Question
A gas A is transferred by a stagnant gaseous film C inside a capillary tube (see figure). A catalyst was placed at the bottom of
A gas A is transferred by a stagnant gaseous film C inside a capillary tube (see figure). A catalyst was placed at the bottom of the tube, which in contact with gas A, reacts and generates gas B according to the irreversible reaction below:
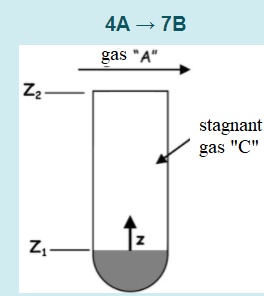
The reaction takes place instantaneously ("rapid") and all the gas "A" turns into "B" on the flat surface of the catalyst inside the capillary tube (at Z1 = 0 cm). The product B is transferred in the opposite direction to the flow of A. The concentration of gas A at the mouth of the capillary tube (at Z2 = 3.75 cm) is 4.5% in moles. Assuming that in this process there is no accumulation and that the system is at a constant temperature and pressure of 398 K and 101.3 kPa, respectively, determine:
a) the distribution profile of the molar fraction of A from the mouth of the tube to the flat surface of the catalyst.
b) the molar concentration (mol.m-3) of A at z = 2.25 cm.
Data: Consider ideal gases with the universal gas constant equal to 8.31 m3.Pa.K-1.mol-1.
4A 7B gas "A" Z2 stagnant gas "C" z ZStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


