Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
A skydiver with mass m experiences a constant downward gravitational force F, mg where g is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity.
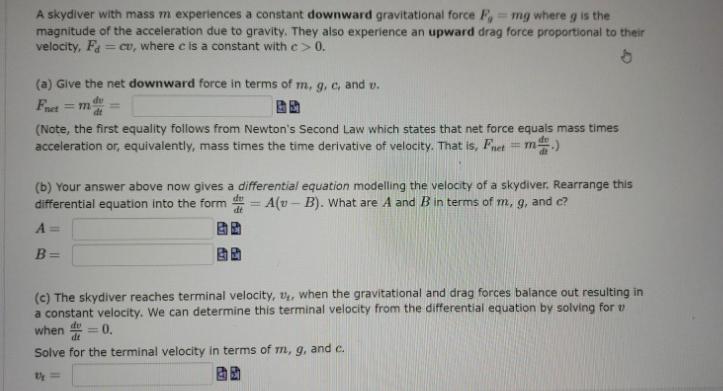
A skydiver with mass m experiences a constant downward gravitational force F, mg where g is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity. They also experience an upward drag force proportional to their velocity, Fa=cu, where c is a constant with c> 0. (a) Give the net downward force in terms of m, g, c, and v. Fnet = (Note, the first equality follows from Newton's Second Law which states that net force equals mass times acceleration or, equivalently, mass times the time derivative of velocity. That is, Fnet = m.) (b) Your answer above now gives a differential equation modelling the velocity of a skydiver. Rearrange this differential equation into the form A(v-B). What are A and B in terms of m, g, and c? A= B= (c) The skydiver reaches terminal velocity, t, when the gravitational and drag forces balance out resulting in a constant velocity. We can determine this terminal velocity from the differential equation by solving for when = 0. Solve for the terminal velocity in terms of m, g, and c. By=
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
downward force Fg mg upward force ev a Fret Now Fg F...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


