Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A B D F Dayton, Inc. Annual Income Statement (Values in Millions) Common Size 2012 2011 2012 2011 Sales $ 178,909 $ 187,510 Cost
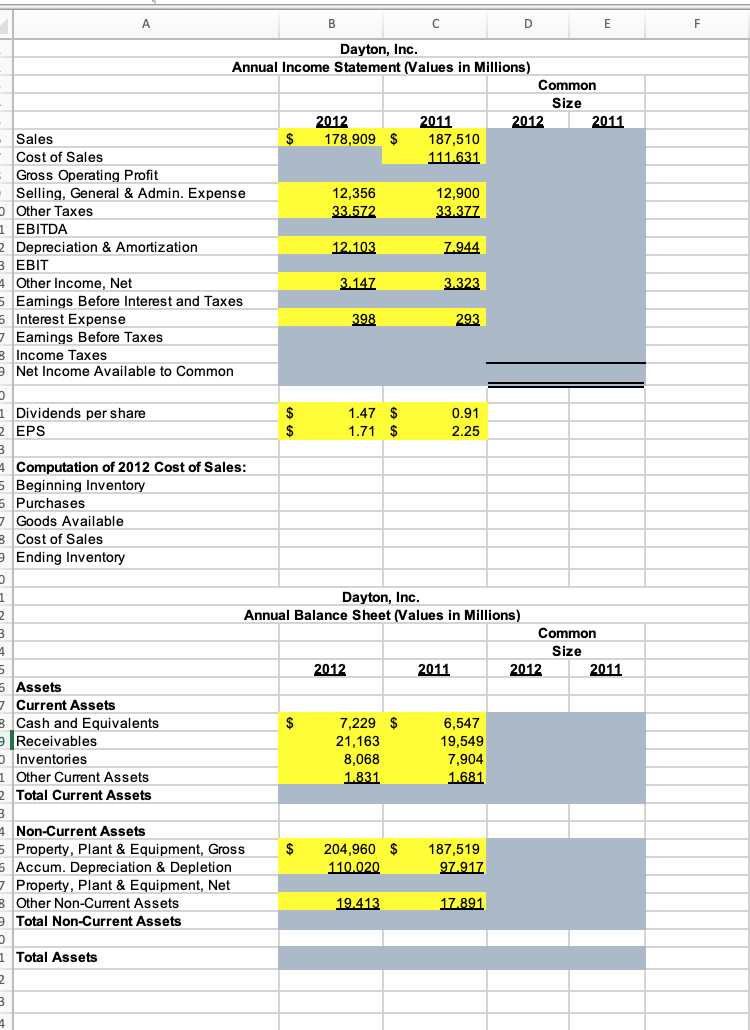
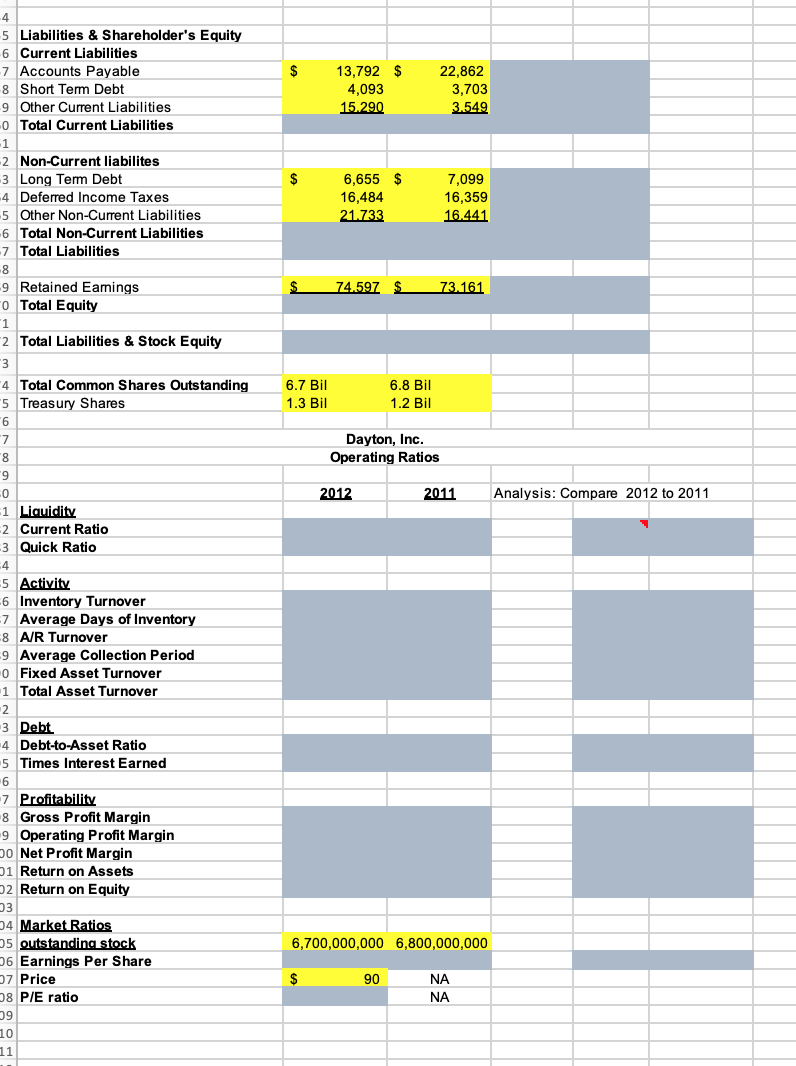

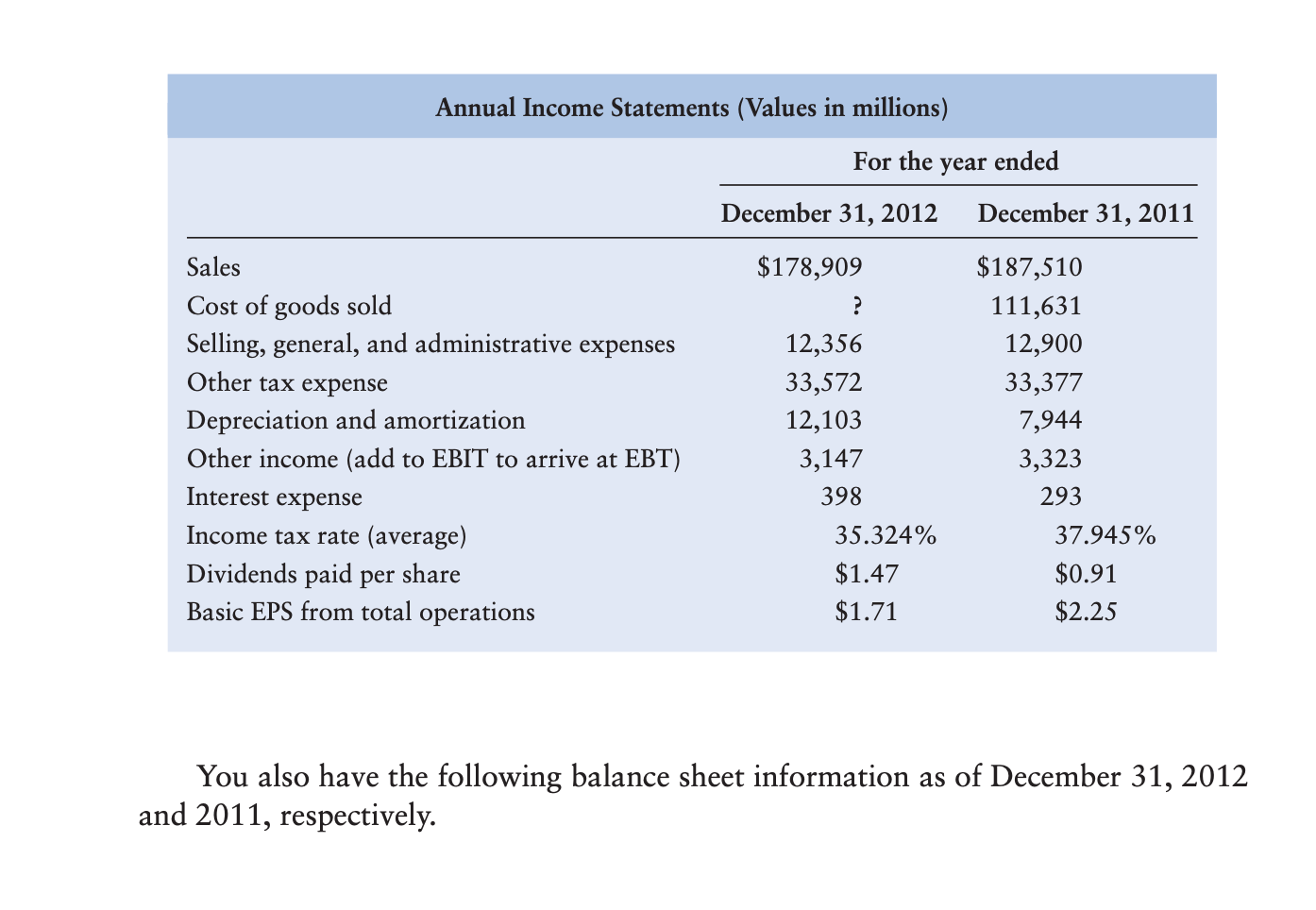
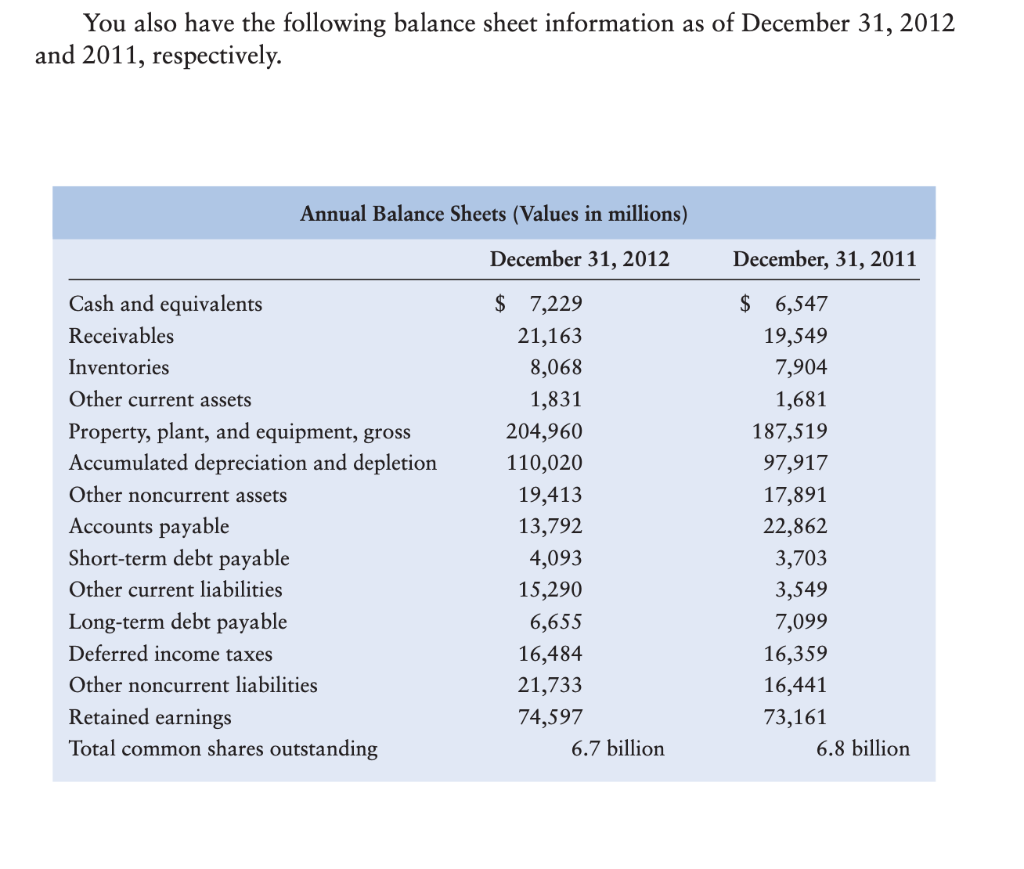
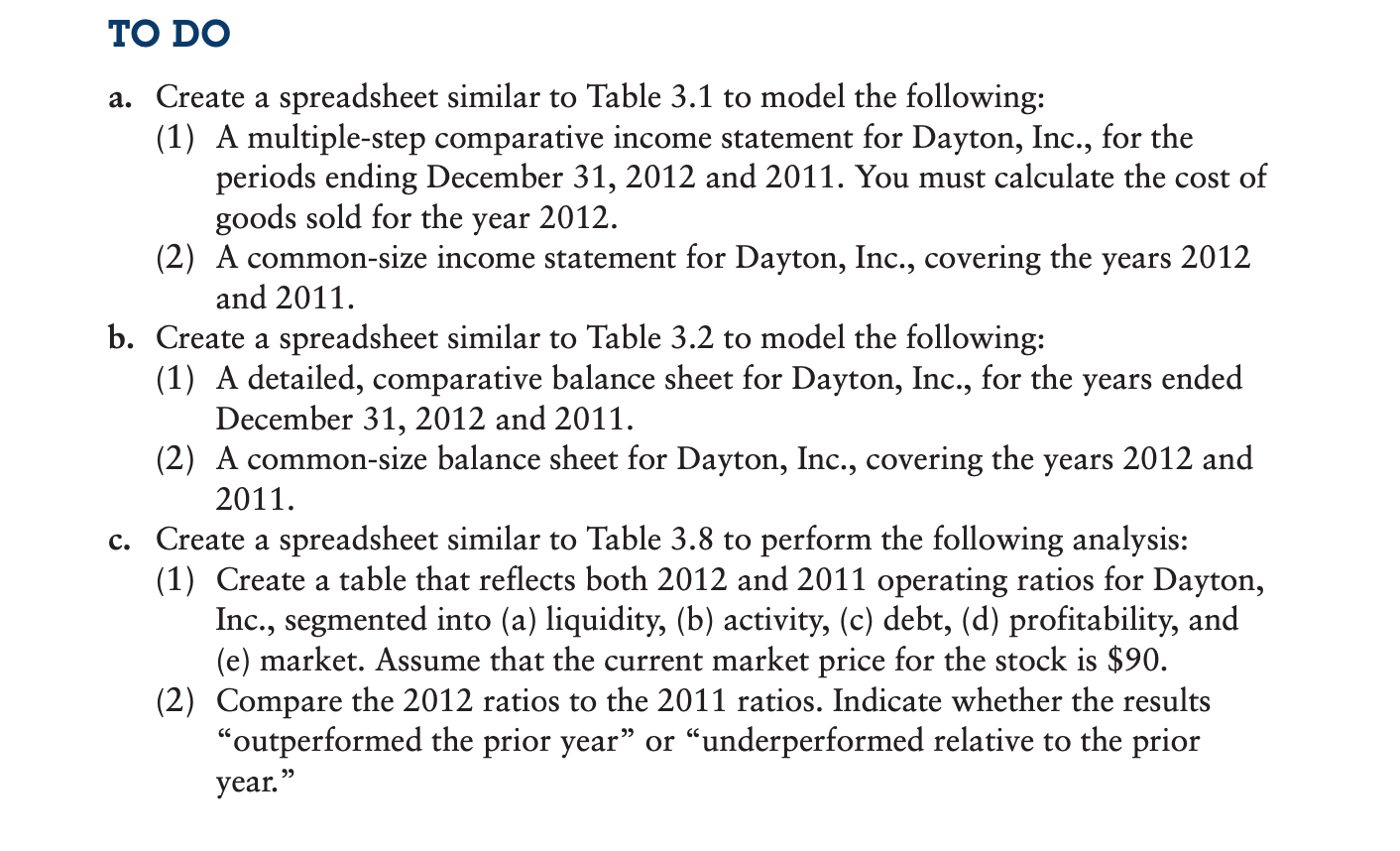
A B D F Dayton, Inc. Annual Income Statement (Values in Millions) Common Size 2012 2011 2012 2011 Sales $ 178,909 $ 187,510 Cost of Sales 111.631 Gross Operating Profit Selling, General & Admin. Expense 12,356 12,900 Other Taxes 33.572 33.377 EBITDA Depreciation & Amortization EBIT 12.103 7.944 4 Other Income, Net 5 Eamings Before Interest and Taxes 5 Interest Expense 3.147 3.323 398 293 Eamings Before Taxes B Income Taxes 9 Net Income Available to Common 1 Dividends per share 2 EPS $ 1.47 $ 1.71 $ 0.91 $ 2.25 Computation of 2012 Cost of Sales: 5 Beginning Inventory 5 Purchases 7 Goods Available 3 Cost of Sales eEnding Inventory Dayton, Inc. Annual Balance Sheet (Values in Millions) Common Size 2012 2011 2012 2011 Assets Current Assets $ 7,229 $ Cash and Equivalents Receivables p Inventories 21,163 8,068 1.831 6,547 19,549 7,904 Other Current Assets 1.681 Total Current Assets 4 Non-Curret Assets 204,960 $ 110.020 $ 187,519 Property, Plant & Equipment, Gross Accum. Depreciation & Depletion 7 Property, Plant & Equipment, Net B Other Non-Current Assets 97.917 19.413 17.891 Total Non-Current Assets 1 Total Assets 4 5 Liabilities & Shareholder's Equity 6 Current Liabilities 13,792 $ 4,093 -7 Accounts Payable 8 Short Tem Debt 9 Other Current Liabilities 0 Total Current Liabilities -1 $ 22,862 3,703 3.549 15.290 2 Non-Current liabilites $ 6,655 $ 16,484 21.733 3 Long Tem Debt 7,099 4 Deferred Income Taxes 16.359 5 Other Non-Current Liabilities 6 Total Non-Current Liabilities 7 Total Liabilities 16.441 -8 -9 Retained Eamings -o Total Equity 1 -2 Total Liabilities & Stock Equity 74.597 $ 73.161 3 -4 Total Common Shares Outstanding 6.7 Bil 6.8 Bil 5 Treasury Shares 1.3 Bil 1.2 Bil Dayton, Inc. 8, Operating Ratios 6- 2012 2011 Analysis: Compare 2012 to 2011 1 Liquidity 2 Current Ratio 3 Quick Ratio 4 -5 Activity 6 Inventory Turnover 7 Average Days of Inventory -8 A/R Turnover 9 Average Collection Period 0 Fixed Asset Turnover 1 Total Asset Turnover 2 3 Debt 4 Debt-to-Asset Ratio 5 Times Interest Earned 6 7 Profitability 8 Gross Profit Margin 9 Operating Profit Margin p0 Net Profit Margin 01 Return on Assets 22 Return on Equity D3 24 Market Ratios 05 outstanding stock D6 Earnings Per Share D7 Price D8 P/E ratio 09 6,700,000,000 6,800,000,000 $ 90 NA NA 10 11 The income statement and balance sheet are the basic reports that a firm constructs for use by management and for distribution to stockholders, regulatory bodies, and the general public. They are the primary sources of historical financial information about the firm. Dayton Products, Inc., is a moderate-sized manufacturer. The company's management has asked you to perform a detailed financial statement analysis of the firm. CHAPTER 3 Financial Statements and Ratio Analysis 111 The income statements for the years ending December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively, are presented in the table below. (Note: Purchases of inventory during 2012 amounted to $109,865.) Annual Income Statements (Values in millions) For the year ended December 31, 2012 December 31, 2011 Sales $178,909 $187,510 Cost of goods sold ? 111,631 Selling, general, and administrative expenses 12,356 12,900 Other tax expense 33,572 33,377 Depreciation and amortization Other income (add to EBIT to arrive at EBT) 12,103 7,944 3,147 3,323 Interest expense 398 293 Income tax rate (average) 35.324% 37.945% Dividends paid per share Basic EPS from total operations $1.47 $0.91 $1.71 $2.25 You also have the following balance sheet information as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. You also have the following balance sheet information as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Annual Balance Sheets (Values in millions) December 31, 2012 December, 31, 2011 Cash and equivalents $ 7,229 $ 6,547 Receivables 21,163 19,549 Inventories 8,068 7,904 Other current assets 1,831 1,681 Property, plant, and equipment, gross Accumulated depreciation and depletion 204,960 187,519 110,020 97,917 Other noncurrent assets 19,413 17,891 Accounts payable Short-term debt payable 13,792 22,862 4,093 3,703 Other current liabilities 15,290 3,549 Long-term debt payable Deferred income taxes 6,655 7,099 16,484 16,359 Other noncurrent liabilities 21,733 16,441 Retained earnings 74,597 73,161 Total common shares outstanding 6.7 billion 6.8 billion O DO a. Create a spreadsheet similar to Table 3.1 to model the following: (1) A multiple-step comparative income statement for Dayton, Inc., for the periods ending December 31, 2012 and 2011. You must calculate the cost of goods sold for the (2) A common-size income statement for Dayton, Inc., covering the years 2012 and 2011. year 2012. b. Create a spreadsheet similar to Table 3.2 to model the following: (1) A detailed, comparative balance sheet for Dayton, Inc., for the December 31, 2012 and 2011. (2) A common-size balance sheet for Dayton, Inc., covering the years 2012 and years ended 2011. c. Create a spreadsheet similar to Table 3.8 to perform the following analysis: (1) Create a table that reflects both 2012 and 2011 operating ratios for Dayton, Inc., segmented into (a) liquidity, (b) activity, (c) debt, (d) profitability, and (e) market. Assume that the current market price for the stock is $90. (2) Compare the 2012 ratios to the 2011 ratios. Indicate whether the results outperformed the prior year" or underperformed relative to the prior year."
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.46 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Financial Analysis of Dayton Inc Dayton Inc Annual Income Statement Values in Millio...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


