Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
a. Prepare a worksheet to consolidate the separate 2021 financial statements for Gibson and Keller. b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have

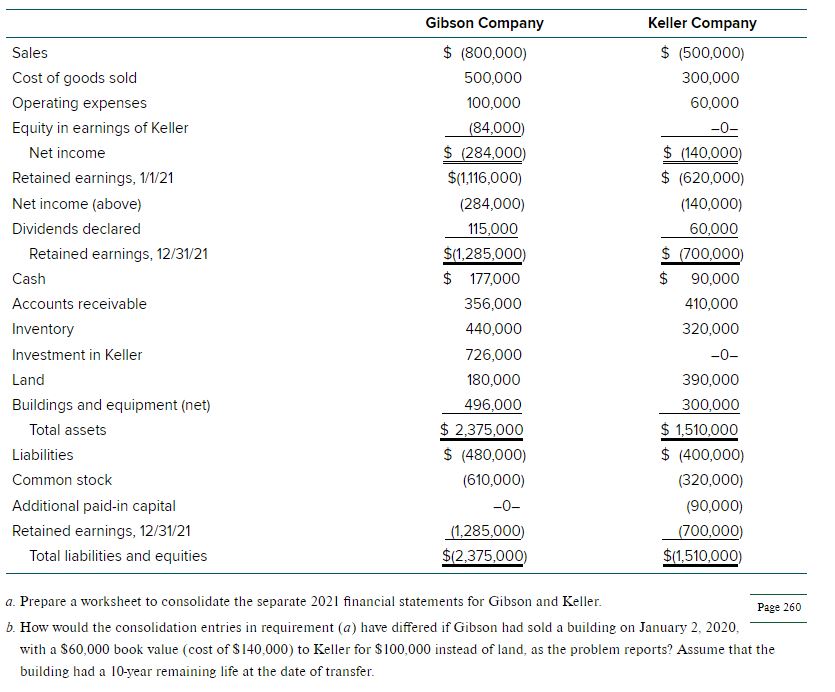

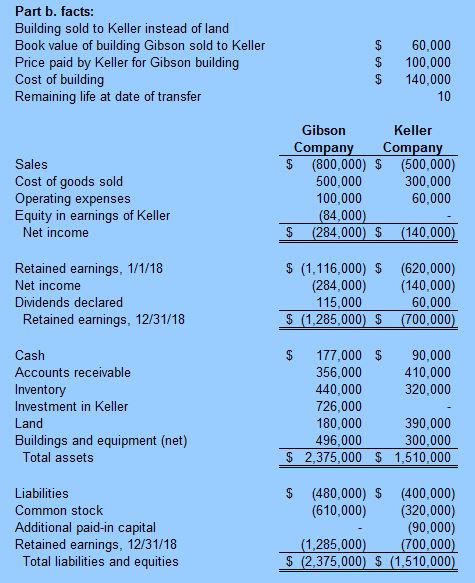




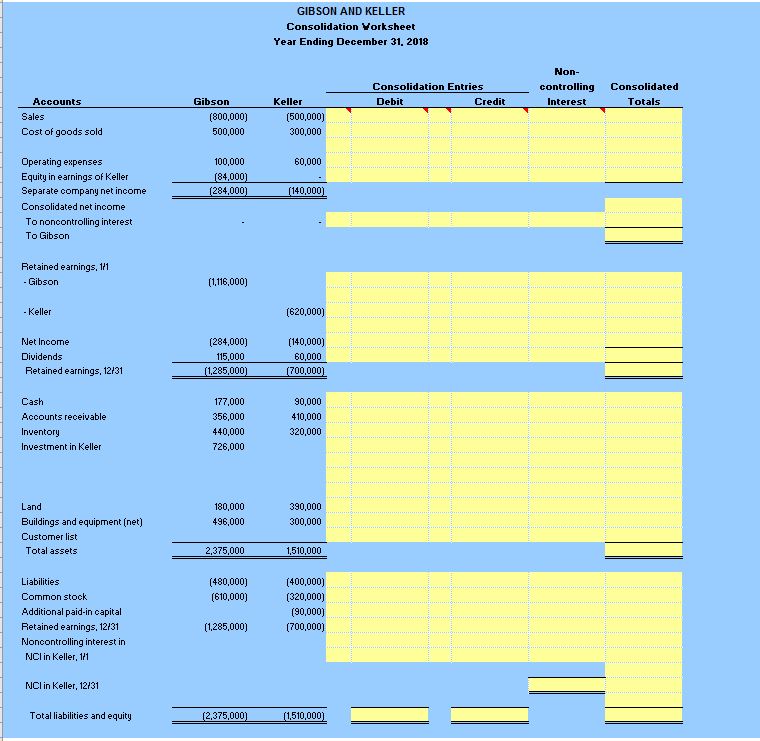
 a. Prepare a worksheet to consolidate the separate 2021 financial statements for Gibson and Keller. b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building on January 2, 2020, with a $60,000 book value (cost of $140,000 ) to Keller for $100,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Assume that the building had a 10-year remaining life at the date of transfer. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest Keller reported net income Excess fair value amortization 2017 intra-entity gross profit recognized in 2018 2018 intra-entity gross profit deferred Keller realized income 2018 Outside ownership percentage Net income attributable to n noncontrolling interest 36. The individual financial statements for Gibson Company and Keller Company for the year ending December 31, 2021, follow. Gibson acquired a 60 percent interest in Keller on January 1, 2020, in exchange for various considerations totaling $570,000. At the acquisition date, the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was $380,000 and Keller's book value was $850,000. Keller had developed internally a customer list that was not recorded on its books but had an acquisition-date fair value of $100,000. This intangible asset is being amortized over 20 years. Gibson uses the partial equity method to account for its investment in Keller. Gibson sold Keller land with a book value of $60,000 on January 2,2020, for $100,000. Keller still holds this land at the end of the current year. Keller regularly transfers inventory to Gibson. In 2020, it shipped inventory costing $100,000 to Gibson at a price of $150,000. During 2021, intra-entity shipments totaled $200,000, although the original cost to Keller was only $140,000. In each of these years, 20 percent of the merchandise was not resold to outside parties until the period following the transfer. Gibson owes Keller $40,000 at the end of 2021. Part b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building with a $600,000 book value (cost of $140,000 ) to Keller for $100,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Parta.facts:GibsonacquiredinterestinKeller1/1/2017VariousconsiderationsgivenforacquisitionFairvalueofnoncontrollinginterestatacquisitionKellersbookvalueValueassignedtoKellercustomerlistKellercustomerlist-lifeforpurposesofamortizationBookvalueoflandGibsonsoldtoKelleron1/2/2017PricepaidbyKellerforGibsonslandCostofinventoryshippedbyKellertoGibsonin2017PricepaidbyGibsonfor2017inventoryCostofintra-entityshipmentsbyKellertoGibsonin2018PricepaidbyGibsonfor2018intra-entityshipmentsPercentageofinventorynotresoldinperiodfollowingtransferAmountGibsonowesKelleratendof2018$$$$$$$$$$$60%570,000380,000850,000100,0002060,000100,000100,000150,000140,000200,00020%40,000 Entry Entry Entry Entry Part A. Consideration transferred Noncontrolling interest fair value Subsidiary fair value at acquisition-date Book value Fair value in excess of bookvalue Excess fair value assignment to customer list \begin{tabular}{cc} RemainingLifeinyears & AnnualEscessAmort. \\ \hline \end{tabular} Consolidation entries: Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry GIBSON AND KELLER Consolidation Yorksheet Year Ending December 31. 2018 Non- Consolidation Entries \begin{tabular}{l} Accounts \\ \hline Sales \\ Cost of goods sold \\ Operating expenses \\ Equity in earnings of Keller \\ Separate company net income \end{tabular} Consolidated net income To noncontrolling interest To Gibson Retained earnings, 111 - Gibson - Keller Net Income Dividends Retained earnings, 12/31 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Keller Land Buildings and equipment (net) Customer list Total assets Liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12131 Noncontrolling interest in NCl in Keller, 1+1 NCl in Keller, 12131 Total liabilities and equity (1,116,000) (620,000) \begin{tabular}{rr} (284,000) & (140,000) \\ 115,000 & 60,000 \\ \hline[1,285,000) & {[700,000]} \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} 177,000 90,000 356,000 410,000 440,000320,000 726,000 180,000 390,000 496,000 300,000 \begin{tabular}{rr} \hline 2,375,000 & 1,510,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} (480,000) (400,000) (610,000) (320,000) (90,000) (1,285,000) (700,000) controlling Consolidated Interest Totals Credit Debit
a. Prepare a worksheet to consolidate the separate 2021 financial statements for Gibson and Keller. b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building on January 2, 2020, with a $60,000 book value (cost of $140,000 ) to Keller for $100,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Assume that the building had a 10-year remaining life at the date of transfer. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest Keller reported net income Excess fair value amortization 2017 intra-entity gross profit recognized in 2018 2018 intra-entity gross profit deferred Keller realized income 2018 Outside ownership percentage Net income attributable to n noncontrolling interest 36. The individual financial statements for Gibson Company and Keller Company for the year ending December 31, 2021, follow. Gibson acquired a 60 percent interest in Keller on January 1, 2020, in exchange for various considerations totaling $570,000. At the acquisition date, the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was $380,000 and Keller's book value was $850,000. Keller had developed internally a customer list that was not recorded on its books but had an acquisition-date fair value of $100,000. This intangible asset is being amortized over 20 years. Gibson uses the partial equity method to account for its investment in Keller. Gibson sold Keller land with a book value of $60,000 on January 2,2020, for $100,000. Keller still holds this land at the end of the current year. Keller regularly transfers inventory to Gibson. In 2020, it shipped inventory costing $100,000 to Gibson at a price of $150,000. During 2021, intra-entity shipments totaled $200,000, although the original cost to Keller was only $140,000. In each of these years, 20 percent of the merchandise was not resold to outside parties until the period following the transfer. Gibson owes Keller $40,000 at the end of 2021. Part b. How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building with a $600,000 book value (cost of $140,000 ) to Keller for $100,000 instead of land, as the problem reports? Parta.facts:GibsonacquiredinterestinKeller1/1/2017VariousconsiderationsgivenforacquisitionFairvalueofnoncontrollinginterestatacquisitionKellersbookvalueValueassignedtoKellercustomerlistKellercustomerlist-lifeforpurposesofamortizationBookvalueoflandGibsonsoldtoKelleron1/2/2017PricepaidbyKellerforGibsonslandCostofinventoryshippedbyKellertoGibsonin2017PricepaidbyGibsonfor2017inventoryCostofintra-entityshipmentsbyKellertoGibsonin2018PricepaidbyGibsonfor2018intra-entityshipmentsPercentageofinventorynotresoldinperiodfollowingtransferAmountGibsonowesKelleratendof2018$$$$$$$$$$$60%570,000380,000850,000100,0002060,000100,000100,000150,000140,000200,00020%40,000 Entry Entry Entry Entry Part A. Consideration transferred Noncontrolling interest fair value Subsidiary fair value at acquisition-date Book value Fair value in excess of bookvalue Excess fair value assignment to customer list \begin{tabular}{cc} RemainingLifeinyears & AnnualEscessAmort. \\ \hline \end{tabular} Consolidation entries: Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry Entry GIBSON AND KELLER Consolidation Yorksheet Year Ending December 31. 2018 Non- Consolidation Entries \begin{tabular}{l} Accounts \\ \hline Sales \\ Cost of goods sold \\ Operating expenses \\ Equity in earnings of Keller \\ Separate company net income \end{tabular} Consolidated net income To noncontrolling interest To Gibson Retained earnings, 111 - Gibson - Keller Net Income Dividends Retained earnings, 12/31 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Keller Land Buildings and equipment (net) Customer list Total assets Liabilities Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12131 Noncontrolling interest in NCl in Keller, 1+1 NCl in Keller, 12131 Total liabilities and equity (1,116,000) (620,000) \begin{tabular}{rr} (284,000) & (140,000) \\ 115,000 & 60,000 \\ \hline[1,285,000) & {[700,000]} \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} 177,000 90,000 356,000 410,000 440,000320,000 726,000 180,000 390,000 496,000 300,000 \begin{tabular}{rr} \hline 2,375,000 & 1,510,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} (480,000) (400,000) (610,000) (320,000) (90,000) (1,285,000) (700,000) controlling Consolidated Interest Totals Credit Debit Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


