Question
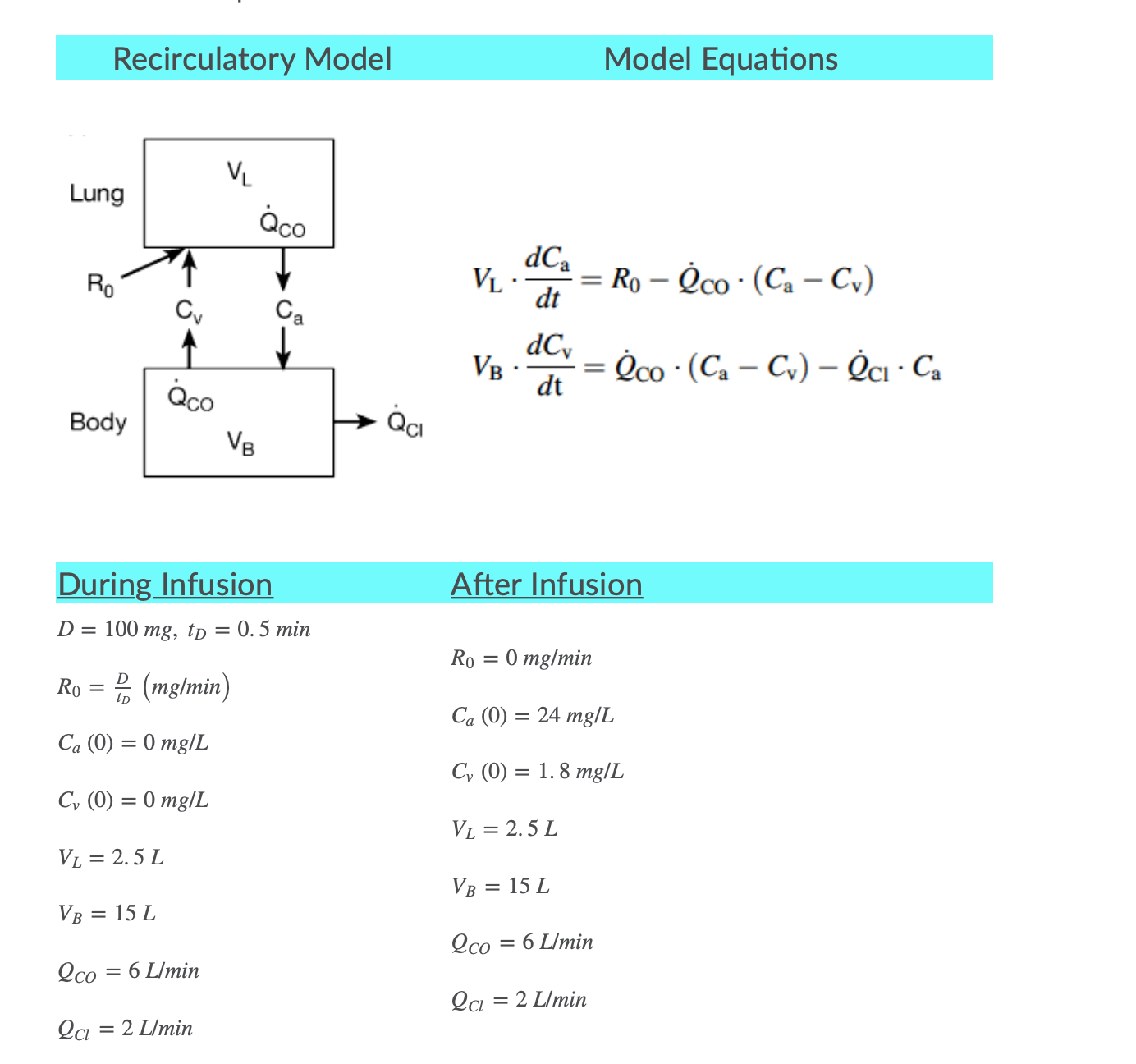
A recirculatory pharmacokinetic model[1]of an anesthetic drug delivered intravenously is shown below. The model incorporates physiological processes that are important determinants of intravenous anesthetic disposition
A recirculatory pharmacokinetic model[1]of an anesthetic drug delivered intravenously is shown below. The model incorporates physiological processes that are important determinants of intravenous anesthetic disposition including cardiac output, lung kinetics, and injection rate of intravenous bolus administration of the drug. The two compartments represent the lungs and body with respective distribution volumes, VLand VB. QCOis cardiac output, or rate of circulation of blood (L/min) between the two compartments.Cvrepresents drug concentrations (mg/L) in the venous circulation upstream of the drug infusion site and returning from the body to the lungs.Carepresents drug concentrations (mg/L) in the arterial circulation emerging from the lungs and entering the rest of the body.QClis the clearance rate, or rate of removal of the drug (L/min).R0is the drug infusion rate (mg/min).During bolus injection, infusion can be treated as dose (D, mg) given over a time interval equal to the duration of the injection (tD) and expressed as R0= D / tD(mg/min). After bolus injection, the infusion rate is zero (R0= 0). The system of differential equations for the model are derived by mass balance of the rates that drug enters and leaves the compartments
A) Find general solutions for the system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) given in the problem statement analytically (by hand) for the homogeneous case (after infusion).You do not need to apply initial conditions.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


