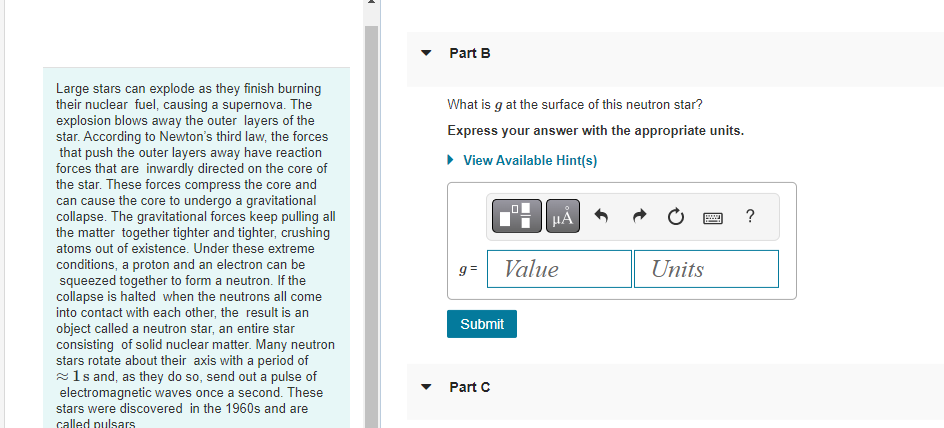
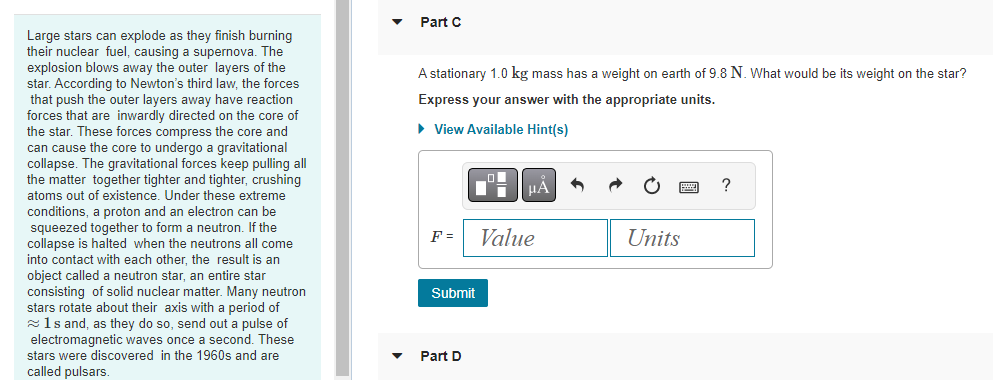
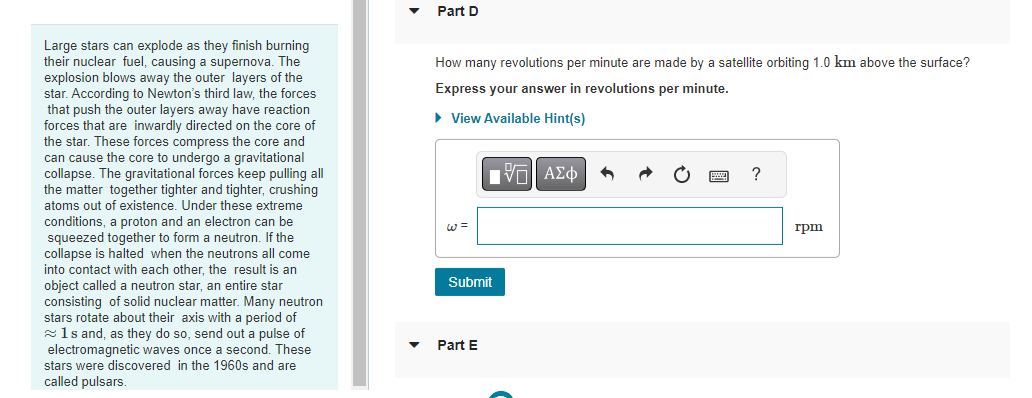
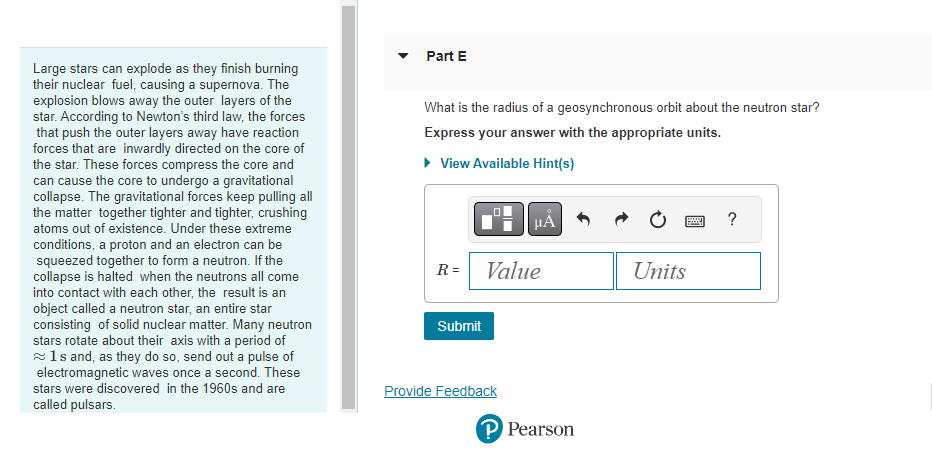
A 1.4 x 1021 kg moon orbits a distant planet in a circular orbit of radius 1.5 108 m. It experiences a 1.1 x 1019 N gravitational pull from the planet. Part A What is the moon's orbital period in earth days? View Available Hint(s) T = Submit ? d The asteroid belt circles the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. One asteroid has a period of 5.7 earth years. Part A What is the asteroid's orbital radius? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) H r = Value ? Units The asteroid belt circles the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. One asteroid has a period of 5.7 earth years. Part B What is the asteroid's orbital speed? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) v= Value Units ? Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of 1s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars. Part A Consider a neutron star with a mass equal to the sun, a radius of 19 km, and a rotation period of 1.0 s. What is the speed of a point on the equator of the star? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) Vrot = Value Submit Dart D ? Units Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of 1s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars Part B What is g at the surface of this neutron star? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) g= Value Units Submit Part C ? Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of 1s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars. Part C A stationary 1.0 kg mass has a weight on earth of 9.8 N. What would be its weight on the star? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) F= Value Units Submit Part D ? Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of 1s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars. Part D How many revolutions per minute are made by a satellite orbiting 1.0 km above the surface? Express your answer in revolutions per minute. View Available Hint(s) Submit Part E ? rpm Large stars can explode as they finish burning their nuclear fuel, causing a supernova. The explosion blows away the outer layers of the star. According to Newton's third law, the forces that push the outer layers away have reaction forces that are inwardly directed on the core of the star. These forces compress the core and can cause the core to undergo a gravitational collapse. The gravitational forces keep pulling all the matter together tighter and tighter, crushing atoms out of existence. Under these extreme conditions, a proton and an electron can be squeezed together to form a neutron. If the collapse is halted when the neutrons all come into contact with each other, the result is an object called a neutron star, an entire star consisting of solid nuclear matter. Many neutron stars rotate about their axis with a period of 1s and, as they do so, send out a pulse of electromagnetic waves once a second. These stars were discovered in the 1960s and are called pulsars. Part E What is the radius of a geosynchronous orbit about the neutron star? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) H ? Units R = Value Submit Provide Feedback ? Pearson Two 65 kg astronauts leave earth in a spacecraft, sitting 1.0 m apart. Part A How far are they from the center of the earth when the gravitational force between them is as strong as the gravitational force of the earth on one of the astronauts? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? r = Value Units Submit Request Answer
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


