Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A basic explanation of how a personal water craft (also frequently called a jet ski) works is a pump-jet that intakes water from below
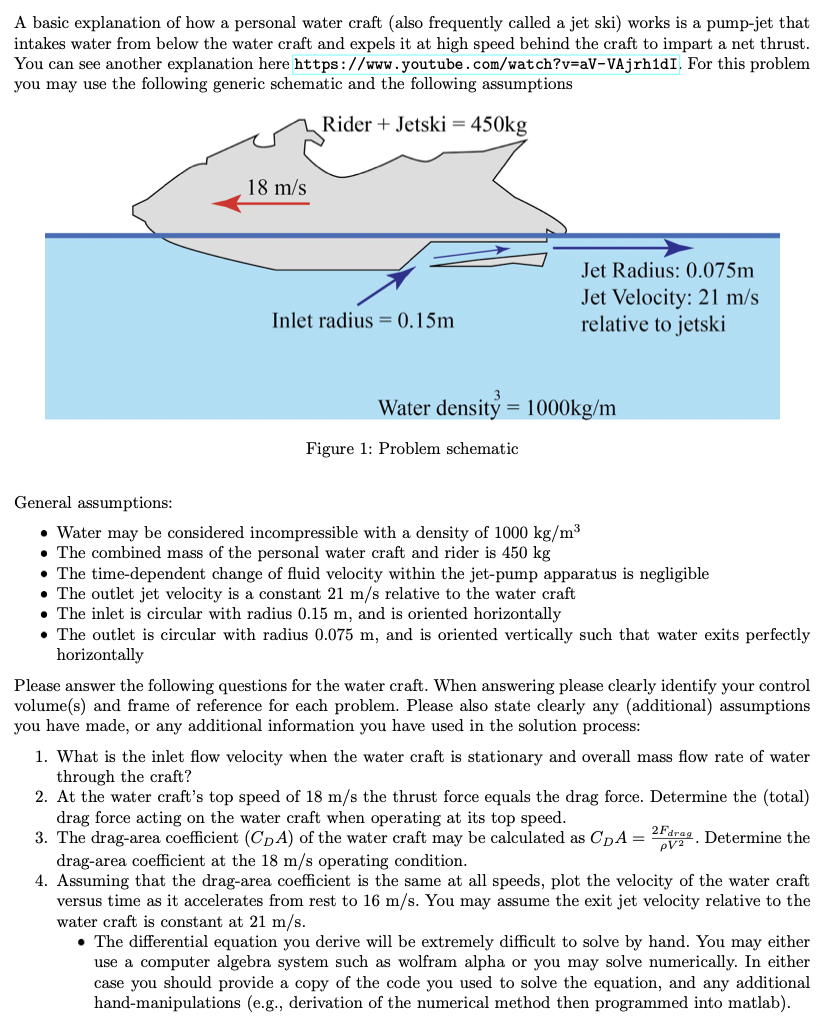
A basic explanation of how a personal water craft (also frequently called a jet ski) works is a pump-jet that intakes water from below the water craft and expels it at high speed behind the craft to impart a net thrust. You can see another explanation here https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aV-VAjrh1dI. For this problem you may use the following generic schematic and the following assumptions Rider + Jetski = 450kg 18 m/s Inlet radius= 0.15m Jet Radius: 0.075m Jet Velocity: 21 m/s relative to jetski Water density = 1000kg/m Figure 1: Problem schematic General assumptions: Water may be considered incompressible with a density of 1000 kg/m The combined mass of the personal water craft and rider is 450 kg The time-dependent change of fluid velocity within the jet-pump apparatus is negligible The outlet jet velocity is a constant 21 m/s relative to the water craft The inlet is circular with radius 0.15 m, and is oriented horizontally The outlet is circular with radius 0.075 m, and is oriented vertically such that water exits perfectly horizontally Please answer the following questions for the water craft. When answering please clearly identify your control volume(s) and frame of reference for each problem. Please also state clearly any (additional) assumptions you have made, or any additional information you have used in the solution process: 1. What is the inlet flow velocity when the water craft is stationary and overall mass flow rate of water through the craft? 2. At the water craft's top speed of 18 m/s the thrust force equals the drag force. Determine the (total) drag force acting on the water craft when operating at its top speed. 3. The drag-area coefficient (CDA) of the water craft may be calculated as CDA = 25drag. Determine the drag-area coefficient at the 18 m/s operating condition. 4. Assuming that the drag-area coefficient is the same at all speeds, plot the velocity of the water craft versus time as it accelerates from rest to 16 m/s. You may assume the exit jet velocity relative to the water craft is constant at 21 m/s. The differential equation you derive will be extremely difficult to solve by hand. You may either use a computer algebra system such as wolfram alpha or you may solve numerically. In either case you should provide a copy of the code you used to solve the equation, and any additional hand-manipulations (e.g., derivation of the numerical method then programmed into matlab).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


