Question: a. Write a java program to implement the Quick Sort algorithm that sorts an array of integers. We discussed two pivot picking strategies: specific

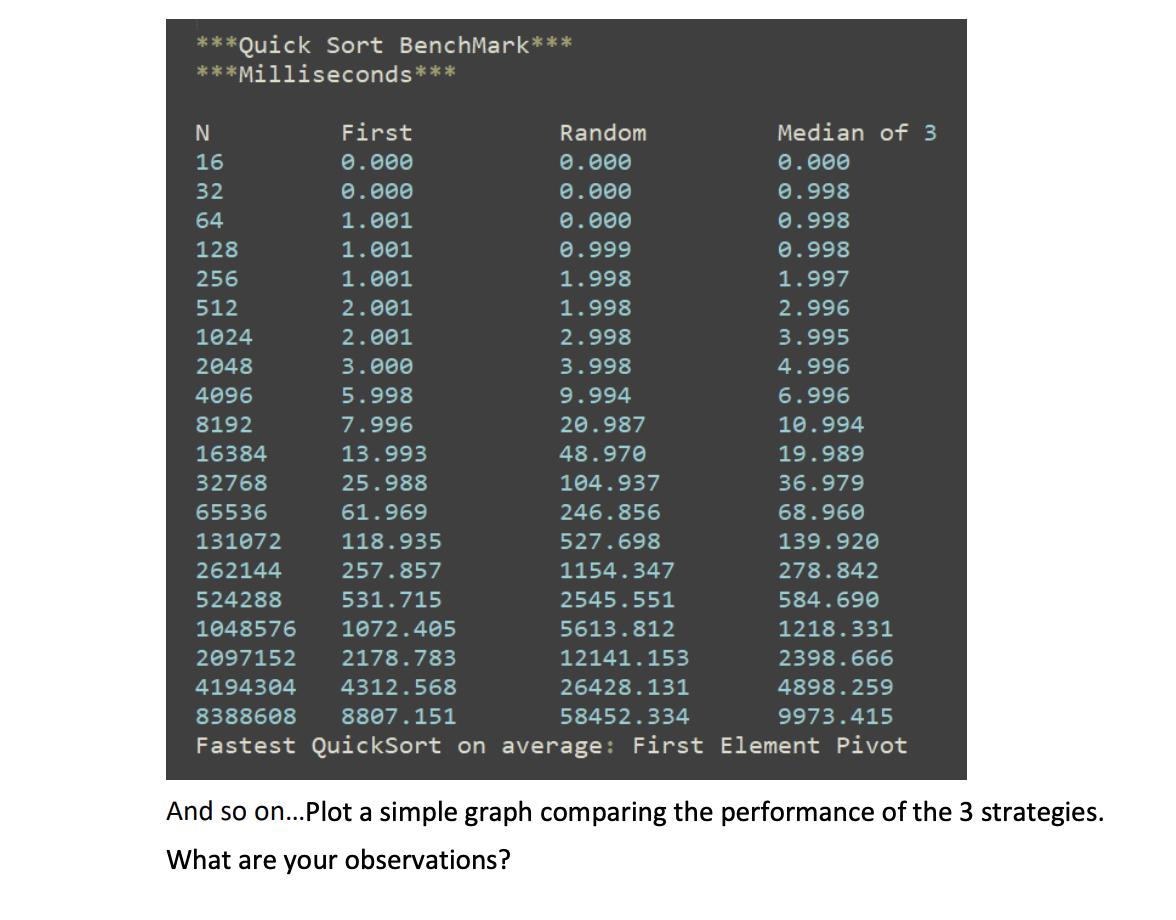

a. Write a java program to implement the Quick Sort algorithm that sorts an array of integers. We discussed two pivot picking strategies: specific element (first/middle/last), and median of 3. Implement both these strategies and add a third one that uses a random element as a pivot. You may want to implement a Quick Sort that takes a variable to be used to choose the strategy each time. Note: This is not a multi-pivot Quick Sort, but rather a sort that allows choice of pivot picking strategy. b. Use a set of 24 random integers to test your algorithm. A Boolean method that checks if an array is sorted can be used to avoid printing before and after arrays to the console. is Sorted (int[] array) { boolean for (int i = 0; i < array.length 1; i++) { if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) return false; C. } return true; } Add code to compare the performance of the different pivot picking strategies in part a by timing how long it takes to sort arrays of growing input sizes. For each array of size N, run multiple trials. A table could help document the timing results, for example: Activate Windows Go to Settings to activate Windows. ***Quick Sort BenchMark*** ***Milliseconds*** N 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024 2048 4096 8192 16384 32768 65536 First 0.000 0.000 1.001 1.001 1.001 2.001 2.001 3.000 5.998 7.996 13.993 25.988 61.969 131072 118.935 262144 257.857 524288 531.715 1048576 1072.405 2097152 2178.783 4194304 4312.568 8388608 8807.151 Fastest QuickSort on average: First Element Pivot Random 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.999 1.998 1.998 2.998 3.998 9.994 20.987 48.970 104.937 246.856 527.698 1154.347 2545.551 5613.812 12141.153 26428.131 58452.334 Median of 3 0.000 0.998 0.998 0.998 1.997 2.996 3.995 4.996 6.996 10.994 19.989 36.979 68.960 139.920 278.842 584.690 1218.331 2398.666 4898.259 9973.415 And so on... Plot a simple graph comparing the performance of the 3 strategies. What are your observations? 2. MergeSort. a. Write a java program to sort an array of integers using the Merge Sort Algorithm. Use the issorted () method to test with an array of 24 random integers. b. Just like in Q1c, add code to perform a comparison of the performance of MergeSort and QuickSort. For QuickSort, use the pivot picking strategy that performed best in Question 1. When you are done, plot the results in a graph. Are your observations consistent with the theoretical analysis of the running time for these algorithms? 3. Extra Credit Quick Sort is a fast algorithm that generally works well with large amounts of data. However, when lists are smaller, Quick Sort may run slower than other sorting algorithms due to the overhead of recursion. When sorting large lists with Quick Sort, many, many sub lists will have to be sorted and this may slow its overall performance. Implement a smarter Quick Sort algorithm that cuts off when the list size is reduced to a threshold, say, 10, then switches to a different sorting method of your choice. Compare the performance of this smarter Quick Sort to the previous one in Q1. Is there any significant difference for large inputs?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
import javautilArrays import javautilRandom public class SortingComparison Quick Sort w... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


