Question
A physicist performs an experiment to evaluate the number of moles of a gas inside a container. The container is kept at a constant room
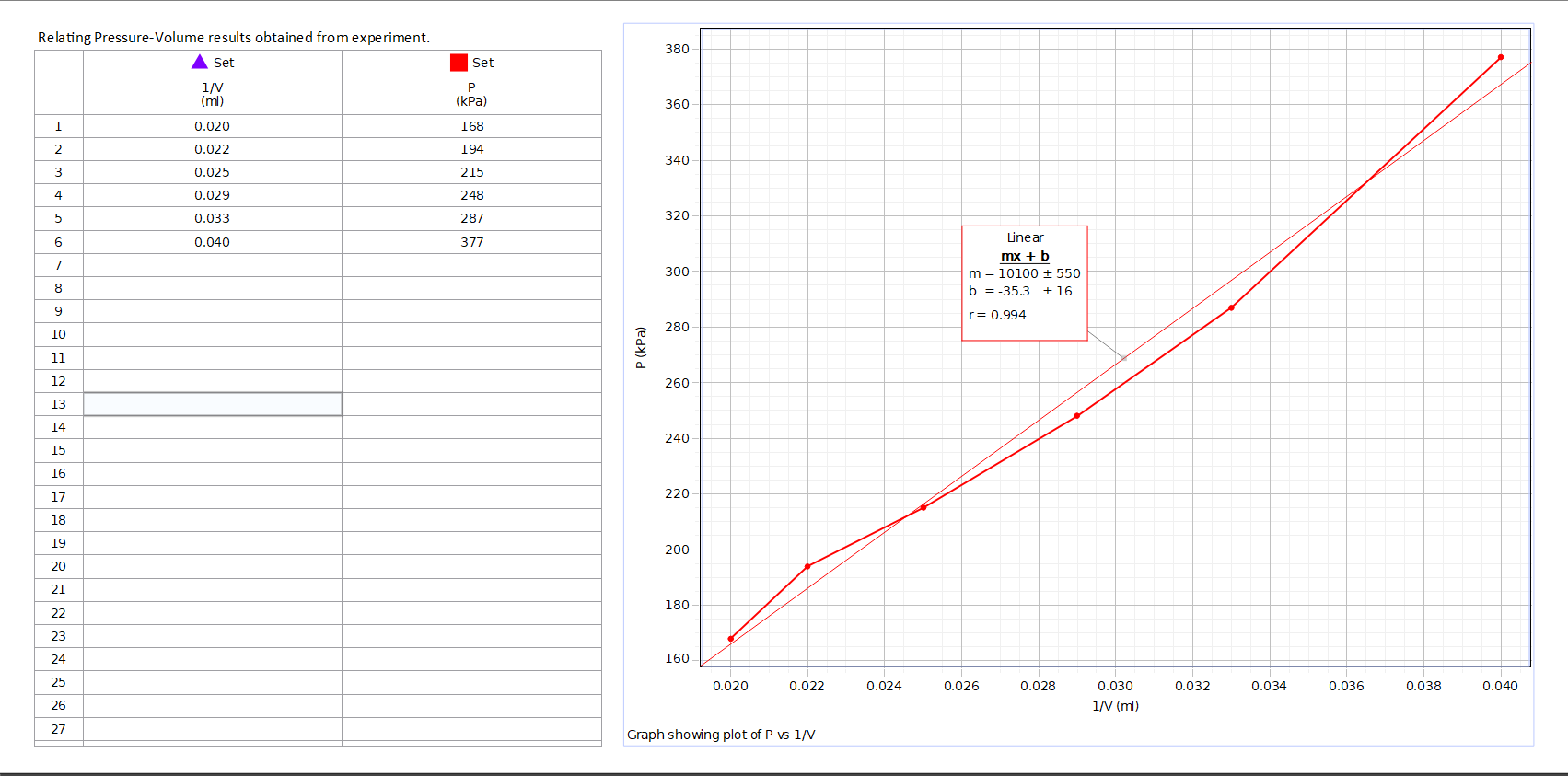
A physicist performs an experiment to evaluate the number of moles of a gas inside a container. The container is kept at a constant room temperature of 23 C and is built in such a way that the number of moles stays constant. The physicist changes the volume to different values and measures the corresponding (absolute) pressures. The table below shows the results of the experiment.
Assuming the gas obeys the ideal gas law, use the value of the slope m to find the number of moles. The slope calculated is related to the Universal Gas Constant, R, with the following equation: m = nRT.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


