A beam in pure bending (M shown in the figure) has a cross-section with height h = 70.0mm and width/thickness (into page) b=25.0mm. The
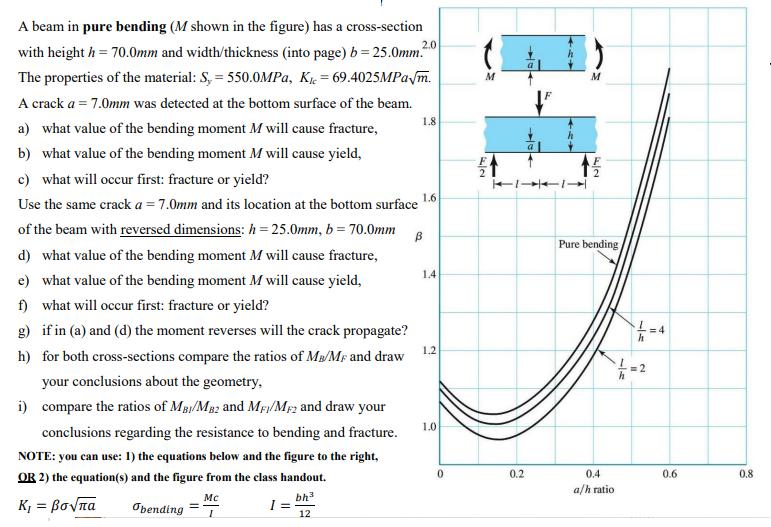
A beam in pure bending (M shown in the figure) has a cross-section with height h = 70.0mm and width/thickness (into page) b=25.0mm. The properties of the material: S, = 550.0MPa, K = 69.4025MPa/m. A crack a = 7.0mm was detected at the bottom surface of the beam. a) what value of the bending moment M will cause fracture, b) what value of the bending moment M will cause yield, c) what will occur first: fracture or yield? Use the same crack a = 7.0mm and its location at the bottom surface of the beam with reversed dimensions: h=25.0mm, b = 70.0mm d) what value of the bending moment M will cause fracture, e) what value of the bending moment M will cause yield, f) what will occur first: fracture or yield? g) if in (a) and (d) the moment reverses will the crack propagate? h) for both cross-sections compare the ratios of MB/MF and draw your conclusions about the geometry, i) compare the ratios of MBI/MB2 and MF/MF and draw your conclusions regarding the resistance to bending and fracture. NOTE: you can use: 1) the equations below and the figure to the right, OR 2) the equation(s) and the figure from the class handout. bh = Obending 12 Mc 1 = 2.0 1.8 1.6 B 1.4 1.2 1.0 0 M K 0.2 a 11-1 M Pure bending/ 0.4 a/h ratio -15 2 0.6 0.8
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a For the original crosssection the bending moment that will cause fracture can be calculated using ...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


