Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(a) As shown in Fig. 3, two immiscible, incompressible, viscous fluids having the same density (p) but different viscosities (p and pg) are driven into
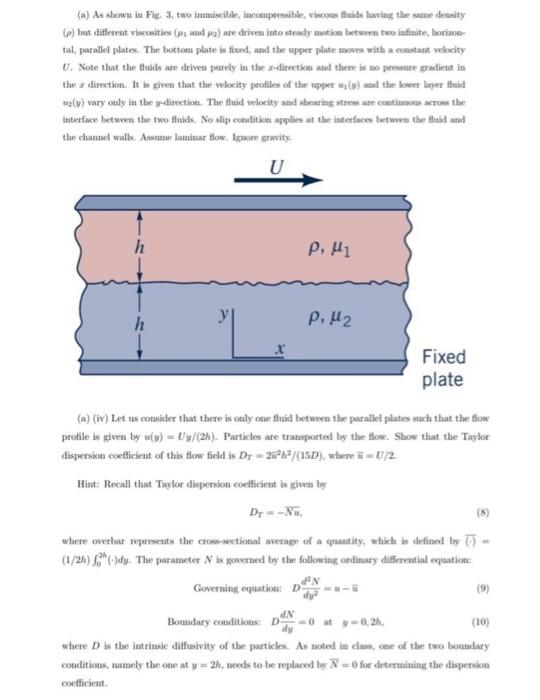 (a) As shown in Fig. 3, two immiscible, incompressible, viscous fluids having the same density (p) but different viscosities (p and pg) are driven into steady motion between two infinite, horizon- tal, parallel plates. The bottom plate is fixed, and the upper plate moves with a constant velocity U. Note that the fluids are driven purely in the 2-direction and there is no pressure gradient in the direction. It is given that the velocity profiles of the upper wi() and the lower layer fluid (v) vary only in the y-direction. The fluid velocity and shearing stress are continuous across the interface between the two fluids. No slip condition applies at the interfaces between the fluid and the channel walls. Assume laminar flow. Ignore gravity. U P, H1 h , Fixed plate (a) (iv) Let us consider that there is only one fluid between the parallel plates such that the flow profile is given by u(y) - Uy/(2h). Particles are transported by the flow. Show that the Taylor dispersion coefficient of this flow field is Dr=2h/(15D), where = U/2 Hint: Recall that Taylor dispersion coefficient is given by Dy=-Nu, where overbar represents the cross-sectional average of a quantity, which is defined by (-) (1/24) (-)dy. The parameter N is governed by the following ordinary differential equation: N Governing equation: D (9) Boundary conditions: D -0 at y=0,2h, dN dy (10) where D is the intrinsic diffusivity of the particles. As noted in class, one of the two boundary conditions, namely the one at y = 2h, needs to be replaced by N=0 for determining the dispersion coefficient
(a) As shown in Fig. 3, two immiscible, incompressible, viscous fluids having the same density (p) but different viscosities (p and pg) are driven into steady motion between two infinite, horizon- tal, parallel plates. The bottom plate is fixed, and the upper plate moves with a constant velocity U. Note that the fluids are driven purely in the 2-direction and there is no pressure gradient in the direction. It is given that the velocity profiles of the upper wi() and the lower layer fluid (v) vary only in the y-direction. The fluid velocity and shearing stress are continuous across the interface between the two fluids. No slip condition applies at the interfaces between the fluid and the channel walls. Assume laminar flow. Ignore gravity. U P, H1 h , Fixed plate (a) (iv) Let us consider that there is only one fluid between the parallel plates such that the flow profile is given by u(y) - Uy/(2h). Particles are transported by the flow. Show that the Taylor dispersion coefficient of this flow field is Dr=2h/(15D), where = U/2 Hint: Recall that Taylor dispersion coefficient is given by Dy=-Nu, where overbar represents the cross-sectional average of a quantity, which is defined by (-) (1/24) (-)dy. The parameter N is governed by the following ordinary differential equation: N Governing equation: D (9) Boundary conditions: D -0 at y=0,2h, dN dy (10) where D is the intrinsic diffusivity of the particles. As noted in class, one of the two boundary conditions, namely the one at y = 2h, needs to be replaced by N=0 for determining the dispersion coefficient

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


