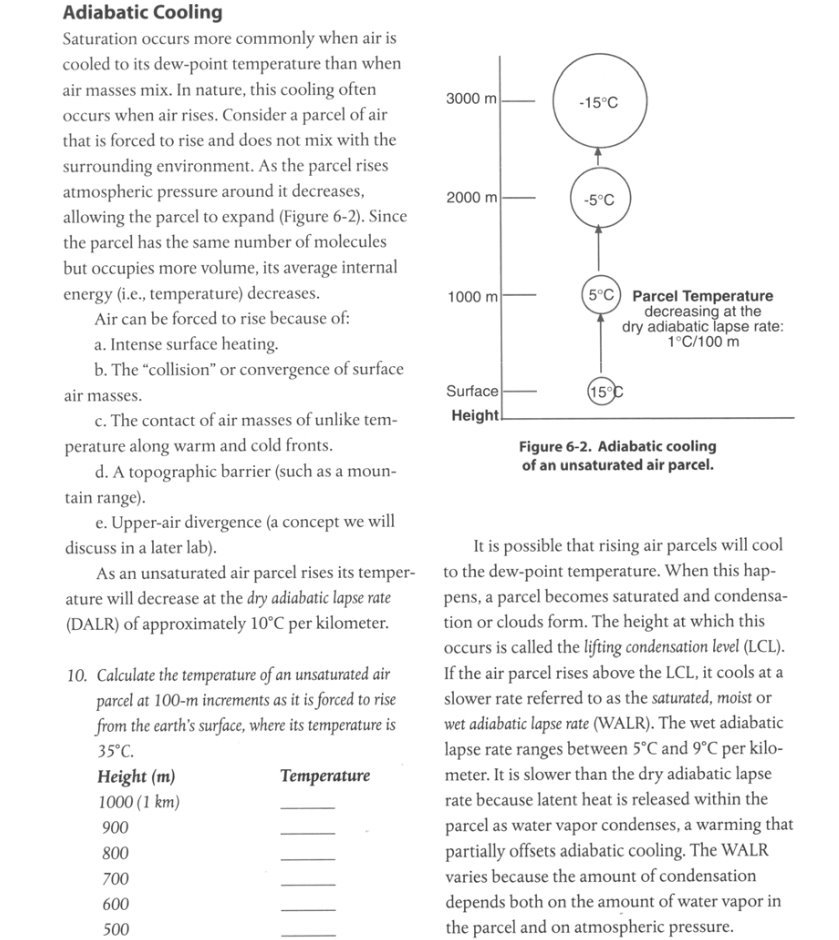
Adiabatic Cooling Saturation occurs more commonly when air is cooled to its dew-point temperature than when air masses mix. In nature, this cooling often occurs when air rises. Consider a parcel of air 3000 m -15 C that is forced to rise and does not mix with the surrounding environment. As the parcel rises atmospheric pressure around it decreases, 2000 m -5.C allowing the parcel to expand (Figure 6-2). Since the parcel has the same number of molecules but occupies more volume, its average internal energy (i.e., temperature) decreases. 1000 m Parcel Temperature Air can be forced to rise because of: decreasing at the a. Intense surface heating. dry adiabatic lapse rate: 1 C/100 m b. The "collision" or convergence of surface air masses. Surface 150 c. The contact of air masses of unlike tem- Height perature along warm and cold fronts. Figure 6-2. Adiabatic cooling d. A topographic barrier (such as a moun- of an unsaturated air parcel. tain range). e. Upper-air divergence (a concept we will discuss in a later lab). It is possible that rising air parcels will cool As an unsaturated air parcel rises its temper- to the dew-point temperature. When this hap- ature will decrease at the dry adiabatic lapse rate pens, a parcel becomes saturated and condensa- (DALR) of approximately 10'C per kilometer. tion or clouds form. The height at which this occurs is called the lifting condensation level (LCL). 10. Calculate the temperature of an unsaturated air If the air parcel rises above the LCL, it cools at a parcel at 100-m increments as it is forced to rise slower rate referred to as the saturated, moist or from the earth's surface, where its temperature is wet adiabatic lapse rate (WALR). The wet adiabatic 35 C. lapse rate ranges between 5"C and 9"C per kilo- Height (m) Temperature meter. It is slower than the dry adiabatic lapse 1000 (1 km) rate because latent heat is released within the 900 parcel as water vapor condenses, a warming that 800 partially offsets adiabatic cooling. The WALK 700 varies because the amount of condensation 600 depends both on the amount of water vapor in 500 the parcel and on atmospheric pressure