A telephone counseling service for adolescents tested whether the length of calls would be affected by a special telephone system that had a better sound quality. Over the past several?years, the lengths of telephone calls?(in minutes) were normally distributed with ?=15 and ?=6. The service arranged to have the special phone system loaned to them for one day. On that?day, the mean length of the 45 calls they received was 18 minutes. Test whether the length of calls has changed using the?5% significance level. Complete parts?(a) through?(d)
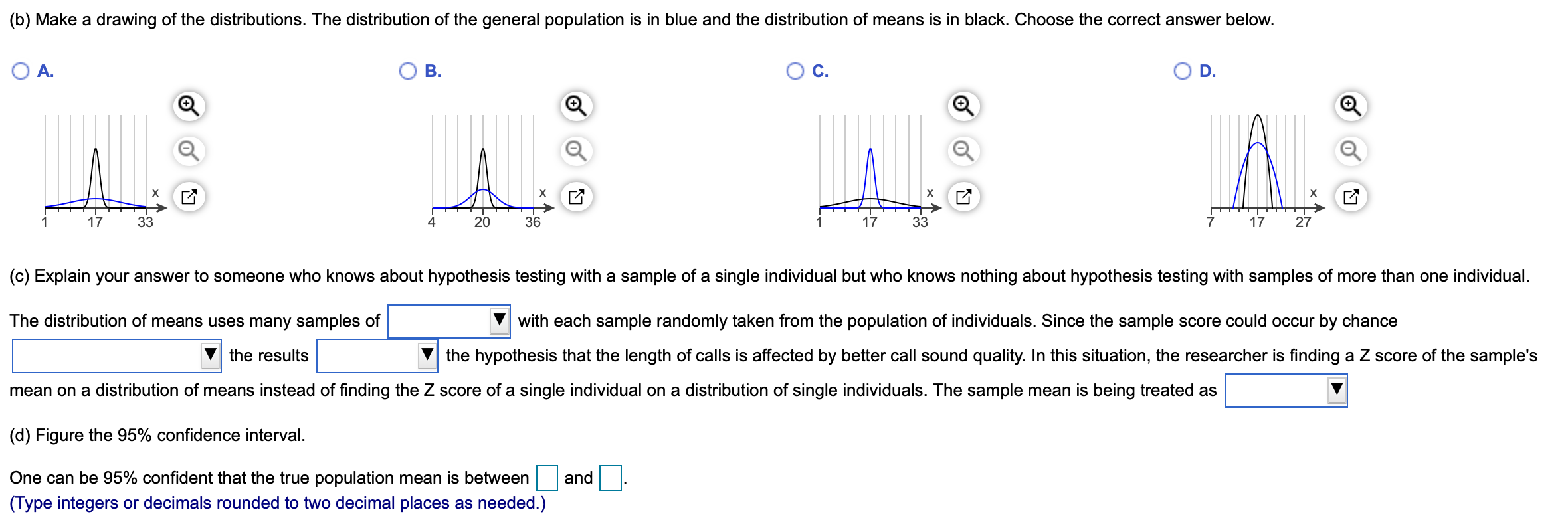
PS: for The part C: (c) Explain your answer to someone who knows about hypothesis testing with a sample of a single individual but who knows nothing about hypothesis testing with samples of more than one individual.
The distribution of means uses many samples of (the same size, different size) with each sample randomly taken from the population of individuals. Since the sample score could occur by chance (5% of the time or less/more than 5% of the time)
the results (support/do not support) the hypothesis that the length of calls is affected by better call sound quality. In this?situation, the researcher is finding a Z score of the?sample's mean on a distribution of means instead of finding the Z score of a single individual on a distribution of single individuals. The sample mean is being treated as (a single score/45 scores)
Atelephone counseling service for adolescents tested whether the length of calls would be affected by a special telephone system that had a better sound quality. Over the past several years, the lengths of telephone calls (in minutes) were normally distributed with p = 17 and o = 8. The service arranged to have the special phone system loaned to them for one day. On that day, the mean length of the 41 calls they received was 20 minutes. Test whether the length of calls has changed using the 5% signicance level. Complete parts (a) through (d). Click here to view p_age 1 of the table. Click here to view page 2 of the table. Click here to view {age 3 of the table. Click here to view p_age 4 of the table. (a) Carry out a Z test using the five steps of hypothesis testing. What is the null hypothesis? Choose the correct answer below. 0 A. There is a difference in the mean length of calls with the special system compared to the population mean based on the regular system. 0 B. The mean length of calls will be longer with the special system compared to the population mean based on the regular system. C. There is no difference in the mean length of calls with the special system compared to the population mean based on the regular system. O D. There is no difference in call length between the special system and the regular system. Assume that the distribution of means is approximately normal. What are the cutoff sample scores on the comparison distribution at which the null hypothesis should be rejected? (Type integers or decimals rounded to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Determine the sample's Z score on the comparison distribution. Z = (Type an integer or a decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.) Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis. Explain. Choose the correct answer below. 0 A. The sample score is not extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis. The research hypothesis is true. O B. The sample score is extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis. The research hypothesis is false. 0 C. The sample score is extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis. The research hypothesis is supported. 0 D. The sample score is not extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis. The experiment is inconclusive. (b) Make a drawing of the distributions. The distribution of the general population is in blue and the distribution of means is in black. Choose the correct answer below. O A. O B. O C. O D. X X X X 33 36 33 (c) Explain your answer to someone who knows about hypothesis testing with a sample of a single individual but who knows nothing about hypothesis testing with samples of more than one individual. The distribution of means uses many samples of with each sample randomly taken from the population of individuals. Since the sample score could occur by chance the results the hypothesis that the length of calls is affected by better call sound quality. In this situation, the researcher is finding a Z score of the sample's mean on a distribution of means instead of finding the Z score of a single individual on a distribution of single individuals. The sample mean is being treated as (d) Figure the 95% confidence interval. One can be 95% confident that the true population mean is between and. (Type integers or decimals rounded to two decimal places as needed.)