Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
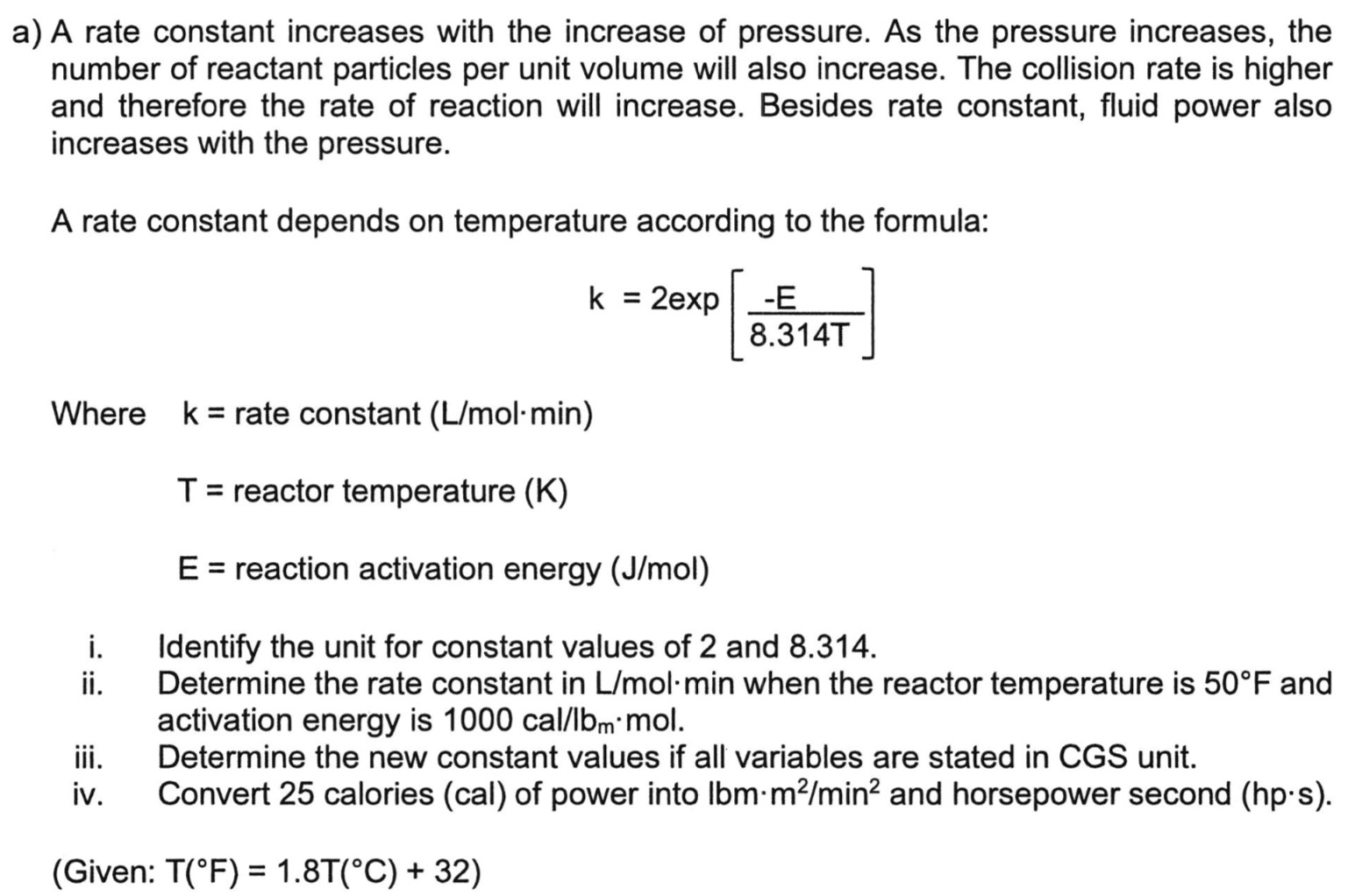
a ) A rate constant increases with the increase of pressure. As the pressure increases, the number of reactant particles per unit volume will also
a A rate constant increases with the increase of pressure. As the pressure increases, the number of reactant particles per unit volume will also increase. The collision rate is higher and therefore the rate of reaction will increase. Besides rate constant, fluid power also increases with the pressure.
A rate constant depends on temperature according to the formula:
exp
Where rate constant
reactor temperature
reaction activation energy
i Identify the unit for constant values of and
ii Determine the rate constant in when the reactor temperature is and activation energy is m
iii. Determine the new constant values if all variables are stated in CGS unit.
iv Convert calories cal of power into and horsepower second hps
Given:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


