Question
A parent company acquired its 70% interest in its subsidiary on January 1, 2017. On the acquisition date, the total fair value of the controlling
A parent company acquired its 70% interest in its subsidiary on January 1, 2017. On the acquisition date, the total fair value of the controlling interest and the noncontrolling interest was $280,000 in excess of the book value of the subsidiarys Stockholders Equity. All of that excess was allocated to a Royalty Agreement, which had a zero book value in the subsidiarys financial statements (i.e., there is no Goodwill).
The Royalty Agreement has a 7-year estimated remaining economic life on the acquisition date. Both companies use straight line amortization, with no terminal value.
In January 2020, the subsidiary sold Equipment to the parent for a cash price of $200,000. The subsidiary acquired the equipment at a cost of $384,000 and depreciated the equipment over its 10-year useful life using the straight-line method (no salvage value). The subsidiary had depreciated the equipment for 6 years at the time of sale. The parent retained the depreciation policy of the subsidiary and depreciated the equipment over its remaining 4-year useful life.
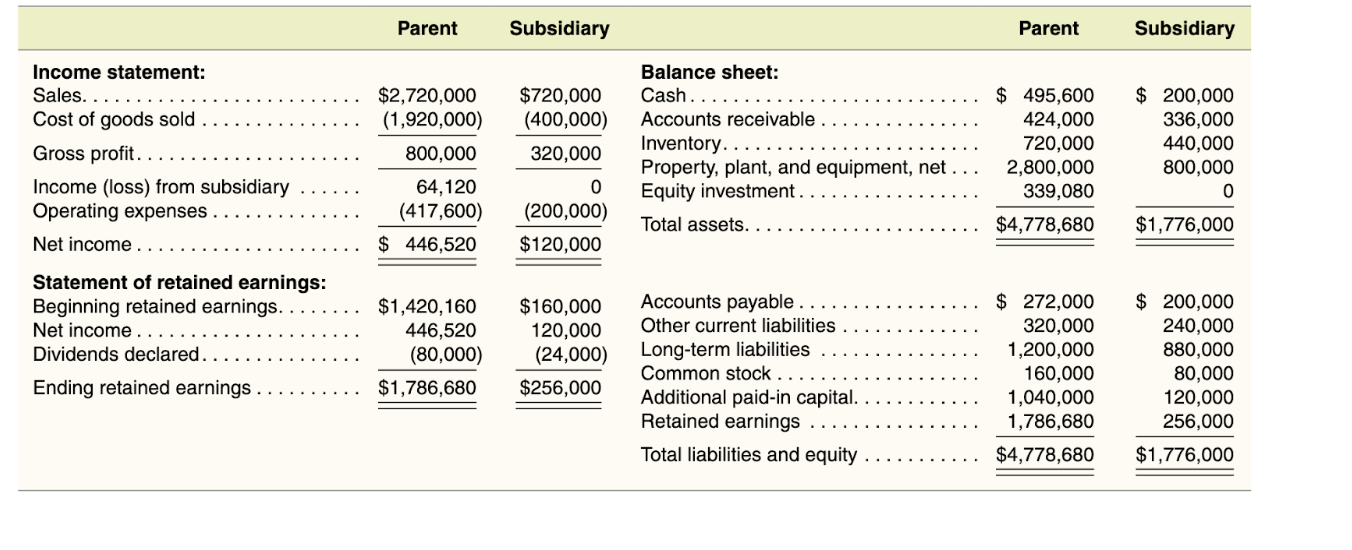
Following are pre-consolidation financial statements of the parent and its subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2022. The parent uses the equity method to account for its Equity Investment.
- Disaggregate and document the activity for the 100% Acquisition Accounting Premium (AAP), the controlling interest AAP and the noncontrolling interest AAP.
- Calculate and organize the profits and losses on intercompany transactions and balances.
- Compute the pre-consolidation Equity Investment account beginning and ending balances starting with the stockholders equity of the subsidiary.
- Reconstruct the activity in the parents pre-consolidation Equity Investment T-account for the year of consolidation.
- Independently compute the owners equity attributable to the noncontrolling interest beginning and ending balances starting with the owners equity of the subsidiary.
- Independently calculate consolidated net income, controlling interest net income and noncontrolling interest net income.
- Prepare the C, E, A, D, and I entries and post them to the worksheet.
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & Parent & Subsidiary & & Parent & Subsidiary \\ \hline Income statement: & & & Balance sheet: & & \multirow[b]{2}{*}{$200,000} \\ \hline Sales........... & $2,720,000 & $720,000 & Cash........ & 495,600 & \\ \hline Cost of goods sold. & (1,920,000) & (400,000) & Accounts receivable. & 424,000 & 336,000 \\ \hline Gross profit........... & 800,000 & 320,000 & Inventory. ...... & \begin{tabular}{r} 720,000 \\ 2,800,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} 440,000 \\ 800,000 \end{tabular} \\ \hline Income (loss) from subsidiary & \multirow{2}{*}{\begin{tabular}{r} 64,120 \\ (417,600) \\ \end{tabular}} & \multirow{2}{*}{\begin{tabular}{r} 0 \\ (200,000) \end{tabular}} & & & \\ \hline Operating expenses. & & & Total assets. . & $4,778,680 & \multirow[t]{2}{*}{$1,776,000} \\ \hline Net income . & $446,520 & $120,000 & Totar asoets. & 44,170,000 & \\ \hline \multicolumn{6}{|l|}{ Statement of retained earnings: } \\ \hline Beginning retained earnings. & \begin{tabular}{r} $1,420,160 \\ 446,520 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{r} $160,000 \\ 120,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} Accounts payable.... \\ Other current liabilities \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{rl} $ & 272,000 \\ 320,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{aligned}\( \$ 200,000 \\ 240,000\end{aligned} \) \\ \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Net income.. \\ Dividends declared. . . . . . \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} 446,520 \\ (80,000) \end{tabular} & (24,000) & Long-term liabilities .. & 1,200,000 & 880,000 \\ \hline \multirow{4}{*}{ Ending retained earnings. } & $1,786,680 & $256,000 & Common stock.... & 160,000 & 80,000 \\ \hline & & & Additional paid-in capital. & 1,040,000 & 120,000 \\ \hline & & & Retained earnings & 1,786,680 & 256,000 \\ \hline & & & Total liabilities and equity . . & $4,778,680 & $1,776,000 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline & Parent & Subsidiary & & Parent & Subsidiary \\ \hline Income statement: & & & Balance sheet: & & \multirow[b]{2}{*}{$200,000} \\ \hline Sales........... & $2,720,000 & $720,000 & Cash........ & 495,600 & \\ \hline Cost of goods sold. & (1,920,000) & (400,000) & Accounts receivable. & 424,000 & 336,000 \\ \hline Gross profit........... & 800,000 & 320,000 & Inventory. ...... & \begin{tabular}{r} 720,000 \\ 2,800,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} 440,000 \\ 800,000 \end{tabular} \\ \hline Income (loss) from subsidiary & \multirow{2}{*}{\begin{tabular}{r} 64,120 \\ (417,600) \\ \end{tabular}} & \multirow{2}{*}{\begin{tabular}{r} 0 \\ (200,000) \end{tabular}} & & & \\ \hline Operating expenses. & & & Total assets. . & $4,778,680 & \multirow[t]{2}{*}{$1,776,000} \\ \hline Net income . & $446,520 & $120,000 & Totar asoets. & 44,170,000 & \\ \hline \multicolumn{6}{|l|}{ Statement of retained earnings: } \\ \hline Beginning retained earnings. & \begin{tabular}{r} $1,420,160 \\ 446,520 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{r} $160,000 \\ 120,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} Accounts payable.... \\ Other current liabilities \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{rl} $ & 272,000 \\ 320,000 \end{tabular} & \begin{aligned}\( \$ 200,000 \\ 240,000\end{aligned} \) \\ \hline \begin{tabular}{l} Net income.. \\ Dividends declared. . . . . . \end{tabular} & \begin{tabular}{l} 446,520 \\ (80,000) \end{tabular} & (24,000) & Long-term liabilities .. & 1,200,000 & 880,000 \\ \hline \multirow{4}{*}{ Ending retained earnings. } & $1,786,680 & $256,000 & Common stock.... & 160,000 & 80,000 \\ \hline & & & Additional paid-in capital. & 1,040,000 & 120,000 \\ \hline & & & Retained earnings & 1,786,680 & 256,000 \\ \hline & & & Total liabilities and equity . . & $4,778,680 & $1,776,000 \\ \hline \end{tabular}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


