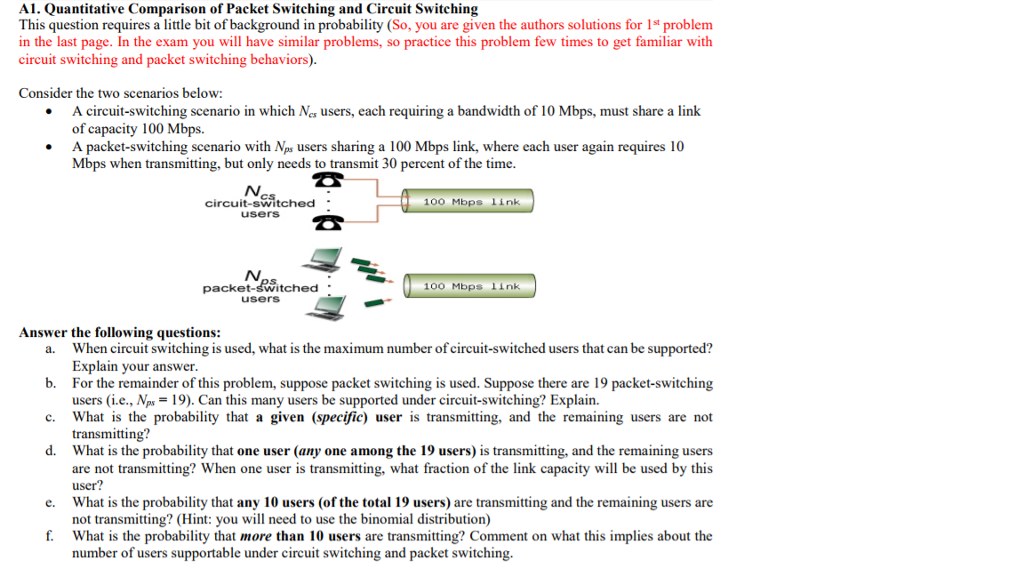
A1. Quantitative Comparison of Packet Switching and Circuit Switching This question requires a tle bit of background in probability (So, you are given the authors solutions for 1st problem in the last page. In the exam you will have similar problems, so practice this problem few times to get familiar with circu it switching and packet switching behaviors) Consider the two scenarios below: circuit-switching scenario in which Nes users, each requiring a bandwidth of 10 Mbps, must share a link of capacity 100 Mbps. packet-switching scenario with Nps users sharing a 100 Mbps link, where each user again requires 10 Mbps when transmitting, but only needs to transmit 30 percent of the time A A CS circuit-switched users 100 Mbps link packet-sWitched 100 Mbps Link userS Answer the following questions: When circuit switching is used, what is the maximum number of circuit-switched users that can be supported? Explain your answer For the remainder of this problem, suppose packet switching is used. Suppose there are 19 packet-switching users (i.e., Nps 19). Can this many users be supported under circuit-switching? Explain. What is the probability that a given (specific) user is transmitting, and the remaining users are not transmitting? What is the probability that one user (any one among the 19 users) is transmitting, and the remaining users are not transmitting? When one user is transmitting, what fraction of the link capacity will be used by this user? What is the probability that any 10 users (of the total 19 users) are transmitting and the remaining users are not transmitting? (Hint: you will need to use the binomial distribution) What is the probability that more than 10 users are transmitting? Comment on what this implies about the number of users supportable under circuit switching and packet switching. a. b. c. d. e. f. A1. Quantitative Comparison of Packet Switching and Circuit Switching This question requires a tle bit of background in probability (So, you are given the authors solutions for 1st problem in the last page. In the exam you will have similar problems, so practice this problem few times to get familiar with circu it switching and packet switching behaviors) Consider the two scenarios below: circuit-switching scenario in which Nes users, each requiring a bandwidth of 10 Mbps, must share a link of capacity 100 Mbps. packet-switching scenario with Nps users sharing a 100 Mbps link, where each user again requires 10 Mbps when transmitting, but only needs to transmit 30 percent of the time A A CS circuit-switched users 100 Mbps link packet-sWitched 100 Mbps Link userS Answer the following questions: When circuit switching is used, what is the maximum number of circuit-switched users that can be supported? Explain your answer For the remainder of this problem, suppose packet switching is used. Suppose there are 19 packet-switching users (i.e., Nps 19). Can this many users be supported under circuit-switching? Explain. What is the probability that a given (specific) user is transmitting, and the remaining users are not transmitting? What is the probability that one user (any one among the 19 users) is transmitting, and the remaining users are not transmitting? When one user is transmitting, what fraction of the link capacity will be used by this user? What is the probability that any 10 users (of the total 19 users) are transmitting and the remaining users are not transmitting? (Hint: you will need to use the binomial distribution) What is the probability that more than 10 users are transmitting? Comment on what this implies about the number of users supportable under circuit switching and packet switching. a. b. c. d. e. f







