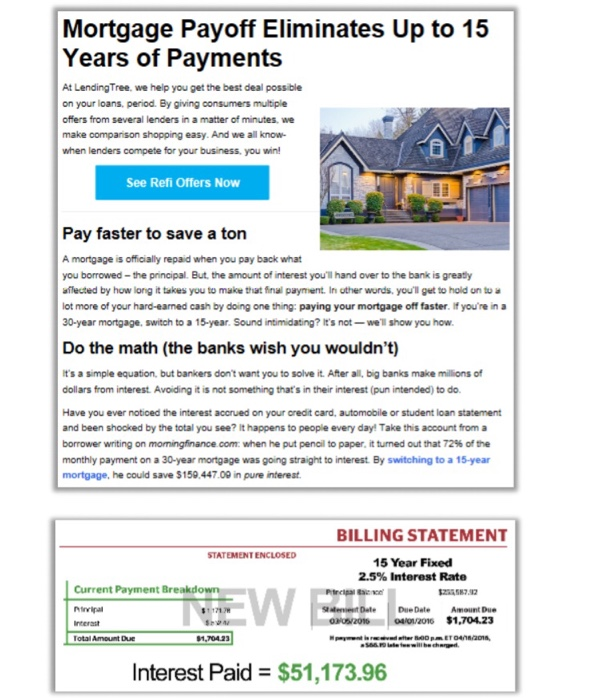
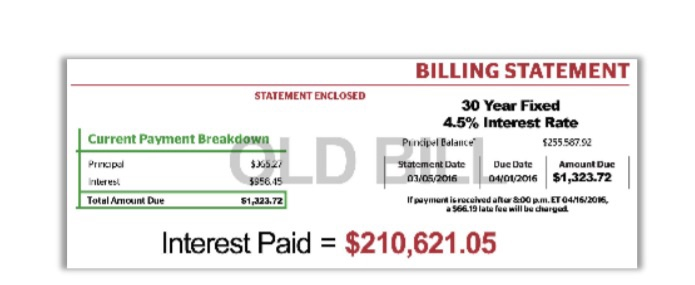
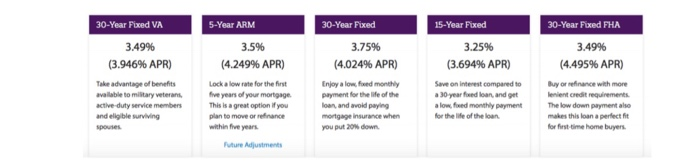
a. Do you think this ad., is fair or deceitful? Why? [Hint I expect you to do a lot more than a couple of lines of waffle! I expect you to do calculations AND look up current market data. For example, I think the ad is possibly deceitful in the following way: They imply that the interest savings for what they offer is magical. Does the table below give you any concern (captured from QuickenLoans)?
In addition, consider the information in Appendix 1 on Mortgage Refinancing. Is there a cost to refinancing a mortgage? Does lendingtree explain these refinancing costs adequately? Finally, and I am not suggesting you should give advice to friends and family, but suppose a family member had brought you this ad. What would you say? How would you support the advice you give?]
Mortgage Payoff Eliminates Up to 15 Years of Payments At Lending Tree, we help you get the best deal possible on your loans, period. By giving consumers multiple offers from several lenders in a matter of minutes, we make comparison shopping easy. And we all know- when lenders compete for your business, you wil See Refi Offers Now Pay faster to save a ton A mortgage is officially repaid when you pay back what you borrowed the principal. But the amount of interest you'll hand over to the bank is greatly flected by how long it takes you to make that final payment. In other words, you'll get to hold on to lot more of your hard-earned cash by doing one thing: paying your mortgage off faster. If you're in a 30-year mortgage, switch to a 15-year. Sound intimidating? It's not-we'll show you how Do the math (the banks wish you wouldn't) it's a simple equation, but bankers don't want you to solve it. After all, big banks make millions of dollars from interest. Avoiding it is not something that's in their interest (pun intended) to do Have you ever noticed the interest accrued on your credit card, automobile or student loan statement and been shocked by the total you see? It happens to people every day! Take this account from a borrower writing on morning finance.com: when he put pencil to paper, it turned out that 72% of the monthly payment on a 30-year mortgage was going straight to interest. By switching to a 15-year mortgage, he could save $150.447.00 in pure interest BILLING STATEMENT STATEMENTENCLOSED 15 Year Fixed 2.5% Interest Rate Current Payment Breakdown w Dale OROS/2018 Due Date 20 A t Due $1,704.23 True 1.04.23 MOTO Interest Paid = $51,173.96 BILLING STATEMENT STATEMENT ENCLOSED Current Payment Breakdown 30 Year Fixed 4.5% Interest Rate Pandipel Balance 5255587.92 Statement Date Due Date Amount Due 03/05/2016 04/01/2016 $1,323.72 If payment is received aftur &00.. ET04/6/2016, Pripul res 5956.15 $1,223.72 Total Amount Due 954.19 lata fee will be durgud Interest Paid = $210,621.05 30-Year Fixed VA 5-Year ARM 15-Year Fixed 30-Year Fixed FHA 3.49% (3.946% APR) 3.5% (4.249% APR) 30-Year Fixed 3.75% (4.024% APR) 3.25% (3.694% APR) 3.49% (4.495% APR) Take advantage of benefits available to military veterans active-duty service members and eligible surviving spouses Lock a low rate for the first five years of your mortgage This is a great option if you plan to move or refinance within five years Enjoy a lowed monthly payment for the life of the loan and word paying mortgage Insurance when you put 20% down. Save an interest compared to a 30 year feedloan, and get alowed monthly payment for the life of the loan Buy or refinance with more lerent credit requirements. The low down payment also makes this loan a perfect fit for first time home buyers Future Adjustments Appendix 1 - When (and When Not) to Refinance Your Mortgage - Investopedia Refinancing Can Save You Money-or Cost Money. Learn the Difference. By INVESTOPEDIA STAFE, Updated Nov 20, 2019 Refinancing a mortgage means paying off an existing loan and replacing it with a new one. There are many reasons why homeowners refinance: to obtain a lower interest rate; to shorten the term of their mortgage; to convert from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate mortgage, or vice versa; to tap into home equity to finance a large purchase, or to consolidate debt. Since refinancing can cost between 3% and 6% of a loan's principal and-as with an original mortgage-requires an appraisal, title search, and application fees, it's important for a homeowner to determine whether refinancing is a wise financial decision. Refinancing to secure a Lower Interest Rate One of the best reasons to refinance is to lower the interest rate on your existing loan. Historically, the rule of thumb is that refinancing is a good idea if you can reduce your interest rate by at least 2%. However, many lenders say 1% savings is enough of an incentive to refinance. KEY TAKEAWAYS A lower interest rate on your mortgage is one of the best reasons to refinance. When interest rates drop, consider refinancing to shorten the term of your mortgage and pay significantly less in interest payments. Switching to a fixed-rate mortgage-or to an adjustable-rate one-can make sense depending on the rates and how long you plan to remain in your current home. consolidating debt can be good reasons to refinance-or doing so can sometimes make the debt trap worse. Reducing your interest rate not only helps you save money, but it also increases the rate at which you build equity in your home, and it can decrease the size of your monthly payment. For example, a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage with an interest rate of 9% on a $100,000 home has a principal and interest payment of $804.62. That same loan at 4.5% reduces your payment to $506.69 Refinancing to Shorten the Loan's Term When interest rates fall, homeowners often have the opportunity to refinance an existing loan for another loan that without much change in the monthly payment, has a significantly shorter term. For a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage on a $100,000 home, refinancing from 9% to 5.5% can cut the term in half to 15 years with only a slight change in the monthly payment from $804.62 to $817.08. Refinancing to Convert to an Adjustable-Rate or Fixed-Rate Mortgage While ARMs often start out offering lower rates than fixed-rate mortgages, periodic adjustments can result in rate increases that are higher than the rate available through a fixed-rate mortgage 2 When this occurs, converting to a fixed-rate mortgage results in a lower interest rate and eliminates concern over future interest rate hikes. Conversely, converting from a fixed-rate loan to an ARM can be a sound financial strategy if interest rates are falling. If rates continue to fall, the periodic rate adjustments on an ARM result in decreasing rates and smaller monthly mortgage payments eliminating the need to refinance every time rates drop. With mortgage interest rates rising, on the other hand, this would be an unwise strategy. Converting to an ARM, which often has a lower monthly payment than a fixed-term mortgage, may be a good idea for homeowners who do not plan to stay in their home for more than a few years. If interest rates are falling, these homeowners can reduce their loan's interest rate and monthly payment, but they will not have to worry about future higher interest rates because they will not live in the home long enough. Refinancing to Tap Equity or Consolidate Debt While the previously mentioned reasons to refinance are all financially sound, mortgage refinancing can be a slippery slope to never-ending debt. Homeowners often access the equity in their homes to cover major expenses, such as the costs of home remodeling or a child's college education. These homeowners may justify the refinancing by the fact that remodeling adds value to the home or that the interest rate on the mortgage loan is less than the rate on money borrowed from another source. Another justification is that the interest on mortgages is tax deductible.3 While these arguments may be true, increasing the number of years that you owe on your mortgage is rarely a smart financial decision nor is spending a dollar on interest to get a 30 cent tax deduction. Also note that since the Tax Cut and Jobs Act went into effect, the size of the loan on which you can deduct interest has dropped from $1 million to $750,000 if you bought your house after Dec. 15, 2017.4 Many homeowners refinance to consolidate their debt. At face value, replacing high-interest debt with a low-interest mortgage is a good idea. Unfortunately, refinancing does not bring automatic financial prudence. Take this step only if you are convinced you can resist the temptation to spend once the refinancing relieves you from debt. It takes years to recoup the 3% to 6% of principal that refinancing costs, so don't do it unless you plan to stay in your current home for more than a few years. Be aware that a large percentage of people who once generated high-interest debt on credit cards, cars, and other purchases will simply do it again after the mortgage refinancing gives them the available credit to do so. This creates an instant quadruple loss composed of wasted fees on the refinancing, lost equity in the house, additional years of increased interest payments on the new mortgage, and the return of high-interest debt once the credit cards are maxed out again- the possible result is an endless perpetuation of the debt cycle and eventual bankruptcy. The Bottom Line Refinancing can be a great financial move if it reduces your mortgage payment, shortens the term of your loan, or helps you build equity more quickly. When used carefully, it can also be a valuable tool for bringing debt under control. Before you refinance, take a careful look at your financial situation and ask yourself: How long do I plan to continue living in the house? How much money will I save by refinancing? The Tax Cut and Jobs Act has changed the size of the loan from which you can deduct interest: it has dropped from $1 million to $750,000 if you bought your house after Dec. 15, 2017. Again, keep in mind that refinancing costs 3% to 6% of the loan's principal. It takes years to recoup that cost with the savings generated by a lower interest rate or a shorter term. So, if you are not planning to stay in the home for more than a few years, the cost of refinancing may negate any of the potential savings. It also pays to remember that a savvy homeowner is always looking for ways to reduce debt, build equity, save money, and eliminate their mortgage payment. Taking cash out of your equity when you refinance does not help to achieve any of those goals. Appendix II - 401(k)s, Charles Schwab What Is a 401(k)? What exactly is a 401(k), and what do you need to think about when you sign up for one? Let's break it down. A 401(k) is an employer sponsored retirement savings plan that includes special tax advantages. Some employers match a portion of their employees' contributions. For example, an employer might offer a 5% dollar-for-dollar match. This means that for every dollar you contribute to your 401(k), your employer will also contribute one dollar, but the match is limited to 5% of your salary. Think of this as "free money," and we recommend you contribute at least the amount needed to receive your full employer match. In this example, keep in mind that if you decide to contribute more than that 5%, your employer won't match the additional contribution. Every 401(k) plan is different, so the options available will depend on your specific plan. Contributions to a traditional 401(k) are not taxed going in, so they can reduce your taxable income. Later on, withdrawals are taxed, including any earnings your contributions had. Mortgage Payoff Eliminates Up to 15 Years of Payments At Lending Tree, we help you get the best deal possible on your loans, period. By giving consumers multiple offers from several lenders in a matter of minutes, we make comparison shopping easy. And we all know- when lenders compete for your business, you wil See Refi Offers Now Pay faster to save a ton A mortgage is officially repaid when you pay back what you borrowed the principal. But the amount of interest you'll hand over to the bank is greatly flected by how long it takes you to make that final payment. In other words, you'll get to hold on to lot more of your hard-earned cash by doing one thing: paying your mortgage off faster. If you're in a 30-year mortgage, switch to a 15-year. Sound intimidating? It's not-we'll show you how Do the math (the banks wish you wouldn't) it's a simple equation, but bankers don't want you to solve it. After all, big banks make millions of dollars from interest. Avoiding it is not something that's in their interest (pun intended) to do Have you ever noticed the interest accrued on your credit card, automobile or student loan statement and been shocked by the total you see? It happens to people every day! Take this account from a borrower writing on morning finance.com: when he put pencil to paper, it turned out that 72% of the monthly payment on a 30-year mortgage was going straight to interest. By switching to a 15-year mortgage, he could save $150.447.00 in pure interest BILLING STATEMENT STATEMENTENCLOSED 15 Year Fixed 2.5% Interest Rate Current Payment Breakdown w Dale OROS/2018 Due Date 20 A t Due $1,704.23 True 1.04.23 MOTO Interest Paid = $51,173.96 BILLING STATEMENT STATEMENT ENCLOSED Current Payment Breakdown 30 Year Fixed 4.5% Interest Rate Pandipel Balance 5255587.92 Statement Date Due Date Amount Due 03/05/2016 04/01/2016 $1,323.72 If payment is received aftur &00.. ET04/6/2016, Pripul res 5956.15 $1,223.72 Total Amount Due 954.19 lata fee will be durgud Interest Paid = $210,621.05 30-Year Fixed VA 5-Year ARM 15-Year Fixed 30-Year Fixed FHA 3.49% (3.946% APR) 3.5% (4.249% APR) 30-Year Fixed 3.75% (4.024% APR) 3.25% (3.694% APR) 3.49% (4.495% APR) Take advantage of benefits available to military veterans active-duty service members and eligible surviving spouses Lock a low rate for the first five years of your mortgage This is a great option if you plan to move or refinance within five years Enjoy a lowed monthly payment for the life of the loan and word paying mortgage Insurance when you put 20% down. Save an interest compared to a 30 year feedloan, and get alowed monthly payment for the life of the loan Buy or refinance with more lerent credit requirements. The low down payment also makes this loan a perfect fit for first time home buyers Future Adjustments Appendix 1 - When (and When Not) to Refinance Your Mortgage - Investopedia Refinancing Can Save You Money-or Cost Money. Learn the Difference. By INVESTOPEDIA STAFE, Updated Nov 20, 2019 Refinancing a mortgage means paying off an existing loan and replacing it with a new one. There are many reasons why homeowners refinance: to obtain a lower interest rate; to shorten the term of their mortgage; to convert from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate mortgage, or vice versa; to tap into home equity to finance a large purchase, or to consolidate debt. Since refinancing can cost between 3% and 6% of a loan's principal and-as with an original mortgage-requires an appraisal, title search, and application fees, it's important for a homeowner to determine whether refinancing is a wise financial decision. Refinancing to secure a Lower Interest Rate One of the best reasons to refinance is to lower the interest rate on your existing loan. Historically, the rule of thumb is that refinancing is a good idea if you can reduce your interest rate by at least 2%. However, many lenders say 1% savings is enough of an incentive to refinance. KEY TAKEAWAYS A lower interest rate on your mortgage is one of the best reasons to refinance. When interest rates drop, consider refinancing to shorten the term of your mortgage and pay significantly less in interest payments. Switching to a fixed-rate mortgage-or to an adjustable-rate one-can make sense depending on the rates and how long you plan to remain in your current home. consolidating debt can be good reasons to refinance-or doing so can sometimes make the debt trap worse. Reducing your interest rate not only helps you save money, but it also increases the rate at which you build equity in your home, and it can decrease the size of your monthly payment. For example, a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage with an interest rate of 9% on a $100,000 home has a principal and interest payment of $804.62. That same loan at 4.5% reduces your payment to $506.69 Refinancing to Shorten the Loan's Term When interest rates fall, homeowners often have the opportunity to refinance an existing loan for another loan that without much change in the monthly payment, has a significantly shorter term. For a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage on a $100,000 home, refinancing from 9% to 5.5% can cut the term in half to 15 years with only a slight change in the monthly payment from $804.62 to $817.08. Refinancing to Convert to an Adjustable-Rate or Fixed-Rate Mortgage While ARMs often start out offering lower rates than fixed-rate mortgages, periodic adjustments can result in rate increases that are higher than the rate available through a fixed-rate mortgage 2 When this occurs, converting to a fixed-rate mortgage results in a lower interest rate and eliminates concern over future interest rate hikes. Conversely, converting from a fixed-rate loan to an ARM can be a sound financial strategy if interest rates are falling. If rates continue to fall, the periodic rate adjustments on an ARM result in decreasing rates and smaller monthly mortgage payments eliminating the need to refinance every time rates drop. With mortgage interest rates rising, on the other hand, this would be an unwise strategy. Converting to an ARM, which often has a lower monthly payment than a fixed-term mortgage, may be a good idea for homeowners who do not plan to stay in their home for more than a few years. If interest rates are falling, these homeowners can reduce their loan's interest rate and monthly payment, but they will not have to worry about future higher interest rates because they will not live in the home long enough. Refinancing to Tap Equity or Consolidate Debt While the previously mentioned reasons to refinance are all financially sound, mortgage refinancing can be a slippery slope to never-ending debt. Homeowners often access the equity in their homes to cover major expenses, such as the costs of home remodeling or a child's college education. These homeowners may justify the refinancing by the fact that remodeling adds value to the home or that the interest rate on the mortgage loan is less than the rate on money borrowed from another source. Another justification is that the interest on mortgages is tax deductible.3 While these arguments may be true, increasing the number of years that you owe on your mortgage is rarely a smart financial decision nor is spending a dollar on interest to get a 30 cent tax deduction. Also note that since the Tax Cut and Jobs Act went into effect, the size of the loan on which you can deduct interest has dropped from $1 million to $750,000 if you bought your house after Dec. 15, 2017.4 Many homeowners refinance to consolidate their debt. At face value, replacing high-interest debt with a low-interest mortgage is a good idea. Unfortunately, refinancing does not bring automatic financial prudence. Take this step only if you are convinced you can resist the temptation to spend once the refinancing relieves you from debt. It takes years to recoup the 3% to 6% of principal that refinancing costs, so don't do it unless you plan to stay in your current home for more than a few years. Be aware that a large percentage of people who once generated high-interest debt on credit cards, cars, and other purchases will simply do it again after the mortgage refinancing gives them the available credit to do so. This creates an instant quadruple loss composed of wasted fees on the refinancing, lost equity in the house, additional years of increased interest payments on the new mortgage, and the return of high-interest debt once the credit cards are maxed out again- the possible result is an endless perpetuation of the debt cycle and eventual bankruptcy. The Bottom Line Refinancing can be a great financial move if it reduces your mortgage payment, shortens the term of your loan, or helps you build equity more quickly. When used carefully, it can also be a valuable tool for bringing debt under control. Before you refinance, take a careful look at your financial situation and ask yourself: How long do I plan to continue living in the house? How much money will I save by refinancing? The Tax Cut and Jobs Act has changed the size of the loan from which you can deduct interest: it has dropped from $1 million to $750,000 if you bought your house after Dec. 15, 2017. Again, keep in mind that refinancing costs 3% to 6% of the loan's principal. It takes years to recoup that cost with the savings generated by a lower interest rate or a shorter term. So, if you are not planning to stay in the home for more than a few years, the cost of refinancing may negate any of the potential savings. It also pays to remember that a savvy homeowner is always looking for ways to reduce debt, build equity, save money, and eliminate their mortgage payment. Taking cash out of your equity when you refinance does not help to achieve any of those goals. Appendix II - 401(k)s, Charles Schwab What Is a 401(k)? What exactly is a 401(k), and what do you need to think about when you sign up for one? Let's break it down. A 401(k) is an employer sponsored retirement savings plan that includes special tax advantages. Some employers match a portion of their employees' contributions. For example, an employer might offer a 5% dollar-for-dollar match. This means that for every dollar you contribute to your 401(k), your employer will also contribute one dollar, but the match is limited to 5% of your salary. Think of this as "free money," and we recommend you contribute at least the amount needed to receive your full employer match. In this example, keep in mind that if you decide to contribute more than that 5%, your employer won't match the additional contribution. Every 401(k) plan is different, so the options available will depend on your specific plan. Contributions to a traditional 401(k) are not taxed going in, so they can reduce your taxable income. Later on, withdrawals are taxed, including any earnings your contributions had