a.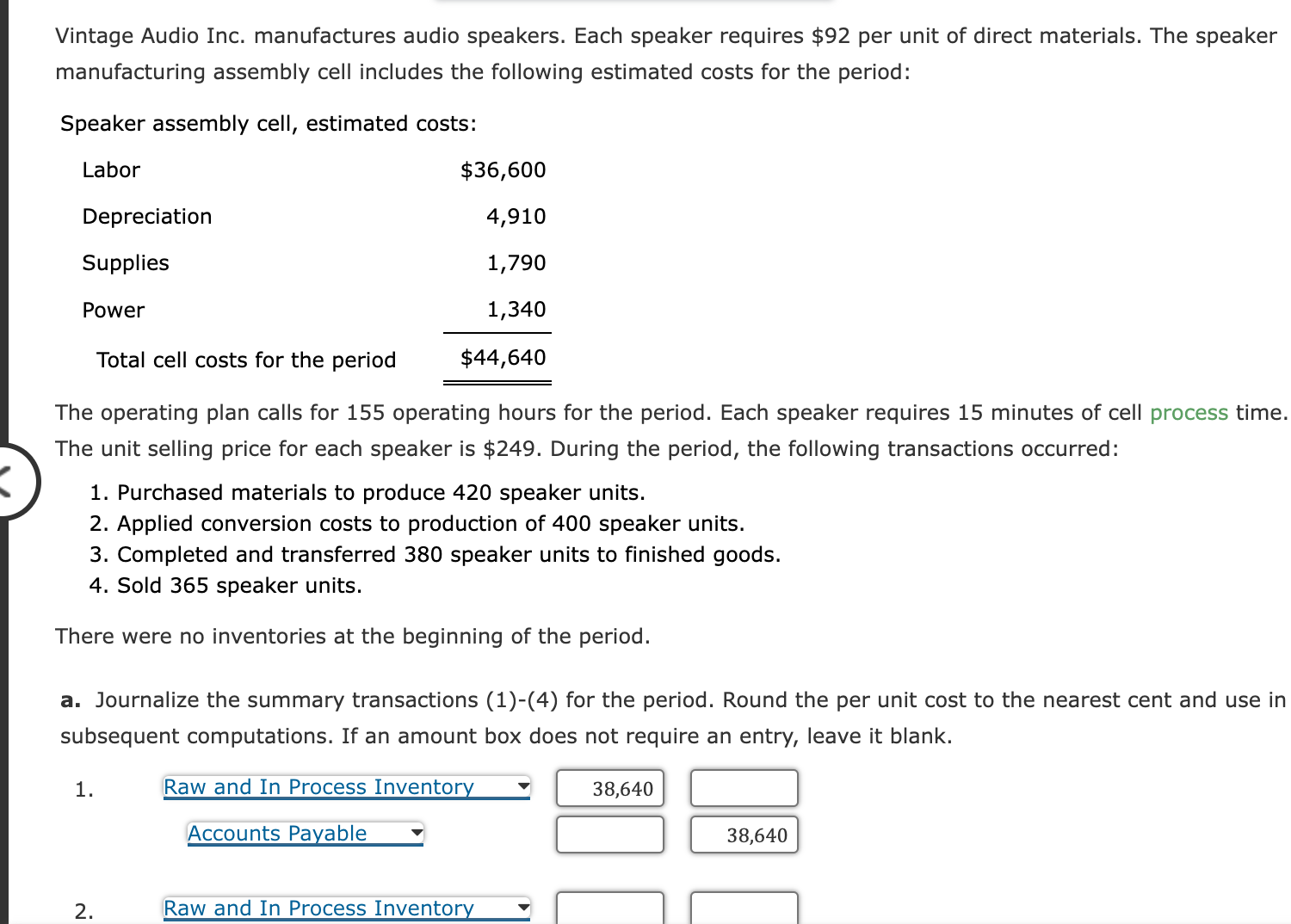
 b.
b.
 note: PLZ answer both questions since chegg policy has changed. If you do not I will downvote and report
note: PLZ answer both questions since chegg policy has changed. If you do not I will downvote and report
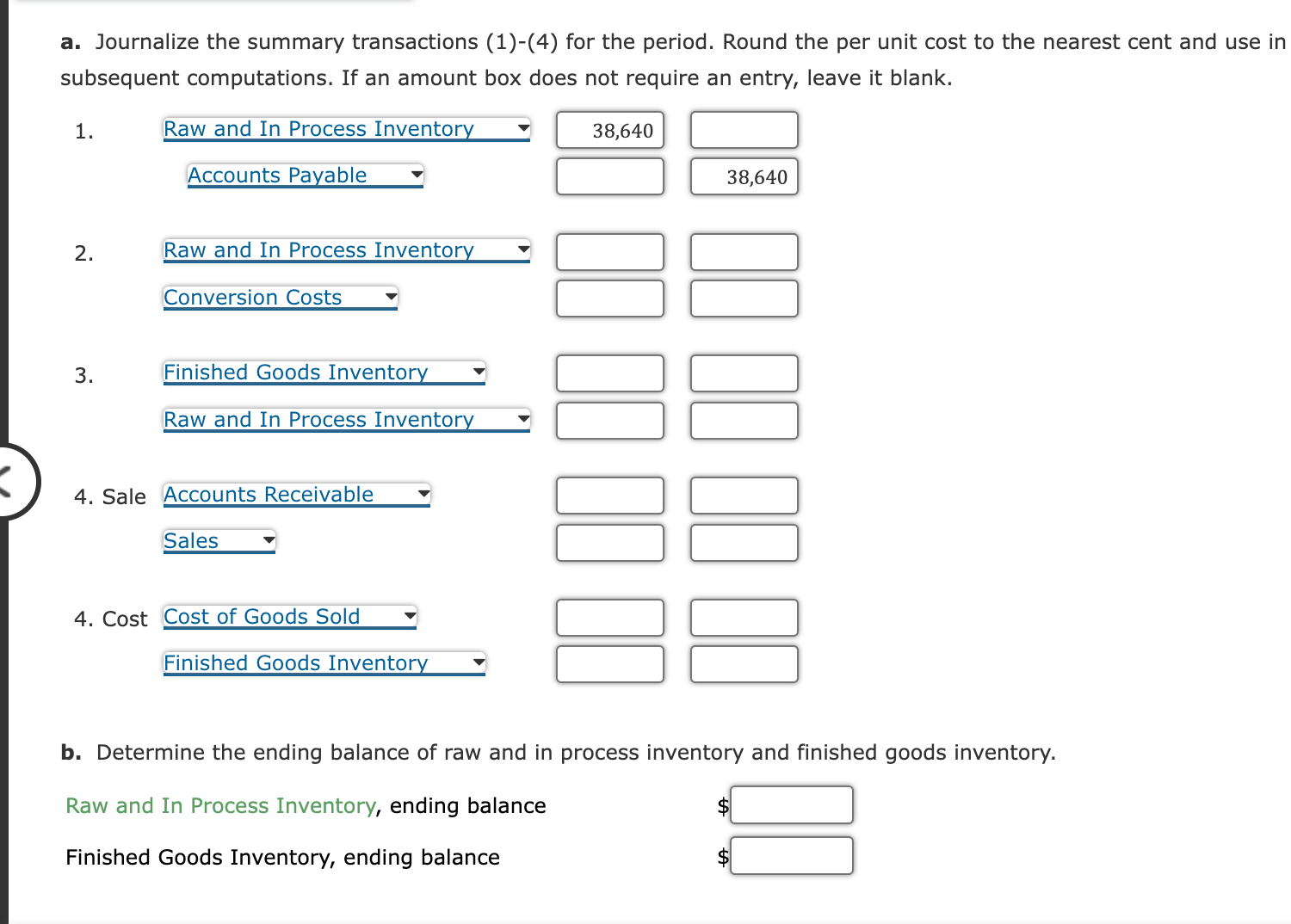
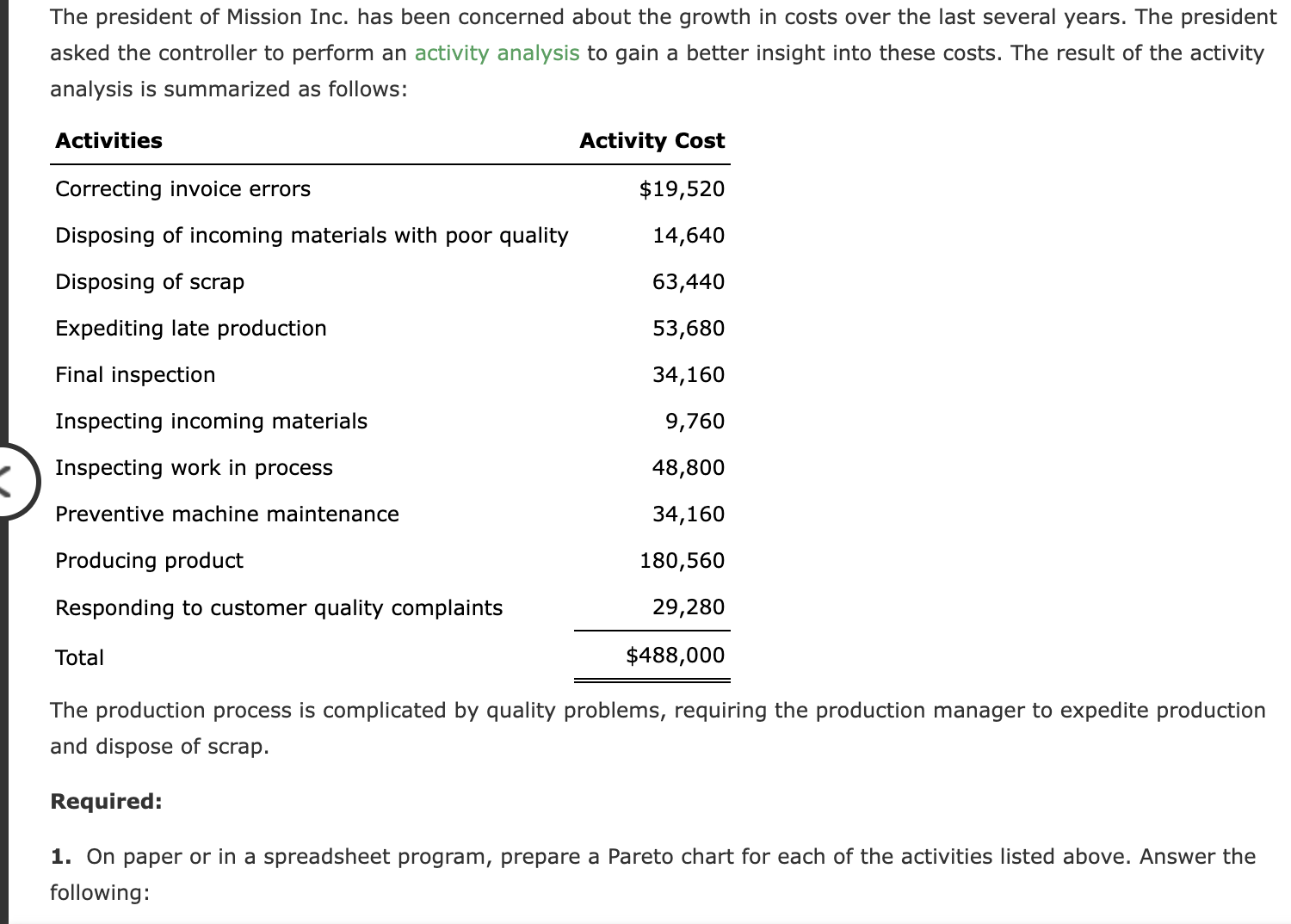
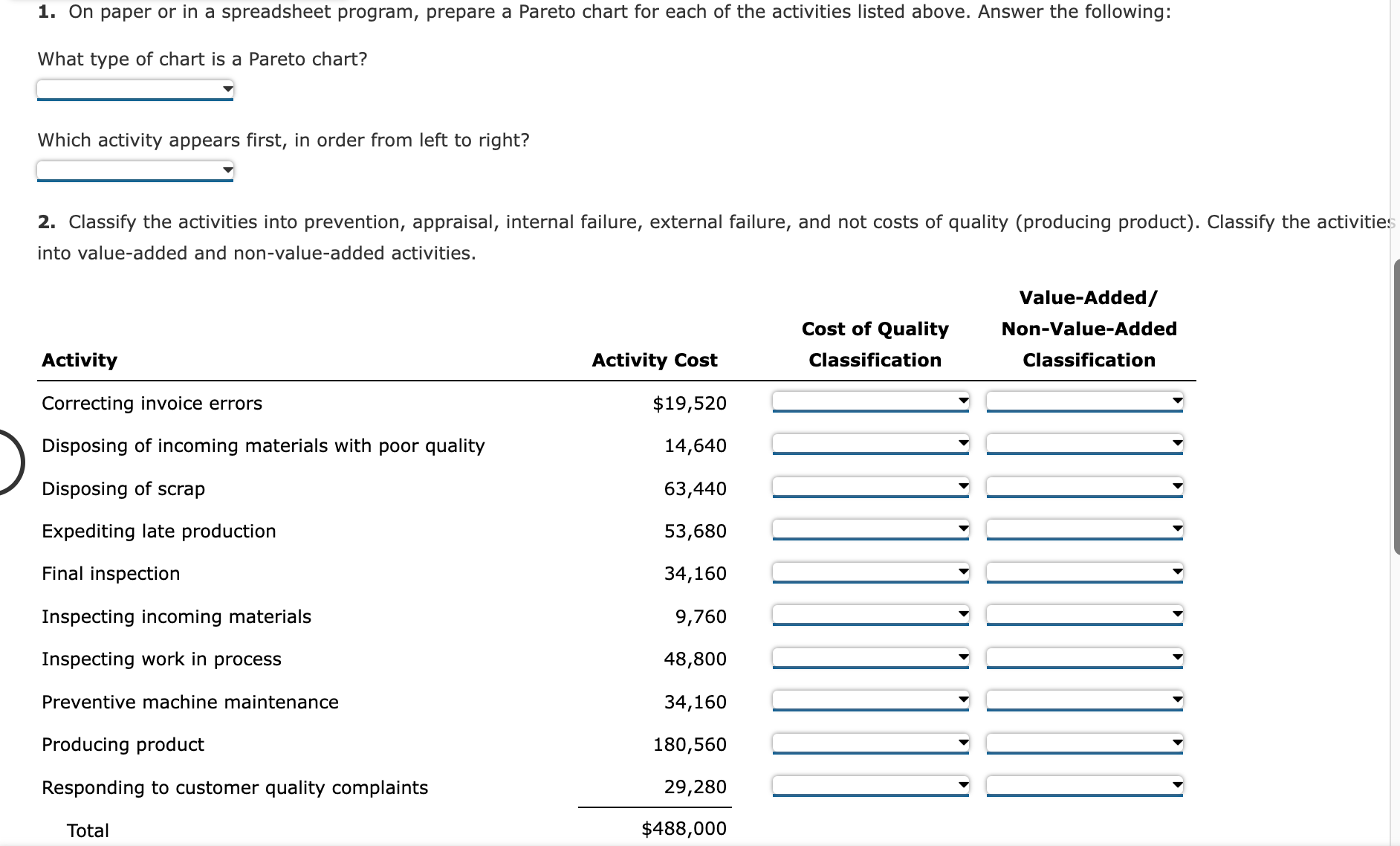
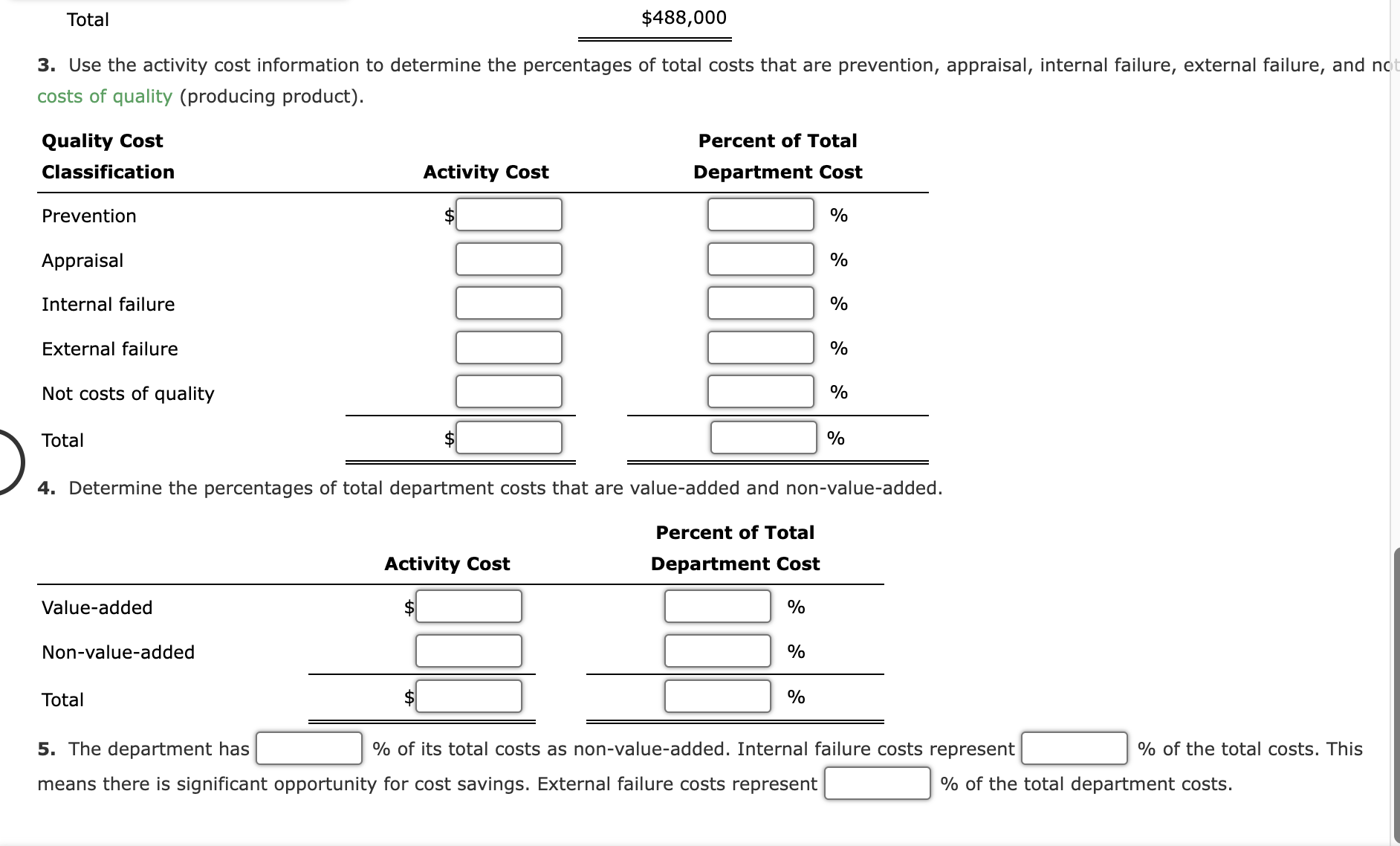
1. On paper or in a spreadsheet program, prepare a Pareto chart for each of the activities listed above. Answer the following: What type of chart is a Pareto chart? Which activity appears first, in order from left to right? 2. Classify the activities into prevention, appraisal, internal failure, external failure, and not costs of quality (producing product). Classify the activitie: into value-added and non-value-added activities. Value-Added/ Cost of Quality Non-Value-Added Activity Classification Classification Correcting invoice errors Disposing of incoming materials with poor quality Disposing of scrap Expediting late production Final inspection Inspecting incoming materials Inspecting work in process Preventive machine maintenance Producing product Responding to customer quality complaints Total $19,520 14,640 63,440 53,680 34,160 9,760 48,800 34,160 180,560 29,280 $488,000 Total $488,000 3. Use the activity cost information to determine the percentages of total costs that are prevention, appraisal, internal failure, external failure, and no costs of quality (producing product). Quality Cost Classification Prevention Appraisal Internal failure External failure Not costs of quality Total Total 4. Determine the percentages of total department costs that are value-added and non-value-added. Vintage Audio Inc. manufactures audio speakers. Each speaker requires $92 per unit of direct materials. The speaker manufacturing assembly cell includes the following estimated costs for the period: Speaker assembly cell, estimated costs: The operating plan calls for 155 operating hours for the period. Each speaker requires 15 minutes of cell process time. The unit selling price for each speaker is $249. During the period, the following transactions occurred: 1. Purchased materials to produce 420 speaker units. 2. Applied conversion costs to production of 400 speaker units. 3. Completed and transferred 380 speaker units to finished goods. 4. Sold 365 speaker units. There were no inventories at the beginning of the period. a. Journalize the summary transactions (1)-(4) for the period. Round the per unit cost to the nearest cent and use in subsequent computations. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 1. Raw and In Process Inventory Accounts Payable 2. Raw and In Process Inventory The president of Mission Inc. has been concerned about the growth in costs over the last several years. The president asked the controller to perform an activity analysis to gain a better insight into these costs. The result of the activity analysis is summarized as follows: Activities Correcting invoice errors Disposing of incoming materials with poor quality Disposing of scrap Expediting late production Final inspection Inspecting incoming materials Inspecting work in process Preventive machine maintenance Producing product Responding to customer quality complaints Total Activity Cost $19,520 14,640 63,440 53,680 34,160 9,760 48,800 34,160 180,560 29,280 $488,000 The production process is complicated by quality problems, requiring the production manager to expedite production and dispose of scrap. Required: 1. On paper or in a spreadsheet program, prepare a Pareto chart for each of the activities listed above. Answer the following: a. Journalize the summary transactions (1)-(4) for the period. Round the per unit cost to the nearest cent and use in subsequent computations. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 1. Raw and In Process Inventory Accounts Payable 2. Raw and In Process Inventory Conversion Costs 3. Finished Goods Inventory Raw and In Process Inventory 4. Sale Accounts Receivable Sales 4. Cost Cost of Goods Sold Finished Goods Inventory b. Determine the ending balance of raw and in process inventory and finished goods inventory. Raw and In Process Inventory, ending balance Finished Goods Inventory, ending balance

 b.
b. 

 note: PLZ answer both questions since chegg policy has changed. If you do not I will downvote and report
note: PLZ answer both questions since chegg policy has changed. If you do not I will downvote and report





