Question
a) h'(2), where h(z) = f(g(x)) h'(2) =6 b) h'(4), where h(x) = g(f(x)) h'(4) =5 c) h'(1), where h(x) = g(g(x)) h'(1) 16
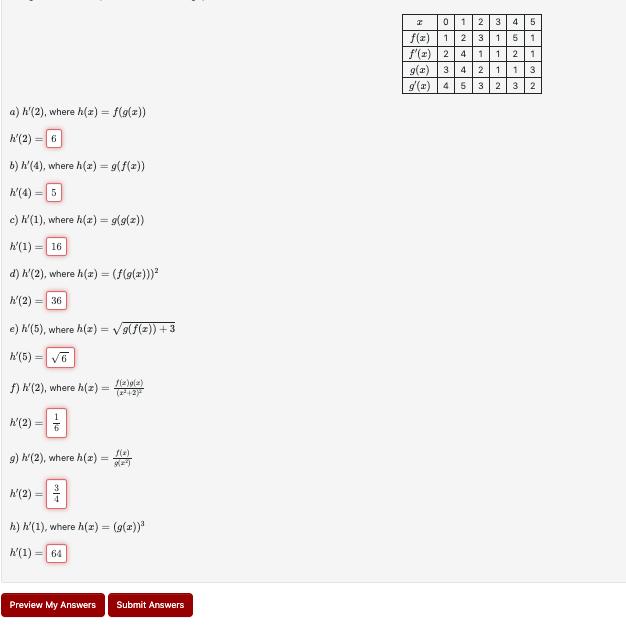
a) h'(2), where h(z) = f(g(x)) h'(2) =6 b) h'(4), where h(x) = g(f(x)) h'(4) =5 c) h'(1), where h(x) = g(g(x)) h'(1) 16 = d) h'(2), where h(x) = (f(g(x))) h'(2) 36 e) h'(5), where h(z) = g(f(z))+3 h'(5) 6 f) h'(2), where h(z). = h'(2) 6 g) h(2), where h(a) h'(2) = 3 = f(z)g(2) (x+2) f(x) (2) h) h'(1), where h(z) = (g(x)) h'(1) 64 = Preview My Answers Submit Answers H 0 1 2 3 1 ** f(x) f'(x) 1 2 1 g(x) 3 4 2 1 1 3 g(x) 45 3 2 3 2 4 5 23151 1 2 4
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a Given hx fgx Differentiating with respect to x we get hx fgxgx Put x 2 we have h2 fg2g2 From table ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications
Authors: Kenneth H. Rosen
7th edition
0073383090, 978-0073383095
Students also viewed these Accounting questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



