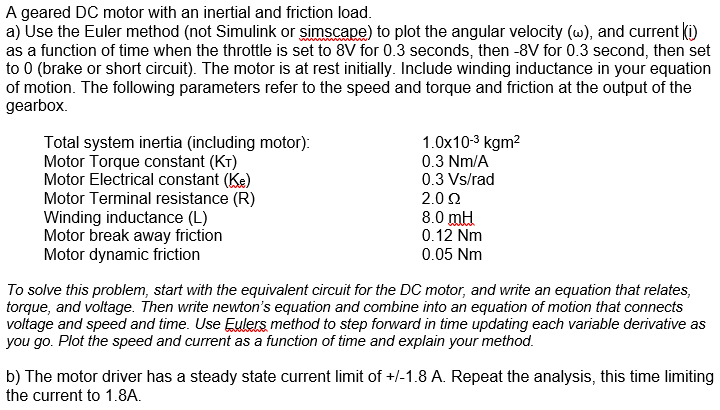
A geared DC motor with an inertial and friction load. a) Use the Euler method (not Simulink or simscape) to plot the angular velocity (w), and current as a function of time when the throttle is set to 8V for 0.3 seconds, then -8V for 0.3 second, then set to 0 (brake or short circuit). The motor is at rest initially. Include winding inductance in your equation of motion. The following parameters refer to the speed and torque and friction at the output of the gearbox Total system inertia (including motor): Motor Torque constant (KT) Motor Electrical constant (Ke) Motor Terminal resistance (R) Winding inductance (L) Motor break away friction Motor dynamic friction 1.0x10-3 kgm2 0.3 Nm/A 0.3 Vs/rad 2.022 8.0 mH 0.12 Nm 0.05 Nm To solve this problem, start with the equivalent circuit for the DC motor, and write an equation that relates, torque, and voltage. Then write newton's equation and combine into an equation of motion that connects voltage and speed and time. Use Eulers method to step forward in time updating each variable derivative as you go. Plot the speed and current as a function of time and explain your method. b) The motor driver has a steady state current limit of +/-1.8 A. Repeat the analysis, this time limiting the current to 1.8A. A geared DC motor with an inertial and friction load. a) Use the Euler method (not Simulink or simscape) to plot the angular velocity (w), and current as a function of time when the throttle is set to 8V for 0.3 seconds, then -8V for 0.3 second, then set to 0 (brake or short circuit). The motor is at rest initially. Include winding inductance in your equation of motion. The following parameters refer to the speed and torque and friction at the output of the gearbox Total system inertia (including motor): Motor Torque constant (KT) Motor Electrical constant (Ke) Motor Terminal resistance (R) Winding inductance (L) Motor break away friction Motor dynamic friction 1.0x10-3 kgm2 0.3 Nm/A 0.3 Vs/rad 2.022 8.0 mH 0.12 Nm 0.05 Nm To solve this problem, start with the equivalent circuit for the DC motor, and write an equation that relates, torque, and voltage. Then write newton's equation and combine into an equation of motion that connects voltage and speed and time. Use Eulers method to step forward in time updating each variable derivative as you go. Plot the speed and current as a function of time and explain your method. b) The motor driver has a steady state current limit of +/-1.8 A. Repeat the analysis, this time limiting the current to 1.8A







