Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A concrete duct is being designed and optimised for transportation of water, with the configuration shown in Figure.1-a. During operation, all external faces are
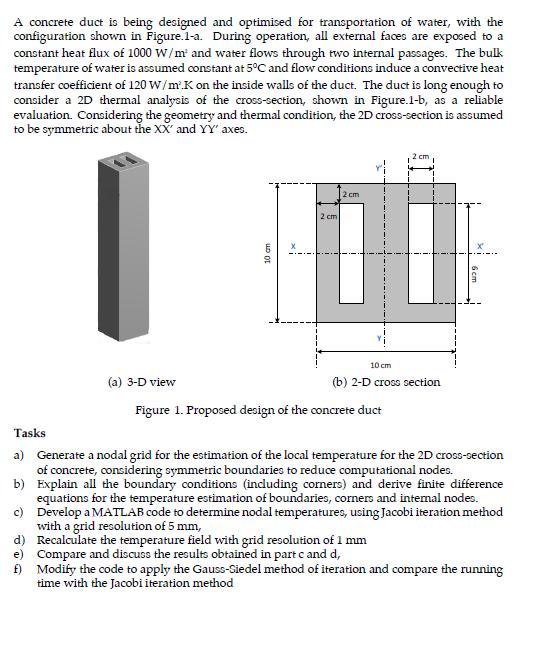
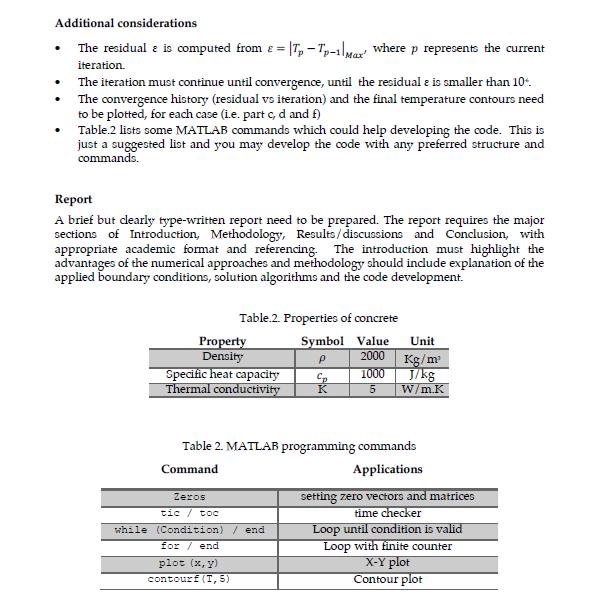
A concrete duct is being designed and optimised for transportation of water, with the configuration shown in Figure.1-a. During operation, all external faces are exposed to a constant heat flux of 1000 W/m and water flows through two internal passages. The bulk temperature of water is assumed constant at 5C and flow conditions induce a convective heat transfer coefficient of 120 W/m.K on the inside walls of the duct. The duct is long enough to consider a 2D thermal analysis of the cross-section, shown in Figure.1-b, as a reliable evaluation. Considering the geometry and thermal condition, the 2D cross-section is assumed to be symmetric about the XX' and YY' axes. (a) 3-D view 10 cm 2 cm 2 cm 2 cm 10 cm (b) 2-D cross section Figure 1. Proposed design of the concrete duct Tasks a) b) Generate a nodal grid for the estimation of the local temperature for the 2D cross-section of concrete, considering symmetric boundaries to reduce computational nodes. Explain all the boundary conditions (including corners) and derive finite difference equations for the temperature estimation of boundaries, corners and internal nodes. Develop a MATLAB code to determine nodal temperatures, using Jacobi iteration method with a grid resolution of 5 mm, c) d) Recalculate the temperature field with grid resolution of 1 mm Compare and discuss the results obtained in part c and d, e) f) Modify the code to apply the Gauss-Siedel method of iteration and compare the running time with the Jacobi iteration method Additional considerations The residual e is computed from = T - Tp-1 Mar where p represents the current iteration. . . The iteration must continue until convergence, until the residual e is smaller than 10. The convergence history (residual vs iteration) and the final temperature contours need to be plotted, for each case (i.e. part c, d and f) Table.2 lists some MATLAB commands which could help developing the code. This is just a suggested list and you may develop the code with any preferred structure and commands. Report A brief but clearly type-written report need to be prepared. The report requires the major sections of Introduction, Methodology, Results/discussions and Conclusion, with appropriate academic format and referencing. The introduction must highlight the advantages of the numerical approaches and methodology should include explanation of the applied boundary conditions, solution algorithms and the code development. Table.2. Properties of concrete Symbol Value P 2000 Property Density Specific heat capacity Thermal conductivity Zeros tic / toc while (Condition) / end for end plot (x, y) contourf (I, 5) Cp 1000 K 5 Table 2. MATLAB programming commands Command Applications Unit Kg/m J/kg W/m.K setting zero vectors and matrices time checker Loop until condition is valid Loop with finite counter X-Y plot Contour plot
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The following tasks are still outstanding Generate a nodal grid for the estimation of the local temperature for the 2D crosssection of concrete considering symmetric boundaries to reduce computational ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


