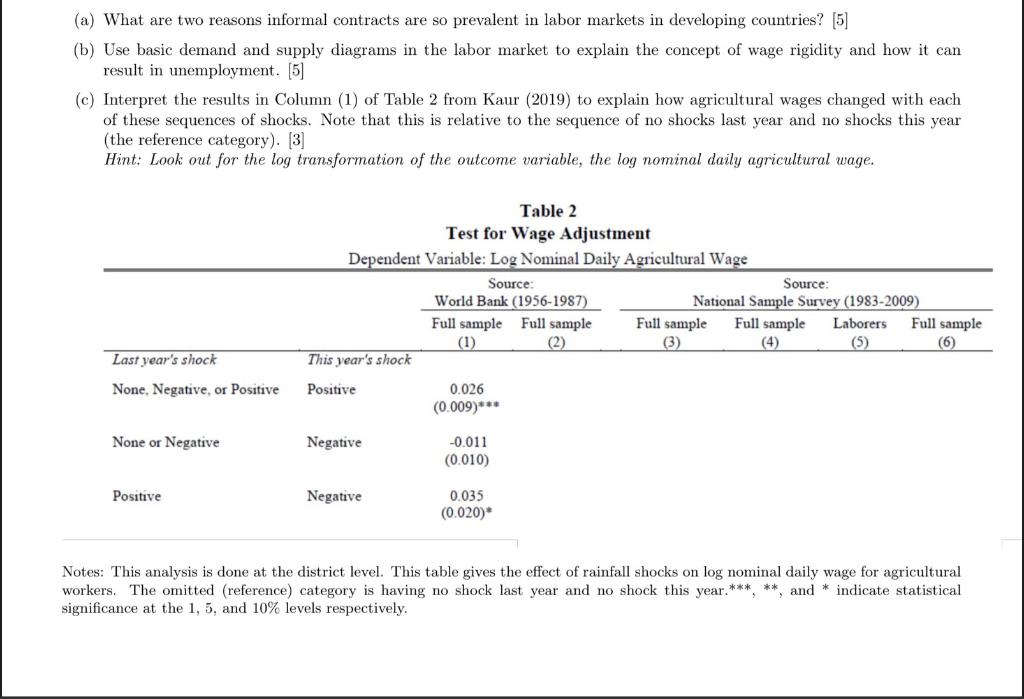
(a) What are two reasons informal contracts are so prevalent in labor markets in developing countries? [5] (b) Use basic demand and supply diagrams in the labor market to explain the concept of wage rigidity and how it can result in unemployment. [5] (c) Interpret the results in Column (1) of Table 2 from Kaur (2019) to explain how agricultural wages changed with each of these sequences of shocks. Note that this is relative to the sequence of no shocks last year and no shocks this year (the reference category). [3] Hint: Look out for the log transformation of the outcome variable, the log nominal daily agricultural wage. Table 2 Test for Wage Adjustment Dependent Variable: Log Nominal Daily Agricultural Wage Source: Source: World Bank (1956-1987) National Sample Survey (1983-2009) Full sample Full sample Full sample Full sample Laborers Full sample (1) (3) (5) (6) This year's shock Positive 0.026 (0.009)*** Last year's shock None. Negative, or Positive None or Negative Negative -0.011 (0.010) Positive Negative 0.035 (0.020)* Notes: This analysis is done at the district level. This table gives the effect of rainfall shocks on log nominal daily wage for agricultural workers. The omitted (reference) category is having no shock last year and no shock this year. ***, **, and * indicate statistical significance at the 1, 5, and 10% levels respectively. (a) What are two reasons informal contracts are so prevalent in labor markets in developing countries? [5] (b) Use basic demand and supply diagrams in the labor market to explain the concept of wage rigidity and how it can result in unemployment. [5] (c) Interpret the results in Column (1) of Table 2 from Kaur (2019) to explain how agricultural wages changed with each of these sequences of shocks. Note that this is relative to the sequence of no shocks last year and no shocks this year (the reference category). [3] Hint: Look out for the log transformation of the outcome variable, the log nominal daily agricultural wage. Table 2 Test for Wage Adjustment Dependent Variable: Log Nominal Daily Agricultural Wage Source: Source: World Bank (1956-1987) National Sample Survey (1983-2009) Full sample Full sample Full sample Full sample Laborers Full sample (1) (3) (5) (6) This year's shock Positive 0.026 (0.009)*** Last year's shock None. Negative, or Positive None or Negative Negative -0.011 (0.010) Positive Negative 0.035 (0.020)* Notes: This analysis is done at the district level. This table gives the effect of rainfall shocks on log nominal daily wage for agricultural workers. The omitted (reference) category is having no shock last year and no shock this year. ***, **, and * indicate statistical significance at the 1, 5, and 10% levels respectively







