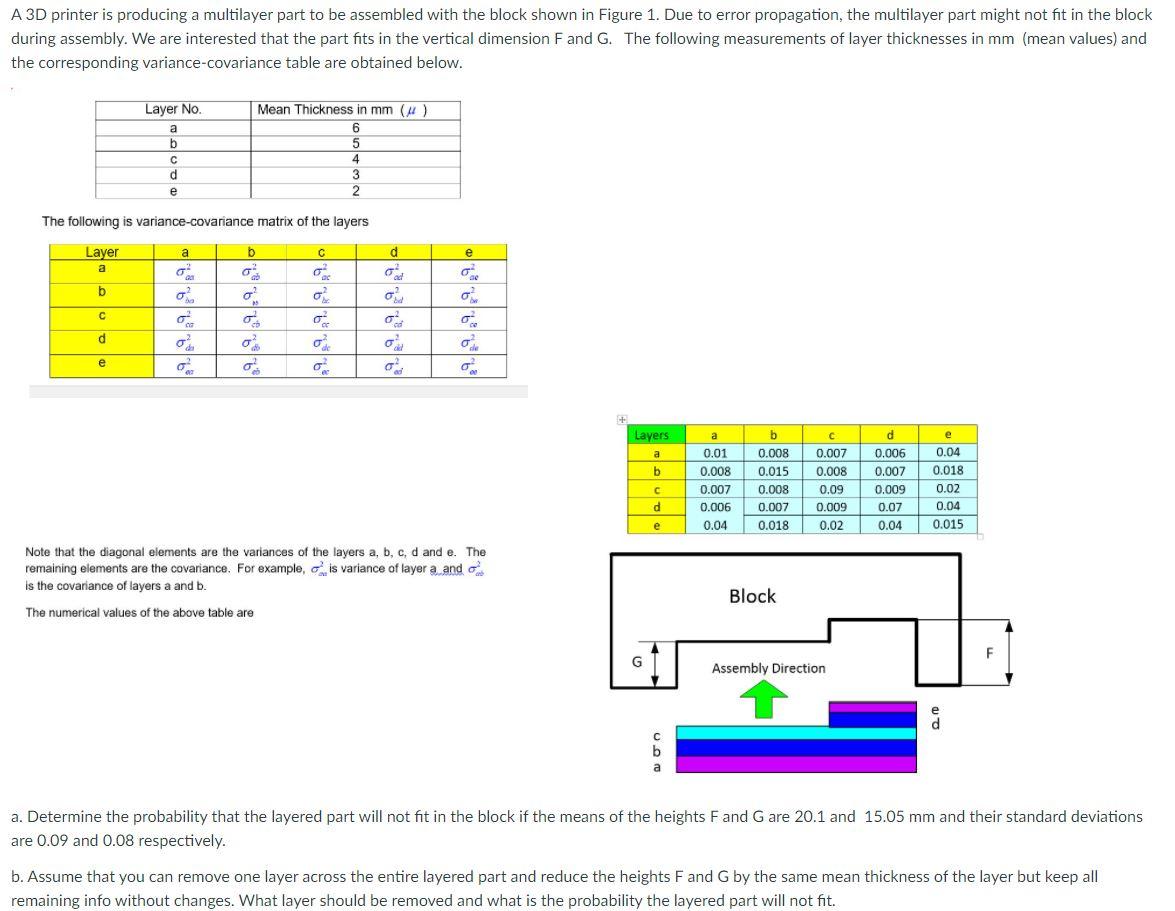
A 3D printer is producing a multilayer part to be assembled with the block shown in Figure 1. Due to error propagation, the multilayer part might not fit in the block during assembly. We are interested that the part fits in the vertical dimension F and G. The following measurements of layer thicknesses in mm (mean values) and the corresponding variance-covariance table are obtained below. Layer No. a b d Mean Thickness in mm (u) 6 5 4 3 2 e The following is variance-covariance matrix of the layers Layer a b d e C o b 8 o o o? 07 co o ca d o o 02 e o ad Layers e a b a 0.01 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.04 b 0.008 0.015 0.008 0.007 0.018 0.007 0.008 0.09 0.009 0.02 d 0.006 0.007 0.009 0.07 0.04 d 0.04 0.018 0.02 0.04 0.015 e Note that the diagonal elements are the variances of the layers a, b, c, d and e. The remaining elements are the covariance. For example, cis variance of layer a anda is the covariance of layers a and b. The numerical values of the above table are Block F Assembly Direction d C b a a. Determine the probability that the layered part will not fit in the block if the means of the heights Fand G are 20.1 and 15.05 mm and their standard deviations are 0.09 and 0.08 respectively. b. Assume that you can remove one layer across the entire layered part and reduce the heights F and G by the same mean thickness of the layer but keep all remaining info without changes. What layer should be removed and what is the probability the layered part will not fit. A 3D printer is producing a multilayer part to be assembled with the block shown in Figure 1. Due to error propagation, the multilayer part might not fit in the block during assembly. We are interested that the part fits in the vertical dimension F and G. The following measurements of layer thicknesses in mm (mean values) and the corresponding variance-covariance table are obtained below. Layer No. a b d Mean Thickness in mm (u) 6 5 4 3 2 e The following is variance-covariance matrix of the layers Layer a b d e C o b 8 o o o? 07 co o ca d o o 02 e o ad Layers e a b a 0.01 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.04 b 0.008 0.015 0.008 0.007 0.018 0.007 0.008 0.09 0.009 0.02 d 0.006 0.007 0.009 0.07 0.04 d 0.04 0.018 0.02 0.04 0.015 e Note that the diagonal elements are the variances of the layers a, b, c, d and e. The remaining elements are the covariance. For example, cis variance of layer a anda is the covariance of layers a and b. The numerical values of the above table are Block F Assembly Direction d C b a a. Determine the probability that the layered part will not fit in the block if the means of the heights Fand G are 20.1 and 15.05 mm and their standard deviations are 0.09 and 0.08 respectively. b. Assume that you can remove one layer across the entire layered part and reduce the heights F and G by the same mean thickness of the layer but keep all remaining info without changes. What layer should be removed and what is the probability the layered part will not fit







