Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A central feature of forming portfolios is understanding your risk aversion. To try and quantify this inherently subjective and psychological phenomenon, fill out the
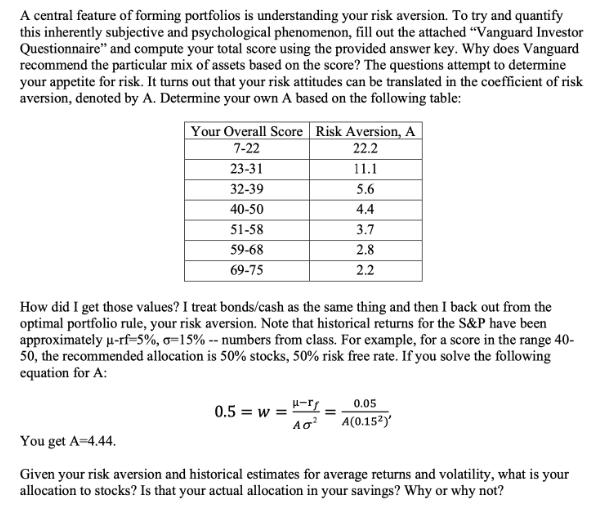
A central feature of forming portfolios is understanding your risk aversion. To try and quantify this inherently subjective and psychological phenomenon, fill out the attached "Vanguard Investor Questionnaire" and compute your total score using the provided answer key. Why does Vanguard recommend the particular mix of assets based on the score? The questions attempt to determine your appetite for risk. It turns out that your risk attitudes can be translated in the coefficient of risk aversion, denoted by A. Determine your own A based on the following table: Your Overall Score Risk Aversion, A 7-22 22.2 23-31 11.1 32-39 5.6 40-50 4.4 51-58 3.7 59-68 2.8 69-75 2.2 How did I get those values? I treat bonds/cash as the same thing and then I back out from the optimal portfolio rule, your risk aversion. Note that historical returns for the S&P have been approximately -rf-5%, -15% -- numbers from class. For example, for a score in the range 40- 50, the recommended allocation is 50% stocks, 50% risk free rate. If you solve the following equation for A: 0.5=w= 0.05 A(0.152) You get A=4.44. Given your risk aversion and historical estimates for average returns and volatility, what is your allocation to stocks? Is that your actual allocation in your savings? Why or why not?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


