Question
A new start-up company from AU has developed an E. coli bacterium that has been genetically modified to produce a new biological antibiotic, and they
A new start-up company from AU has developed an E. coli bacterium that has been genetically modified to produce a new biological antibiotic, and they are in the process of scaling up their process. To test the optimal temperature, the company has carried out three tests in a bioreactor with three different temperatures: 28C, 32C and 37C. During the test, samples are taken every two hours and cell density is measured through a turbidity measurement (OD600). The result can be seen in the figure below.
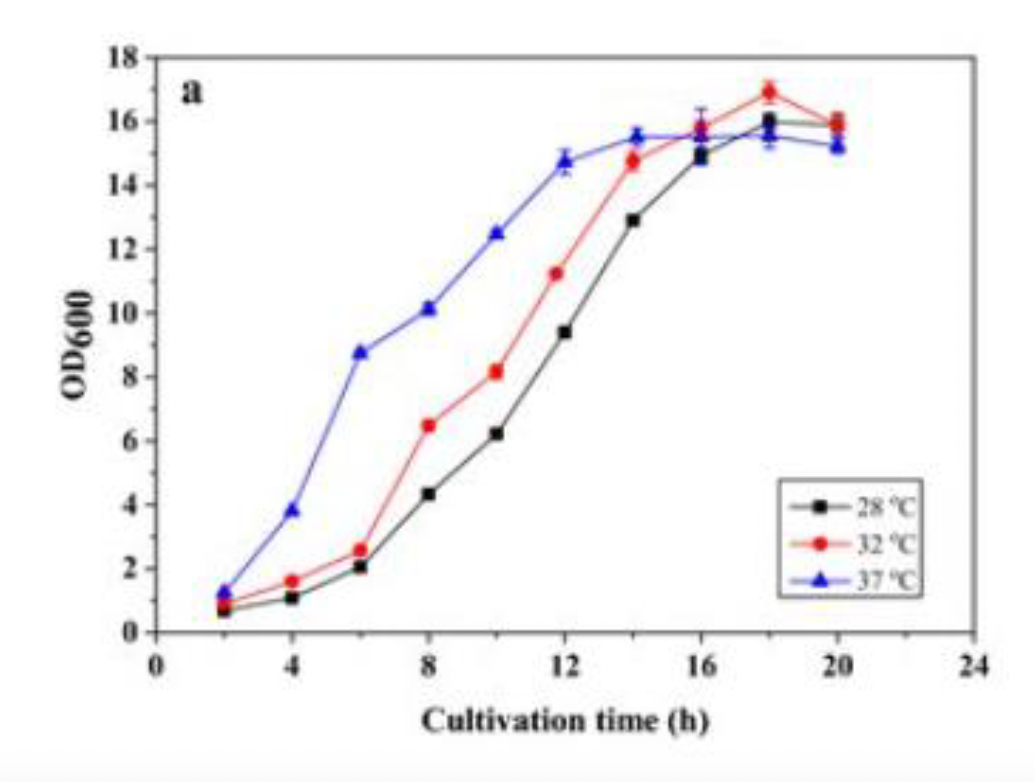
a) Determine from the figure the time interval for each test in which the E. coli bacterium has grown exponentially
b) Calculate the growth constant (k) and generation time (g) for all three exponential growth phases and comment on whether the results make sense when the different temperature tests are compared. (Reading on the graph can be estimated to one decimal accuracy)
c) The biological antibiotic is only produced when the E. coli bacteria transitions to the stationary phase, and it is here that the company can start "harvesting" their actual product. When does the stationary phase occur for each of the three tests?
d) The cell density quickly becomes too high for direct measurement on the spectrophotometer. How many times must the sample be diluted when the bacteria is in the stationary phase? Explain shortly why it is necessary to dilute so many times.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


