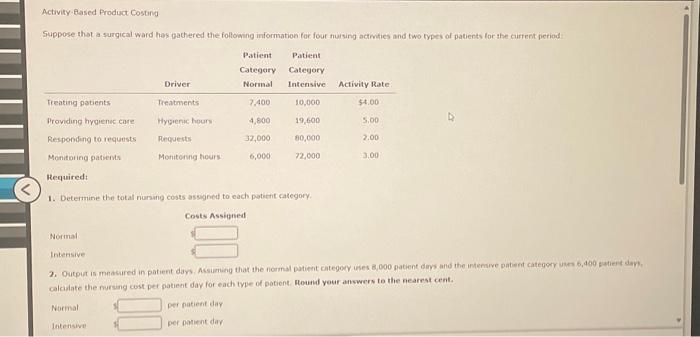
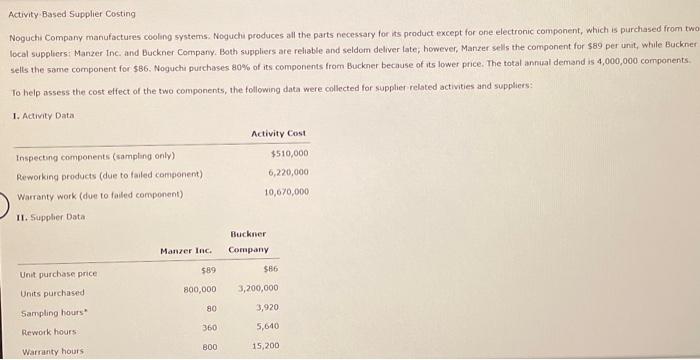
Activity-Based Product Costing Suppose thot a surgical ward hos gathered the following information for four fuising actmities and two types of patients lor the curfent period: Required: 1. Determine the total numing costs assugned to each potient category. calcalate the nursing cost per patient day for each type of patient ntound your answers to the nearrat cent. Normal per patient day Intenswe per patient day 2. Output is measured in patient days. Assuming that the normal patient category uses 8,000 patent days and the intensive patient category uses 6,400 patient days. calculate the nursing cost pet patient day for each type of patient. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Normal per patient day Intensive per patient day 3. Conceptual Connection; The supervisor of the surgical ward has suggested that patient dars is the conly driver needed to assign nursing costs to each type of patient. Calculate the charge per patient day using this approach. Round your answer to the nearest cent. per patient day 4. Refer to the four data analyac types in fahibrit 22 Select which data analytic types apply for Requirements one through three (more than one type may apply). Requirement t's calculation is in nature as it simply describes what is happening. The same 6 for Requirement 2. Aequirement J, howerver, wes both analytic tyoes: actwisy drvers and patent days is expected to remain the same as the carrent peried. a. Uang ABC, repeat Requrements t and 2 , and descritie the data analytic type(s) beng used. b. Describe how Excet simplifes this calculation, including examples of equations that wauld be used. Using Excel with established equations require only that the actwity rates be updated The calculations produced Activity-Based Supplier Costing Noguchi Company manufactures cooling systems. Noguchi produces all the parts necessary for its product except for one electronic component, which is purchased from two local suppliers: Manzer Inc. and Buckner Company. Both suppliers are reliable and seldom deliver late; however, Manzer sells the component for $89 per unit, while Buckner sells the same component for $86. Nogucha purchases 80% of its components from Buckner because of its lower price. The total annual demand is 4,000,000 camponents To help assess the cost effect of the two components, the following data were collected for supplier related activities and suppliers: 1. Activity Data 1. Calculate the cost per component for each supplier, takang into consideration the costs of the suppher-related activities and using the current prices and sales volume. (Note: Round the intermediate calculations to the whole number for the following activity rates: "Reworking products" and "Warranty work". Round the unit cost to two decimal places.) 2a. Suppose that Noguchi loses $5,568,000 in sales per year because it develops a poor reputation due to defective units attributable to failed components. Using wamanty hours, assign the cost of lost sales to each supplier. Manzer $ Buckener $ 2b. By how much would this change the cost of each suppler's component? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Marze! Buckner 3. Bosed on the analysis in Requirements 1 and 2, discuss the importance of activity based suppbier costing for intemal decounon makng. As with product costing, accurate assignment of costs to the cost object is essential for well-grounded deckion:making. Supphers can cause a firm to perform costly activities such as inspection, rework, and warranty work. The of a component is thus more than its purchase price. As thes example shows, the component with the price is actually less expenswe because it causes less demand on intemal costly activities. Thus, the company would likely. the purchases of one supplier in favor of the other. It also might attempt to work with the one supplier which is causng signuficant demands on internal activities to see if the quality of its component can be increased. Activity-Based Product Costing Suppose thot a surgical ward hos gathered the following information for four fuising actmities and two types of patients lor the curfent period: Required: 1. Determine the total numing costs assugned to each potient category. calcalate the nursing cost per patient day for each type of patient ntound your answers to the nearrat cent. Normal per patient day Intenswe per patient day 2. Output is measured in patient days. Assuming that the normal patient category uses 8,000 patent days and the intensive patient category uses 6,400 patient days. calculate the nursing cost pet patient day for each type of patient. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Normal per patient day Intensive per patient day 3. Conceptual Connection; The supervisor of the surgical ward has suggested that patient dars is the conly driver needed to assign nursing costs to each type of patient. Calculate the charge per patient day using this approach. Round your answer to the nearest cent. per patient day 4. Refer to the four data analyac types in fahibrit 22 Select which data analytic types apply for Requirements one through three (more than one type may apply). Requirement t's calculation is in nature as it simply describes what is happening. The same 6 for Requirement 2. Aequirement J, howerver, wes both analytic tyoes: actwisy drvers and patent days is expected to remain the same as the carrent peried. a. Uang ABC, repeat Requrements t and 2 , and descritie the data analytic type(s) beng used. b. Describe how Excet simplifes this calculation, including examples of equations that wauld be used. Using Excel with established equations require only that the actwity rates be updated The calculations produced Activity-Based Supplier Costing Noguchi Company manufactures cooling systems. Noguchi produces all the parts necessary for its product except for one electronic component, which is purchased from two local suppliers: Manzer Inc. and Buckner Company. Both suppliers are reliable and seldom deliver late; however, Manzer sells the component for $89 per unit, while Buckner sells the same component for $86. Nogucha purchases 80% of its components from Buckner because of its lower price. The total annual demand is 4,000,000 camponents To help assess the cost effect of the two components, the following data were collected for supplier related activities and suppliers: 1. Activity Data 1. Calculate the cost per component for each supplier, takang into consideration the costs of the suppher-related activities and using the current prices and sales volume. (Note: Round the intermediate calculations to the whole number for the following activity rates: "Reworking products" and "Warranty work". Round the unit cost to two decimal places.) 2a. Suppose that Noguchi loses $5,568,000 in sales per year because it develops a poor reputation due to defective units attributable to failed components. Using wamanty hours, assign the cost of lost sales to each supplier. Manzer $ Buckener $ 2b. By how much would this change the cost of each suppler's component? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Marze! Buckner 3. Bosed on the analysis in Requirements 1 and 2, discuss the importance of activity based suppbier costing for intemal decounon makng. As with product costing, accurate assignment of costs to the cost object is essential for well-grounded deckion:making. Supphers can cause a firm to perform costly activities such as inspection, rework, and warranty work. The of a component is thus more than its purchase price. As thes example shows, the component with the price is actually less expenswe because it causes less demand on intemal costly activities. Thus, the company would likely. the purchases of one supplier in favor of the other. It also might attempt to work with the one supplier which is causng signuficant demands on internal activities to see if the quality of its component can be increased