Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Activity-Based Customer Costing Deeds Company sells custom-made machine parts to industrial equipment manufacturers by bidding cost plus 40 percent, where cost is defined as manufacturing
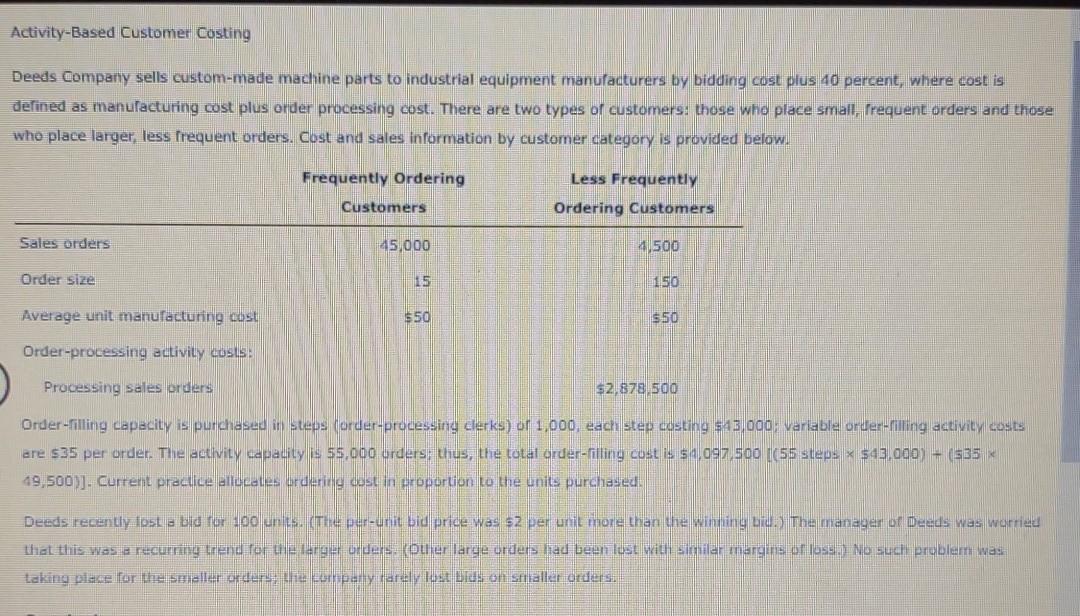
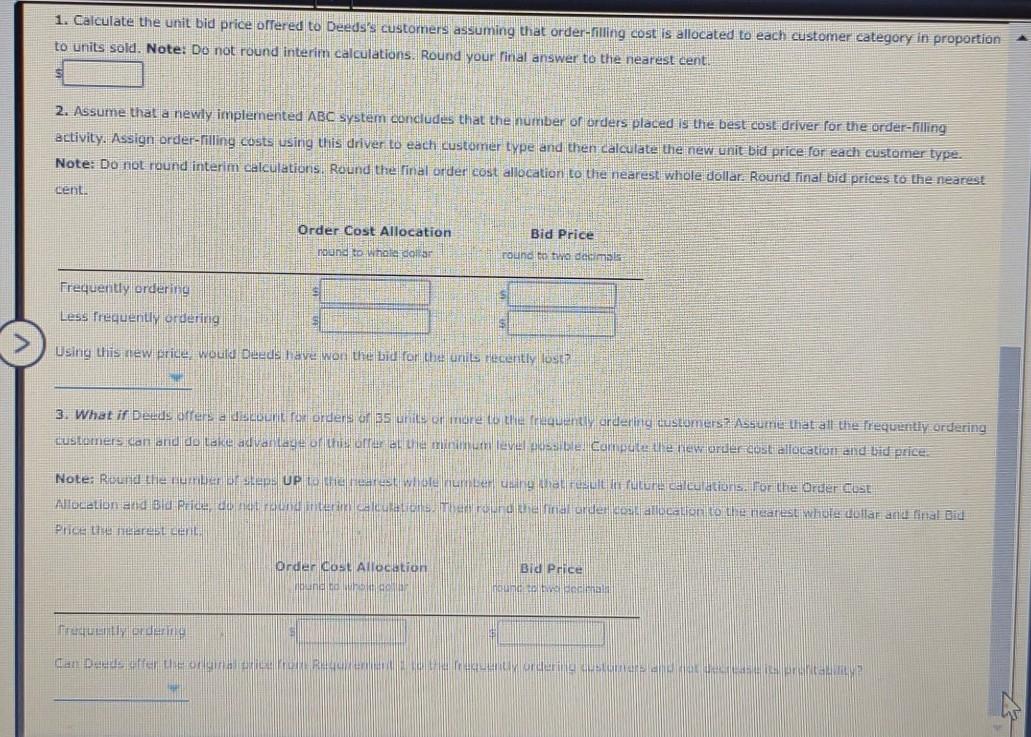
Activity-Based Customer Costing Deeds Company sells custom-made machine parts to industrial equipment manufacturers by bidding cost plus 40 percent, where cost is defined as manufacturing cost plus order processing cost. There are two types of customers: those who place small, rrequent orders and those who place larger, less frequent orders. Cost and sales information by customer category is provided below. Frequently Ordering Customers Less Frequently Ordering Customers Sales orders 45,000 4500 Order size 15 150 Average unit manulacturing cost $50 $50 Order-processing activity costs: Processing Sales orders $2,878 500 Order-filling capacity is purchased in steps forder-processing clerks) or 1,000, each step casting $13,000: variable order-filing activity costs are $35 per order. The activity capacity is 55,000 orders: thus, the total order-filling cost is $ 1.097,500 (55 steps $43.000) 535 19,500)]. Current practice allocates ordering oest in proportion to the units purchased. Deeds recently lost a bid for 100 units. (The per-unit bid price was 52 per unit more than the winning Lid.) The manager of Deeds was worried that this was a recurring trend for le larger unders: (ouer large orders rad been lost with similar margins of lossNo such problem was taking place for the seller orden uie conpally rarely lost blus on smaller orders. 1. Calculate the unit bid price offered to Deeds's customers assuming that order-filling cost is allocated to each customer category in proportion to units sold. Note: Do not round interim calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest cent. 2. Assume that a newly implemented ABC System concludes that the number of orders placed is the best cost driver for the order-filling activity. Assign order-rilling costs using this driver to each customer type and then calculate the new unit bid price for each customer type Note: Do not round interim calculations. Round the final order cost allocation to the nearest whole dollar: Round final bid prices to the nearest cenu. Order Cost Allocation noong to whole dollar Bid Price round to two decimals Frequently ordering S Less frequently ordering Using this new price would Deeds have won the bid for the units recently lost 3. What if Deeds terror orders of 5 unit of more to the requently ordering customers Assume thatall the frequently ordering customers can and do take advantage of there the minimum leve sable Complete new order costi allocation and bid price Note: Round the numbe UP Dearest wolume in the result future calculations. For the Order OUSE Allocation and a pride do mund te luuletion. The rurale na crue allolan to the nearestidote dollar and final Bid Price the resident Order COS Allocation Bid Price bound to be call buna funerden dan Dude eReorginal Activity-Based Customer Costing Deeds Company sells custom-made machine parts to industrial equipment manufacturers by bidding cost plus 40 percent, where cost is defined as manufacturing cost plus order processing cost. There are two types of customers: those who place small, rrequent orders and those who place larger, less frequent orders. Cost and sales information by customer category is provided below. Frequently Ordering Customers Less Frequently Ordering Customers Sales orders 45,000 4500 Order size 15 150 Average unit manulacturing cost $50 $50 Order-processing activity costs: Processing Sales orders $2,878 500 Order-filling capacity is purchased in steps forder-processing clerks) or 1,000, each step casting $13,000: variable order-filing activity costs are $35 per order. The activity capacity is 55,000 orders: thus, the total order-filling cost is $ 1.097,500 (55 steps $43.000) 535 19,500)]. Current practice allocates ordering oest in proportion to the units purchased. Deeds recently lost a bid for 100 units. (The per-unit bid price was 52 per unit more than the winning Lid.) The manager of Deeds was worried that this was a recurring trend for le larger unders: (ouer large orders rad been lost with similar margins of lossNo such problem was taking place for the seller orden uie conpally rarely lost blus on smaller orders. 1. Calculate the unit bid price offered to Deeds's customers assuming that order-filling cost is allocated to each customer category in proportion to units sold. Note: Do not round interim calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest cent. 2. Assume that a newly implemented ABC System concludes that the number of orders placed is the best cost driver for the order-filling activity. Assign order-rilling costs using this driver to each customer type and then calculate the new unit bid price for each customer type Note: Do not round interim calculations. Round the final order cost allocation to the nearest whole dollar: Round final bid prices to the nearest cenu. Order Cost Allocation noong to whole dollar Bid Price round to two decimals Frequently ordering S Less frequently ordering Using this new price would Deeds have won the bid for the units recently lost 3. What if Deeds terror orders of 5 unit of more to the requently ordering customers Assume thatall the frequently ordering customers can and do take advantage of there the minimum leve sable Complete new order costi allocation and bid price Note: Round the numbe UP Dearest wolume in the result future calculations. For the Order OUSE Allocation and a pride do mund te luuletion. The rurale na crue allolan to the nearestidote dollar and final Bid Price the resident Order COS Allocation Bid Price bound to be call buna funerden dan Dude eReorginal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


