Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The production of wine is a multibillion-dollar worldwide industry. In an attempt to develop a model of wine quality as judged by wine experts,


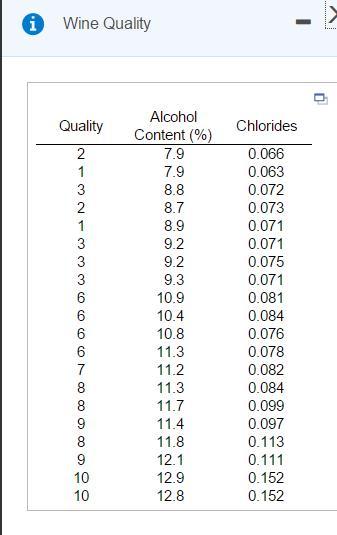
The production of wine is a multibillion-dollar worldwide industry. In an attempt to develop a model of wine quality as judged by wine experts, data was collected from red wine variants. A sample of 20 wines is provided in the accompanying table. Develop a muitiple linear regression model to predict wine quality, measured on a scale from 0 (very bad) to 10 (excellent) based on alcohol content (%) and the amount of chlorides. Complete parts a through g below. E Click the icon to view the table. Wine Quality a. State the multiple regression equation. Let X, represent the alcohol content (%) of wine i and let X2, represent the number of chlorides for wine i. -*Xa (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Alcohol Quality Chlorides b. Interpret the meaning of the slopes, b, and bz, in this problem. Content (%) 7.7 O A. For a given quality, each decrease of the value of b, units in chlorides is estimated to result in a mean increase in alcohol content of one unit. For a given alcohol content, each de result in the mean increase in chlorides of one unit. O B. For a given number of chlorides, each increase of one percentage of alcohol content is estimated to result in a mean increase of wine quality of b, units. For a given alcohol conte result in the mean increase in wine quality of b2 units. 0.065 0.064 0.066 0.072 0.071 0.078 7.6 3 8.7 3 8.4 8.5 8.6 3 8.1 0.074 OC. For every increase of one unit of alcohol content, the estimated number of chiorides and mean wine quality decreases by the values of b, and b, units, respectively. O D. The slopes, b, and b2, cannot be interpreted individually. 3 9.8 0.076 5 7. 10.9 10.7 0.082 0.078 0.076 c. Explain why the regression coefficient, b, has no practical meaning in the context of this problem 6. 10.8 11.3 0.077 11.4 0.086 O A. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean alcohol content when a wine has a 0 quality and O chlorides. O B. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean quality when a wine has a 0% alcohol content and 0 chlorides. 8. 11.7 0.085 0.097 0.092 0.124 11.1 8 11.6 11.5 12.5 OC. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean alcohol content and mean chlorides when there is no quality. 8 9 0.106 O D. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean chiorides when a wine has a 0% alcohol content and 0 quality. 10 12.5 0.155 10 12.6 0.158 d. Predict the mean quality rating for wines that have 11% alcohol content and chlorides of 0.09. The production of wine is a multibillion-dollar worldwide industry. In an attempt to develop a model of wine quality as judged by wine experts, data was collected from red wine variants, A sample of 20 wines is provided in the accompanying table Develop a multiple linear regression model to predict wine quality, measured on a scale from 0 (very bad) to 10 (excellent) based on alcohol content (%) and the amount of chlorides. Complete parts a through g below. A Click the icon to view the table. X O Wine Quality Ine interpretaton or D, nas no pracncai meanng nere pecause it woura correspona to tne estimatea mean quaity wnen a wine nas a u% aiconoi content ana u cnionaes. OC. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean alcohol content and mean chlorides when there is no quality. OD. The interpretation of b, has no practical meaning here because it would correspond to the estimated mean chlorides when a wine has a 0% alcohol content and 0 quality. d. Predict the mean quality rating for wines that have 11% alcohol content and chlorides of 0.09. Alcohol Quality Chlorides Content (%) The wine quality prediction for a wine that has 11% alcohol and 0.09 chlorides is- 7.7 0.065 7.6 0.064 0.066 0.072 0.071 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) 8.7 8.4 8.5 e. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the mean quality rating for cars that have 11% alcohol and 0.09 chlorides. The 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean quality rating for wines that have 11% alcohol and 0.09 chlorides is to 8.6 0.078 0.074 0.076 0.082 0.078 8.1 (Round to one decimal place as needed.) 9.8 10.9 f. Construct a 95% prediction interval estimate for the mean quality rating for cars that have 11% alcohol and 0.09 chlorides 10.7 10.8 11.3 11.4 11.7 0.076 0.077 0.086 The 95% prediction interval estimate of the mean quality rating for wines that have 11% alcohol and 0.09 chlorides is to 6. 7. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) 8. 0.085 g. What conclusions can you reach concerning this regression model? 11.1 11.6 11.5 0.097 0.092 0.124 0.106 0.155 0.158 OA The model uses alcohol content to predict the wine quality. The chlorides of the wine only affects the alcohol content directly. 8 OB. The model can use the alcohol content or chlorides of a wine to predict the mean quality, but not both. OC. The model uses both the alcohol content and chlorides of a wine to predict the mean quality. This produces a better model than if only one variable were included. OD. The model uses the chlorides of a wine to predict the mean quality. The alcohol content of the wine only affects the chlorides directly. 12.5 10 10 12.5 12.6 Wine Quality Alcohol Quality Chlorides Content (%) 7.9 0.066 1 7.9 0.063 0.072 0.073 3 8.8 8.7 1 8.9 0.071 3 9.2 0.071 3 9.2 0.075 3 9.3 0.071 6 10.9 0.081 6 10.4 0.084 6 10.8 0.076 6 11.3 0.078 7 11.2 0.082 11.3 11.7 11.4 8 0.084 8. 0.099 9. 0.097 8 11.8 0.113 9 12.1 0.111 10 12.9 0.152 10 12.8 0.152
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Page...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


