Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A manufacturing company has been selected to assemble a small but important component that will be used during the construction of numerous infrastructure projects.
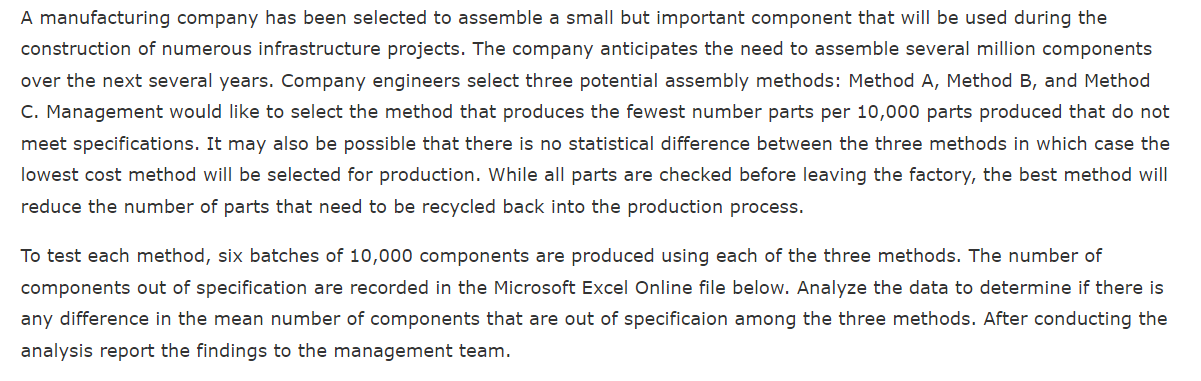
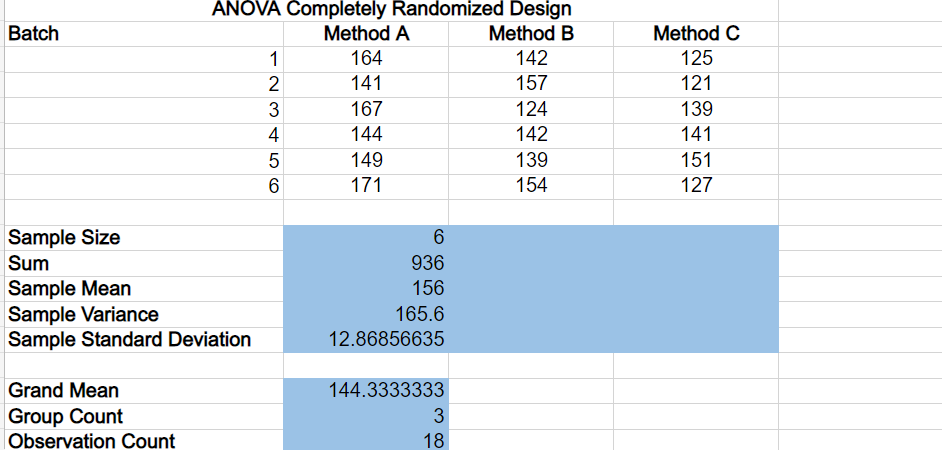

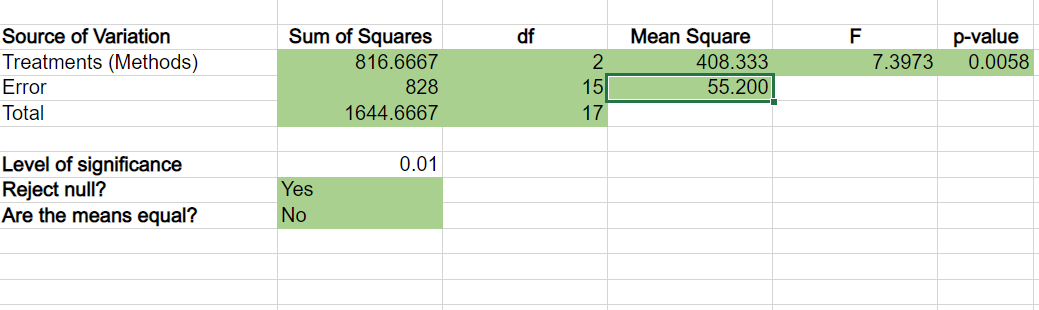
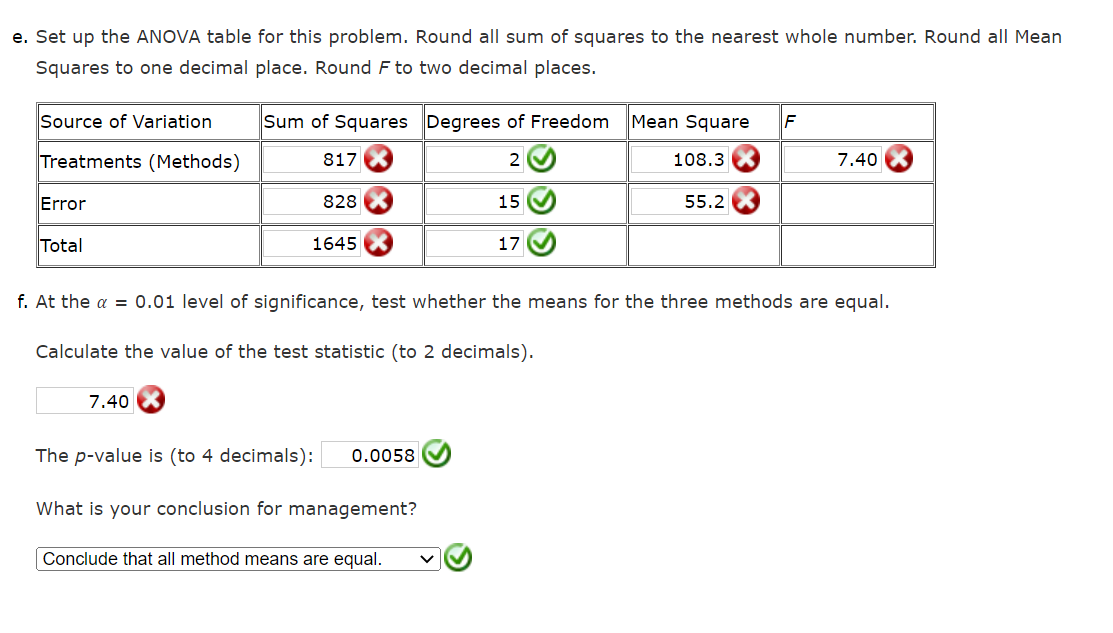
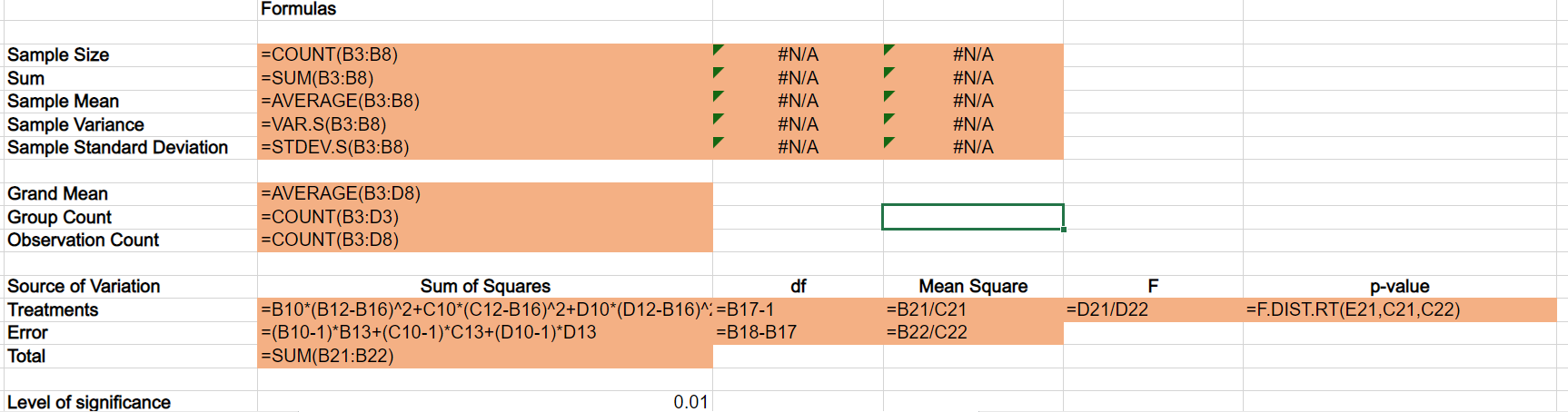

A manufacturing company has been selected to assemble a small but important component that will be used during the construction of numerous infrastructure projects. The company anticipates the need to assemble several million components over the next several years. Company engineers select three potential assembly methods: Method A, Method B, and Method C. Management would like to select the method that produces the fewest number parts per 10,000 parts produced that do not meet specifications. It may also be possible that there is no statistical difference between the three methods in which case the lowest cost method will be selected for production. While all parts are checked before leaving the factory, the best method will reduce the number of parts that need to be recycled back into the production process. To test each method, six batches of 10,000 components are produced using each of the three methods. The number of components out of specification are recorded in the Microsoft Excel Online file below. Analyze the data to determine if there is any difference in the mean number of components that are out of specificaion among the three methods. After conducting the analysis report the findings to the management team. ANOVA Completely Randomized Design Batch Method A Method B Method C 1 164 142 125 23456 2 141 157 121 167 124 139 144 142 141 149 139 151 171 154 127 Sample Size Sum 6 936 Sample Mean 156 Sample Variance 165.6 Sample Standard Deviation 12.86856635 Grand Mean 144.3333333 Group Count 3 Observation Count 18 a. Compute the sum of squares between treatments (assembly methods). 817.7 b. Compute the mean square between treatments (to 1 decimal if necessary). 408.3 c. Compute the sum of squares due to error. 828 d. Compute the mean square due to error (to 1 decimal if necessary). 55.2 Source of Variation Treatments (Methods) Error Total Sum of Squares 816.6667 828 1644.6667 df 2 15 17 Level of significance 0.01 Reject null? Yes Are the means equal? No Mean Square F p-value 408.333 7.3973 0.0058 55.200 e. Set up the ANOVA table for this problem. Round all sum of squares to the nearest whole number. Round all Mean Squares to one decimal place. Round F to two decimal places. Source of Variation Treatments (Methods) Error Total Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square F 817 X 2 828 X 15 1645 17 108.3 X 55.2 X 7.40 X f. At the = 0.01 level of significance, test whether the means for the three methods are equal. Calculate the value of the test statistic (to 2 decimals). 7.40 X The p-value is (to 4 decimals): 0.0058 What is your conclusion for management? [ Conclude that all method means are equal. Sample Size Sum Sample Mean Sample Variance Sample Standard Deviation Grand Mean Group Count Formulas =COUNT(B3:B8) =SUM(B3:B8) |=AVERAGE(B3:B8) =VAR.S(B3:B8) =STDEV.S(B3:B8) =AVERAGE(B3:D8) =COUNT(B3:D3) Observation Count =COUNT(B3:D8) Source of Variation Treatments Error Total Level of significance #N/A # N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A #N/A Sum of Squares =B10*(B12-B16)^2+C10(C12-B16)^2+D10*(D12-B16)=B17-1 =(B10-1)*B13+(C10-1)*C13+(D10-1)*D13 =SUM(B21:B22) -B18-B17 0.01 df Mean Square F =B21/C21 =D21/D22 =B22/C22 p-value =F.DIST.RT(E21,C21,C22) Level of significance Reject null? Are the means equal? |=IF(F21
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


