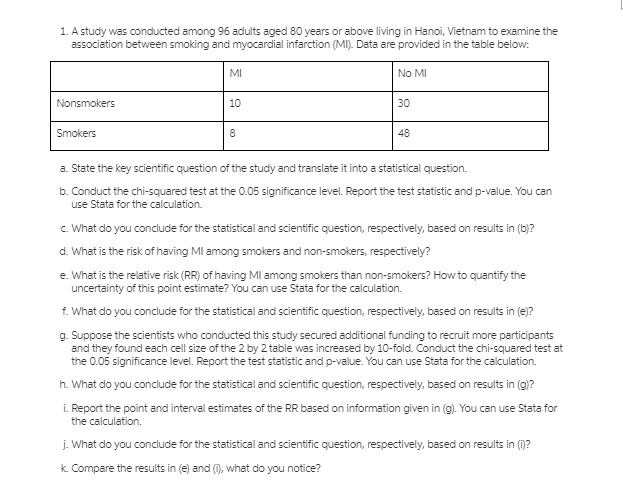
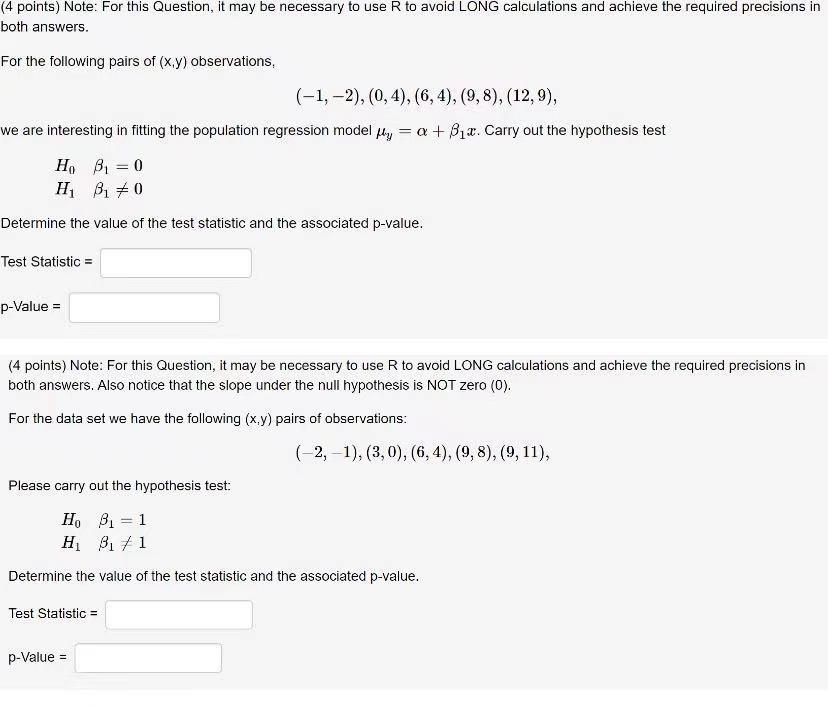
Question
A certain country has four regions: North, East, South, and West. The populations of these regions are 3 million, 4 million, 5 million, and 8
A certain country has four regions: North, East, South, and West. The populations of
these regions are 3 million, 4 million, 5 million, and 8 million, respectively. There are 4
cities in the North, 3 in the East, 2 in the South, and there is only 1 city in the West.
Each person in the country lives in exactly one of these cities.
(a) What is the average size of a city in the country? (This is the arithmetic mean of
the populations of the cities, and is also the expected value of the population of a city
chosen uniformly at random.)
Hint: Give the cities names (labels).
(b) Show that without further information it is impossible to find the variance of the
population of a city chosen uniformly at random. That is, the variance depends on how
the people within each region are allocated between the cities in that region.
(c) A region of the country is chosen uniformly at random, and then a city within that
region is chosen uniformly at random. What is the expected population size of this
randomly chosen city?
Hint: To help organize the calculation, start by finding the PMF of the population size
of the city.
(d) Explain intuitively why the answer to (c) is larger than the answer to .
A hacker is trying to break into a password-protected website by randomly trying to
guess the password. Let m be the number of possible passwords.
(a) Suppose for this part that the hacker makes random guesses (with equal probability),
with replacement. Find the average number of guesses it will take until the hacker guesses
the correct password (including the successful guess).
(b) Now suppose that the hacker guesses randomly, without replacement. Find the average number of guesses it will take until the hacker guesses the correct password (including
the successful guess).
Hint: Use symmetry to find the PMF of the number of guesses.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


