The ACER group, created in Taiwan in 1976, was by 2011 the second-biggest PC and notebook company
Question:
The ACER group, created in Taiwan in 1976, was by 2011 the second-biggest PC and notebook company in the world. With revenue of around $20 billion it employs 8,000 people worldwide. Since its creation, ACER has seen its global organization adapt to follow the management philosophy of its founder Stan Shih, as well as the industry’s evolution.
The global organization has evolved in four stages:
● Stage 1: Initial steps in globalization:
1976–1990 As early as 1979 ACER (known at the time as Multitech) started to export personal computers combining OEM contracts and sales under its own brand. To manage its operations American executives were recruited but were difficult to control. They acted quite autonomously and took many (often misguided) initiatives.
A European office was opened in Germany to coordinate distributors and conduct market research. In emerging countries such as Thailand, Indonesia, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, South Africa, Mexico and India, ACER initiated a series of joint ventures. By 1990 it became obvious that the international operation needed to be reorganized.
● Stage 2: Creating a multinational organization:
1990–2000 Stan Shih organized the global operation according to the client–server principle. The business units are divided into two broad categories: the SBUs, which essentially develop products and manufacture components in world-class factories, and the RBUs, which are locally based and are in charge of assembly, marketing and sales.
Each unit is at the same time client and server, as shown in Figure 14.10.
Stan Shih wanted local company managers to own a local shareholding of equity. ‘At the heart of the client–server organization lies a closely linked team of mature and experienced managers committed to long-term success of their own piece of the ACER group. Mutual understanding and trust, communication and consensus are the cornerstone of ACER management.’31
● Stage 3: The early 2000s In December 2000, J. T. Wang was appointed as the president of ACER, responsible for turning around ACER PCs worldwide. At the time, the ACER group employed around 37,000 people in 232 enterprises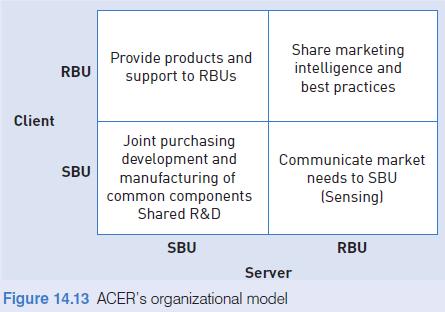
in 41 countries supporting a network of distributors in 100 countries. In 2001 the bursting of the internet bubble precipitated a decline in PC sales. Wang initiated a profound restructuring. He introduced a more centrally integrated approach based on three global principles: One Global Company, One Global Brand and One Global Team.
Questions:
1 What were the major hurdles to ACER becoming a global company? How did it overcome them?
2 During its initial phase of global development, ACER relied on OEM, alliances and acquisitions, and had a decentralized management. Why?
What are the pros and cons of such a strategy?
3 What do you think are the advantages and disadvantages of the client–server principle for global competitiveness?
4 What were the reasons behind ACER’s strategic and organizational changes in 2001 and in 2020? Analyse the advantages and disadvantages of such changes.
Step by Step Answer:

Global Strategic Management
ISBN: 9781350932968
5th Edition
Authors: Philippe Lasserre, Felipe Monteiro





