Question
A wetted-wall column of 2.0-cm inner diameter and 50-cm wetted length is used to oxygenate blood as a continuous, steady-state process, as shown in the
A wetted-wall column of 2.0-cm inner diameter and 50-cm wetted length is used to oxygenate blood as a continuous, steady-state process, as shown in the figure below. Blood containing 1.0 gmole/m3 of dissolved oxygen enters the top of the wetted-wall column at a volumetric flow rate of 7,8x10^-5 cm3/min. Pure, 100% O2 gas at 1.0 atm and 25C enters the bottom of the column at a volumetric gas flow rate of 5,0x10^-4 cm3/min. A very simplified description for estimating the equilibrium solubility of O2 dissolved in blood is
PA,i=H x CA,i
where pa is the partial pressure of O2 in the gas phase, H =0.01 atm m3/gmole for O2 in the blood plasma.
At 25C, the kinematic viscosity of blood is 0.040 cm?/s and the density of blood is 1.025 g/cm3. You may assume that the diffusion coefficient of O2 in blood approximates the diffusion coefficient of O2 in liquid water, which is 2.0 x10-5 cm2/s at 25C.
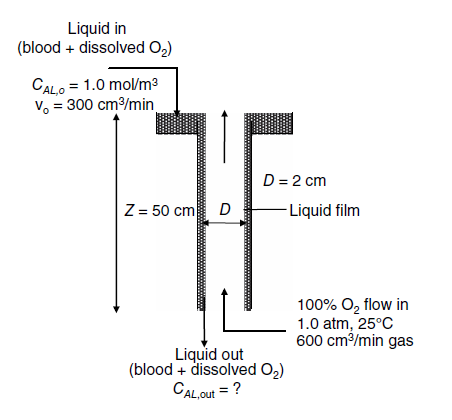
a. What is the mass-transfer coefficient for O2 into the flowing liquid film?
b. What is the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the liquid exiting the bottom of the column, CAL, out?
Pay attention on the equilibrium solubility equation PA,i=H x CA,i. Please, explain step by step the balance mass.
Liquid in (blood + dissolved O2 )Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


