Question
A gaseous mixture flowing in a duct has the following molar composition: 15% carbon monoxide (28.01 g/mol), 2% carbon dioxide (44.01 g/mol), 42% oxygen (32.01
A gaseous mixture flowing in a duct has the following molar composition: 15% carbon monoxide (28.01 g/mol), 2% carbon dioxide (44.01 g/mol), 42% oxygen (32.01 g/mol), 0 g/mol) and 41% nitrogen (28.01 g/mol). A Pitot tube, connected to a U-tube manometer filled with water, is used to measure the velocity at the center of the duct. For the "Pitot probe/U-tube" system, the equation shown below is valid, where V is the local flow velocity of the gas mixture, m is the specific mass of the manometric fluid (1000 kg.m-3), g is the acceleration of gravity (10 ms-2), the specific mass or density of the gaseous mixture, and h the difference in level of the gauge fluid.
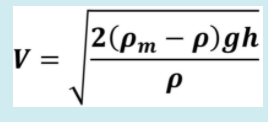
If the absolute velocities of the individual components are 54.0 ms-1 for carbon monoxide, 38 ms-1 for carbon dioxide, 70 ms-1 for oxygen, and 86 ms-1 for nitrogen, what will the reading be? h (in cm) of the manometer? The gas is at 500 K and 300 kPa and behaves like a mixture of ideal gases. Given: R = 8.31 m3.Pa.K-1.mol-1.
2(Pm - p)gh V=Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


