Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
a) The fluorene monomer A and 1,4-dibromo benzene B (Figure Q2) can be copolymerised. What is the structure of the resulting copolymer? What type
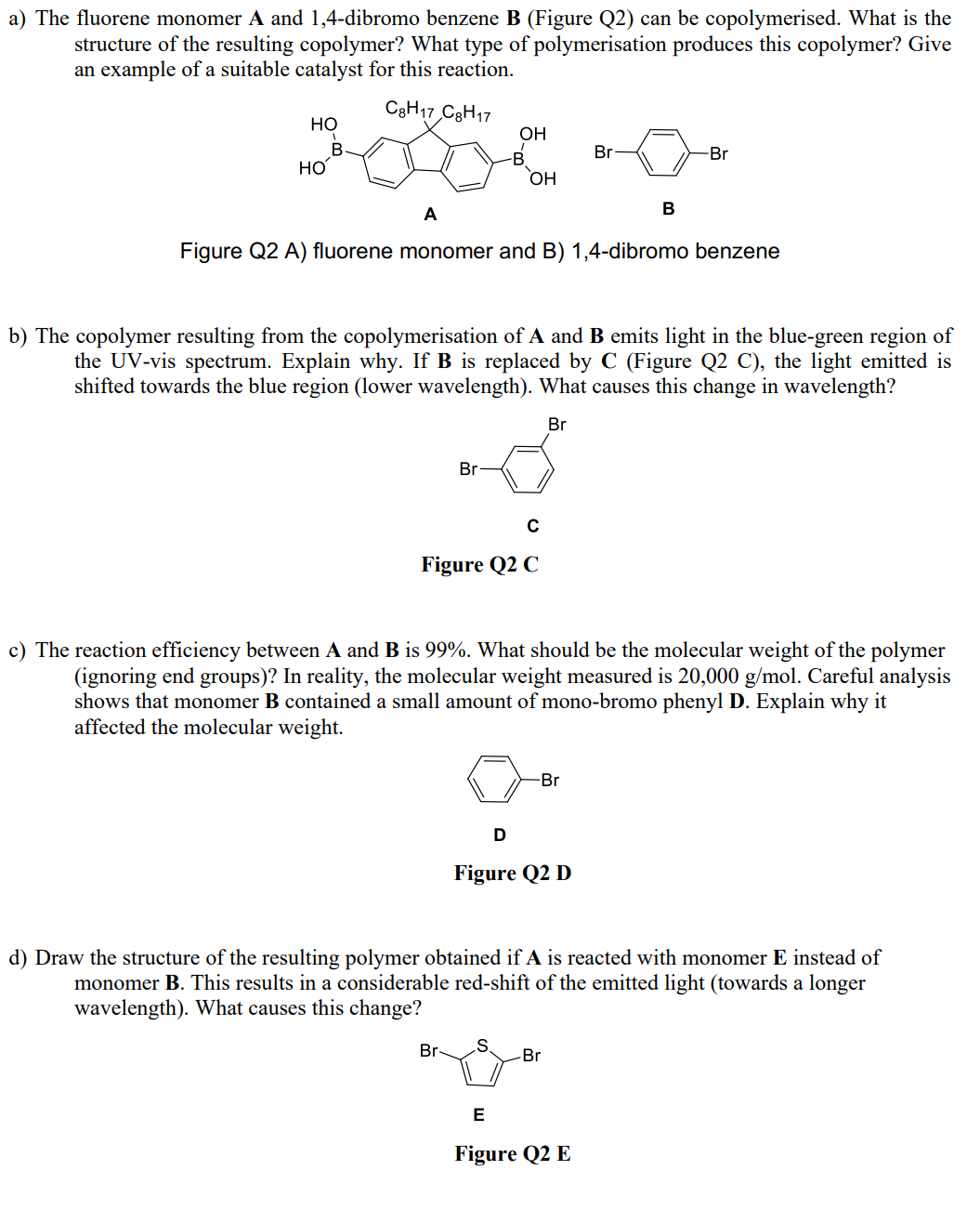
a) The fluorene monomer A and 1,4-dibromo benzene B (Figure Q2) can be copolymerised. What is the structure of the resulting copolymer? What type of polymerisation produces this copolymer? Give an example of a suitable catalyst for this reaction. C8H17 C8H17 HO B 20 HO Br OH -B Br- OH A Figure Q2 A) fluorene monomer and B) 1,4-dibromo benzene C Figure Q2 C b) The copolymer resulting from the copolymerisation of A and B emits light in the blue-green region of the UV-vis spectrum. Explain why. If B is replaced by C (Figure Q2 C), the light emitted is shifted towards the blue region (lower wavelength). What causes this change in wavelength? Br D S c) The reaction efficiency between A and B is 99%. What should be the molecular weight of the polymer (ignoring end groups)? In reality, the molecular weight measured is 20,000 g/mol. Careful analysis shows that monomer B contained a small amount of mono-bromo phenyl D. Explain why it affected the molecular weight. -Br Figure Q2 D Br B -Br d) Draw the structure of the resulting polymer obtained if A is reacted with monomer E instead of monomer B. This results in a considerable red-shift of the emitted light (towards a longer wavelength). What causes this change? Br E Figure Q2 E
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.32 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The image contains a chemistry exam question about the copolymerization of monomers the emission of light by copolymers the molecular weight of polyme...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


