Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A mixture of natural talc and borax is obtained via surface mining techniques and is delivered in open- top trucks to the plant site.
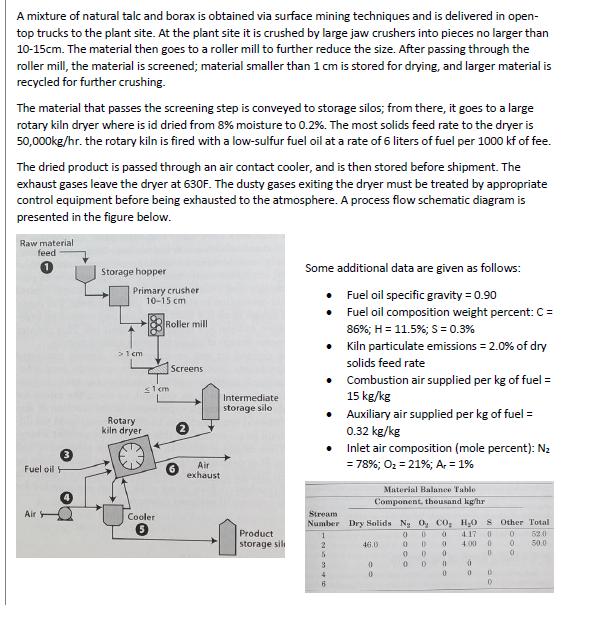

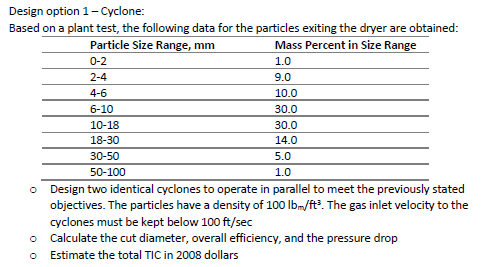

A mixture of natural talc and borax is obtained via surface mining techniques and is delivered in open- top trucks to the plant site. At the plant site it is crushed by large jaw crushers into pieces no larger than 10-15cm. The material then goes to a roller mill to further reduce the size. After passing through the roller mill, the material is screened; material smaller than 1 cm is stored for drying, and larger material is recycled for further crushing. The material that passes the screening step is conveyed to storage silos; from there, it goes to a large rotary kiln dryer where is id dried from 8% moisture to 0.2%. The most solids feed rate to the dryer is 50,000kg/hr. the rotary kiln is fired with a low-sulfur fuel oil at a rate of 6 liters of fuel per 1000 kf of fee. The dried product is passed through an air contact cooler, and is then stored before shipment. The exhaust gases leave the dryer at 630F. The dusty gases exiting the dryer must be treated by appropriate control equipment before being exhausted to the atmosphere. A process flow schematic diagram is presented in the figure below. Raw material feed Storage hopper Primary crusher 10-15 cm Roller mill Some additional data are given as follows: Fuel oil specific gravity = 0.90 Fuel oil composition weight percent: C = 86%; H = 11.5%; S = 0.3% Kiln particulate emissions = 2.0% of dry solids feed rate 3 Fuel oil F >1 cm Rotary kiln dryer 51cm Screens 2 Air exhaust Air Cooler Intermediate storage silo Combustion air supplied per kg of fuel = 15 kg/kg Auxiliary air supplied per kg of fuel = 0.32 kg/kg Inlet air composition (mole percent): Nz = 78%; O = 21%; Ar = 1% Stream Material Balance Table Component, thousand kg/hr. Number Dry Solids Ng Oy Co, HO S Other Total 0 0 0 4.17 0 0 52.0 Product 1 storage sili 2 46.0 0 D 0 4:00 0 0 50.0 5 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 D " 9 4 0 0 0 D 6 0 Requirements #1: overall calculations 1. Calculate the mass emission rate of particles from the dryer, in kg/hr 2. Calculate the percentages of the raw feed that are lost in the crushing step and in the drying step 3. Calculate the mass emission rate of SOfrom the dryer, in kg/hr 4. Calculate the concentration of particles emitted from the dryer, in g/m 5. calculate the concentration of SO in the exhaust, in g/m 6. if emission limits require that less than 10 kg/hr of particles be emitted, calculate the required efficiency of the collection system 7. calculate the volume percent of moisture in the exhaust gases 8. calculate the exhaust gas flow rate, in dry m/hr and in acfm 9. calculate the volume percentages of CO2 and Oin the exhaust gases on a dry basis Design option 1 - Cyclone: Based on a plant test, the following data for the particles exiting the dryer are obtained: Particle Size Range, mm 0-2 2-4 4-6 6-10 10-18 18-30 30-50 Mass Percent in Size Range 1.0 9.0 10.0 30.0 30.0 14.0 5.0 1.0 50-100 Design two identical cyclones to operate in parallel to meet the previously stated objectives. The particles have a density of 100 lbm/ft. The gas inlet velocity to the cyclones must be kept below 100 ft/sec Calculate the cut diameter, overall efficiency, and the pressure drop Estimate the total TIC in 2008 dollars Design option 3 - ESP: Assume that initial calculations have been made, and they show that an ESP is feasible. For a pilot-scale ESP Inlet loading = 5.0gr/ft; Outlet loading 0.10 gr/ft Gas velocity = 5ft/sec Corona power = 12.0 W Gas flow rate = 100 ft/min Collection surface area = 25 ft Design a full-size ESP and give the TIC in 2008 dollars
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


