Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A gas stream containing acetone (58 g/mol) in air flows from a solvent recovery unit at a rate of 142 liters/s at 150C and 1.3

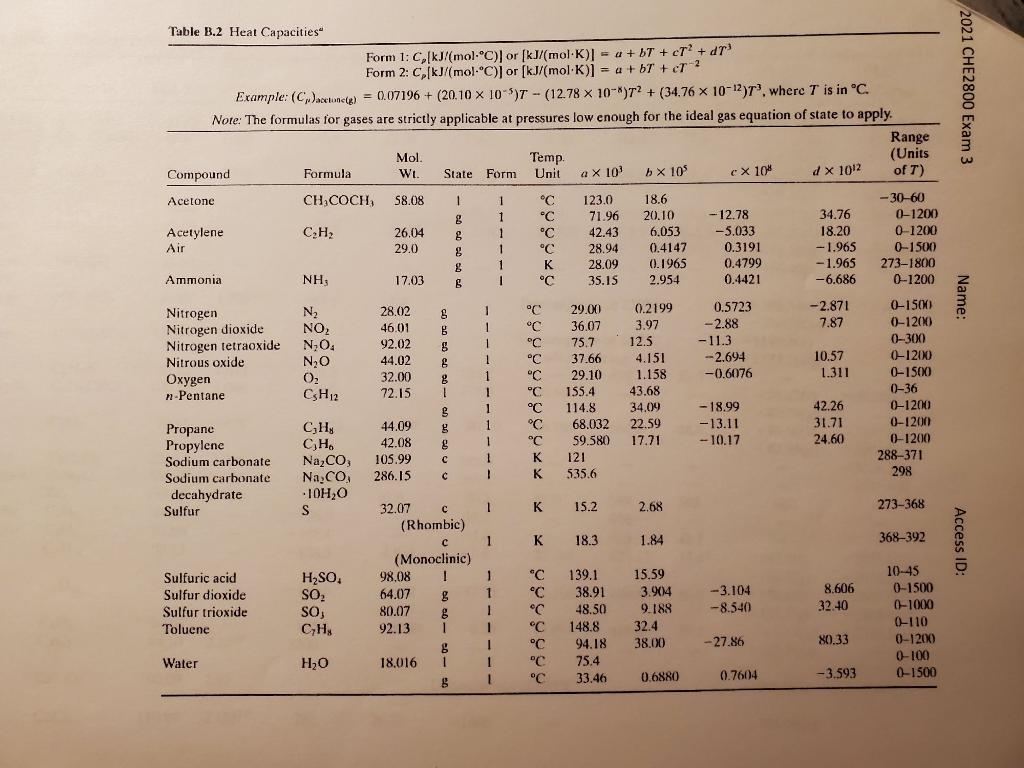
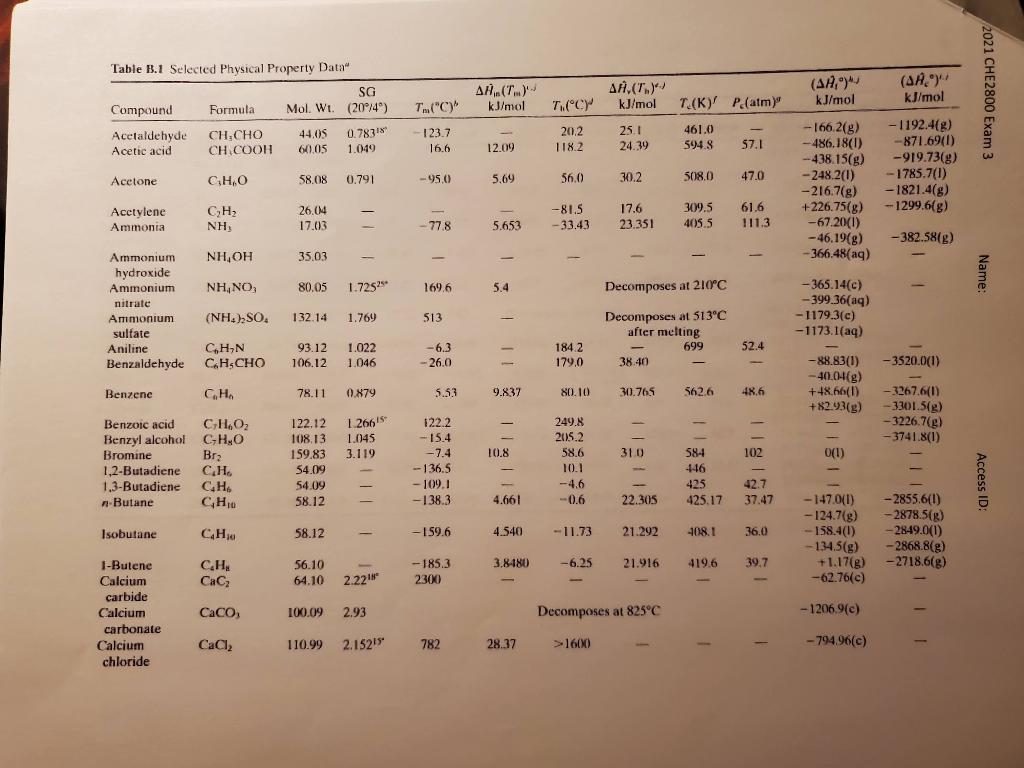
A gas stream containing acetone (58 g/mol) in air flows from a solvent recovery unit at a rate of 142 liters/s at 150C and 1.3 atm. The stream flows into a condenser which liquefies most of the acetone, and the liquid and gas outlet streams are in equilibrium at 0C and 5 atm. Shaft work is delivered to the system at a rate of 25.2 kW to achieve the compression from 1.3 atm to 5.0 atm. To determine the condenser feed stream composition, a 3.00- liter sample of the gas is taken and cooled to a temperature at which essentially all the acetone in the sample is recovered as a liquid. The liquid is weighted to be 0.956 g. Assume ideal gas. Determine 1), the mole fractions of acetone in the feed and product gas streams, and 2), the rate (kW) at which heat must be removed in the condenser. (30 points) Antoine Equation for acetone, P (mm Hg), T [C] + 1210.595 log10 psat = 7.11714 T + 229.664 12 2021 CHE2800 Exam 3 Name: Table B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C,(kJ/(mol-C)) or (kJ/(mol K) = a +bT + ct? + dr Form 2: CkJ/mol-C) or (kJ/mol K)] = a + b + cr ? Example: (Cacetonele) = 0.07196 + (20.10 X 10 )T - (12.78 x 10-)T? + (34.76 x 10-12), where T is in C. Note: The formulas for gases are strictly applicable at pressures low enough for the ideal gas equation of state to apply. Range Mol. Temp. (Units Compound Formula WL. State Form Unit a X 10 b x 10 cx 10" d x 1012 of T) Acetone CH,COCH, 58.08 1 1 C 123.0 18.6 -30-60 8 1 C 71.96 20.10 -12.78 34.76 0-1200 Acetylene CH 26.04 g 1 C 42.43 6.053 -5.033 18.20 0-1200 Air 29.0 g 1 C 28.94 0.4147 0.3191 -1.965 0-1500 8 1 K 28.09 0.1965 0.4799 -1.965 273-1800 Ammonia NH, 17.03 6 1 C 35.15 2.954 0.4421 --6.686 0-1200 Nitrogen N 28.02 S 1 C 29.00 0.2199 0.5723 -2.871 0-1500 Nitrogen dioxide NO 46.01 1 36.07 8 3.97 -2.88 7.87 0-1200 Nitrogen tetraoxide N.O. 92.02 8 1 C 75.7 12.5 - 11.3 0-300 Nitrous oxide N20 44.02 8 1 C 37.66 4.151 -2.694 10.57 0-1200 Oxygen O, 32.00 8 C 29.10 1.158 1.311 0-1500 n-Pentane CH12 72.15 1 1 C 155.4 43.68 0-36 3 1 C 114.8 34.09 -18.99 42.26 0-1200 Propane CH 44.09 B 1 C 68.032 22.59 -13.11 31.71 0-1200 Propylene CH 42.08 1 59.580 17.71 -10.17 24.60 0-1200 Sodium carbonate Na,CO, 105.99 1 121 288-371 Sodium carbonate Na.CO, 286.15 c ! 535.6 298 decahydrate 10H2O Sulfur S S 32.07 1 K 15.2 2.68 273-368 (Rhombic) 1 K 18.3 1.84 368-392 (Monoclinic) Sulfuric acid H2SO, 98.08 T 1 C 139.1 15.59 10-45 Sulfur dioxide SO, 64.07 g 1 C 38.91 3.904 -3.104 8.606 0-1500 Sulfur trioxide SO, 80.07 8 1 C 48.50 9.188 -8.540 32.40 0-1000 Toluene CyHy 92.13 1 1 C 148.8 32.4 0-110 8 I C 94.18 38.00 - 27.86 80.33 0-1200 Water H2O 18.016 1 1 C 75.4 0-100 8 1 C C 33.46 0.6880 0.7604 -3.593 0-1500 -0.6076 x 2 Access ID: ,(,)*) kJ/mol AH.(...) kJ/mol (AH,)" kJ/mol (AA) kJ/mol Table B.1 Selected Physical Property Data SG Compound Formula Mol. Wt. (20/4) Acetaldehyde CL,CHO 44.05 0.7831 Acetic acid CHCOOH 60.05 1.049 2021 CHE2800 Exam 3 T.("C) T.CC T.(K)' P (atm)" 123.7 16.6 20.2 118.2 25.1 24.39 461.0 594.8 12.09 57.1 - 1192.4(8) -871.69(1) -919.73(g) -1785.7(1) -1821.4(8) -1299.68) Acetone ,0 58.08 0.791 -95,0 5.69 56.0 30.2 508.0 47.0 - 166.2(g) - 486,18(0) -438.15(g) -248.2(1) -216.7(8) +226.75(8) - 67.20(1) - 46.19(8) -366.48(aq) 1 Acetylene Ammonia CH NH: 26.014 17.03 --81.5 -33.43 17.6 23.351 309.5 405.5 61.6 111.3 - 778 5.653 -382.58(g) , 35.03 - - Name: ,NO, 80.05 1.72529 169.6 5.4 Decomposes at 210C Ammonium hydroxide Ammonium nitrate Ammonium sulfate Aniline Benzaldehyde -365.14(c) - 399.36(aq) - 1179.3(e) -1173.1(aq) (NH)SO. 132.14 1.769 513 Decomposes at 513C after melting 699 38.40 52.4 CHN C.HSCHO 93.12 106.12 1.022 1.046 -6.3 - 26.0 1842 179,0 -3520.0(1) - 88.83(1) -40046g) +48.66(1) +82.93(g) Benzene C.H. 78.11 0.879 5.53 9.837 80.10 30.765 562.6 48.6 -3267.6(0) - 3301.5(g) -3226.7(g) -3741.8(1) 10.8 310 102 Benzoic acid CH,02 Benzyl alcohol CHO Bromine Brz 1,2-Butadiene CH 1.3-Butadiene CH -Butane CH 0(1) O) 122.12 1.266 108.13 1.045 159.83 3.119 54.09 54.09 58.12 122.2 -15.4 - 7.4 - 136.5 - 109.1 -138.3 249.8 2015.2 58.6 10.1 -4.6 -0.6 584 446 425 425.17 42.7 37.47 Access ID: 4.661 22.305 Isobutane . 58.12 -159.6 4.540 -11.73 21.292 408.1 36.0 -147.0(1) - 2855.6(1) - 124.7(8) -2878.5(8) --158.4(1) - 2849.0(1) - 134.5(g) - 2868.8(3) +1.17(8) -2718.6(8) -62.76(e) 56.10 3.8180 -6.25 21.916 419.6 39.7 C.H. CaC, -185.3 2300 64.10 2.221 1-Butene Calcium carbide Calcium carbonate Calcium chloride Caco, 100.09 2.93 Decomposes at 825C - 1206.9(e) CaCl2 110.99 2.15215 782 28.37 >1600) - 794.96(c)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


