After perusing Westpacs Risk Appetite Statement and Pillar 3 disclosures with regards to liquidity risk management:
a. Comment on whether Westpac Bank's Liquidity Coverage Ratio is consistent with its relevant risk appetite.
b. What are the strategies used by the Bank to manage this ratio?
c. Do you agree with the statement that a well-run bank will keep the highest possible level of this ratio? (Justify your response).

After perusing Westpacs Risk Appetite Statement and Pillar 3 disclosures with regards to liquidity risk management:
a. Comment on whether Westpac Bank's Liquidity Coverage Ratio is consistent with its relevant risk appetite.
b. What are the strategies used by the Bank to manage this ratio?
c. Do you agree with the statement that a well-run bank will keep the highest possible level of this ratio? (Justify your response).
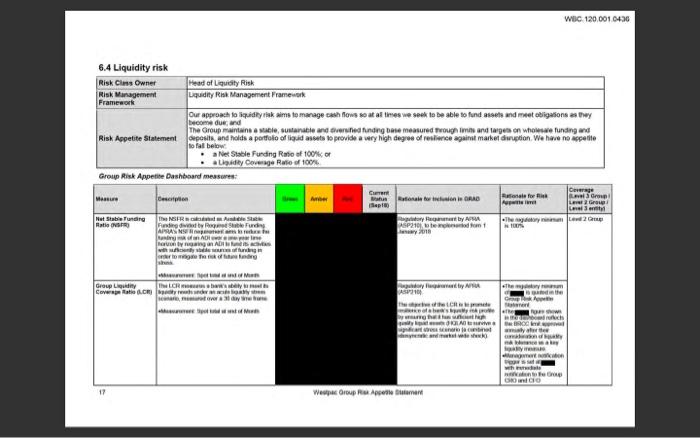
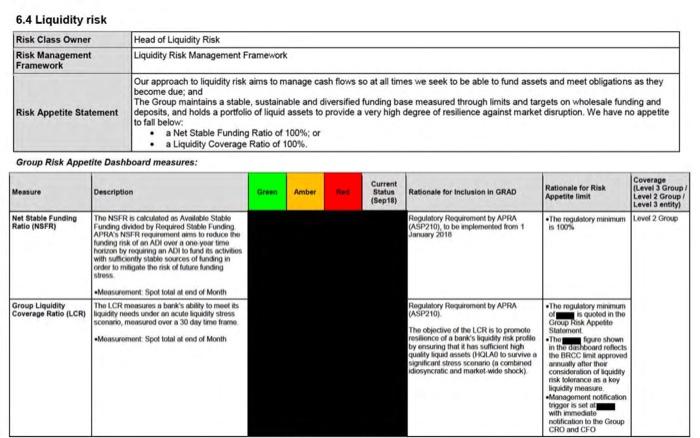
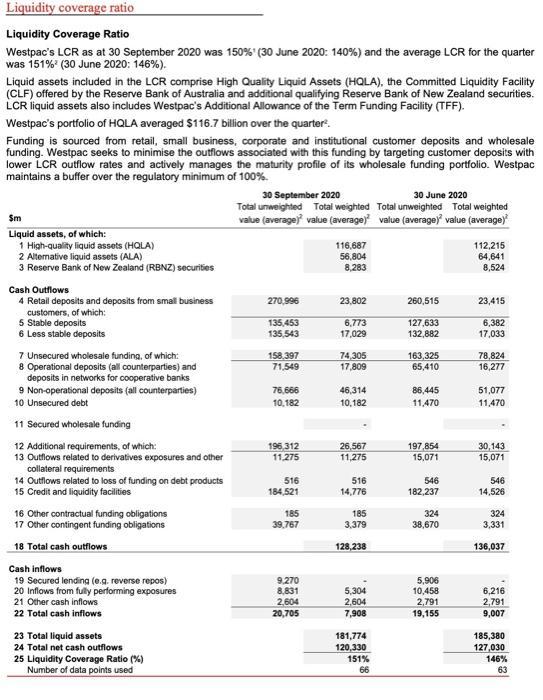
Roskape and risk typce Westpecsaporite for risk is informed by our legitives and business plan. regulatory and and the potential for adverse outcomes that result in material impacts on our customers. Our wat our reputation below target levels in stressed scenarios out regulatorytellinis andior our financial position including the potential for and quidity rates Refer to the State Redes tection of the Web 2000 Annual Report for den on the curent management facing Westec Westpac distinguished between different types of risk and is an integrated aproach toward certifying assessing and managing risks. The review of West's Risk Management Framework, which includes the Risk Management Strategy and Risk Apple Statement together wih he establishment and monitoring of key control rough supporting frews and is la ville Overview of key risk types .nak culture the risk that our outure does not promote and reinforce behavious cation or structures identify understand discuss and confi. This leads to ineffective risk management pour les Group wide and customer outcomes moeding continuous Improvement y aming went integrated into Strategic nik-The risk That Westmoncomite statek choices to not permettre successfully, or does not respond electively to changes in the cerute ennet capital adequacy - the risk the Westpac has an inadequate level or composition of capital to supports nome business active and to meet regulatory capital requiremere under som sperate environments or stressed conditions . Anding and liquidity is the risk that Weste carne mets payment obligation that does not have the appropriate amount, men and composition of tanding and liquidity to support team rederik -Thenak of financial low where a customer or counterparty tails to meet their finance calation to Wester . manat risk - the risk of an adverse impact on camins resulting from charge the value of West position as a result of a change in financial market factors, such as foreign exchanges, terest commodity prices and equity prices. This includes interest rate risk in the banking book them to interest Income from mich between the duration of best in the role of business actives: operational risk the risk of los resulting from date or failed internare, people and systems fomedereverits. This definition excludes strategick Wielewi and regulatory for through inadequate tuled process people and perfromsdal events. These are the primary conduct and compliances your risk the rok that Westpac or is third parties data or technology oly. manipulated or damaged from cybercules or weiter conduct and compliance is the risk of falling to abide by compliance obligation med dus or there kuing to have behavioun and practices that deliver stor for and deutcomes for our customers that support marketing ty . reputational and sustainability risk - the risk that an action inaction, transaction Investment or events reduce bust Westes integrity and competence by clients parties, investors atos, employees or the public and . fnancial criment - the risk that Westpac ale to provenancial rend comply with probe nancial crime registory obligation WS2000 spc Pillar 3 report Controlling and managing ik We have adopted and continue to embed a The Lines of Defence model to aid in and to end management of nak wthin which all employees play an diverse Wewe put in placerisk management framework that deliver subrand de outcomes for our customers the apportare protect Western depositon, policyholders and investors by martineng balance sheet with sound credit quality and buffers over ropullory and meet our regulatory and try obligations The Board is responsible for approving Wespais overall Risk Management Framework for managing francia And non financial risk, including the Westpac Group Risk Management Stathe West Group Risk Appelle Statement and for monitoring the effectiveness of the management by Vespa The Board hot dringuted to the lord sk Committee mponsibility to wish a view of the Group's coment and future risposition rive to trokette and capital stringh: review and frames and policies for managing risk and review and there appropriate, aproveries beyond the prove discretion provided to management In June 2020, the Board Legal Regulatory & Compliance Committee was established a sub-comme of the Board Risk Commits with over franciscrimes munition and registry Investigatiom customer remediation advies and customer complaints compliance and condud risk and material legal and regulatory charge to the Grove WBC 120.001 0436 6.4 Liquidity risk Risk Clms Owner Head of Liquidity Risk Risk Management Liquidity Risk Management Framework Framework Our approach to quity risk is to manage shows so at all times we seek to be able to find assets and meet obligations as they become dus and The Group maintains a sustainable and diverse finding to measured Trough me and targeon whose funding and Risk Appetite Statement posts and holds a portfolo ofiad assets to provide a wry high degree of reforce against market diruption. We have no aspetto to below aNet Stable Funding Ratio of 100.0 aligidity Coverage Rule of 100% Group Risk Appetite Dashboard measures C Coverage Menu Rosie te sien IGRAD Referito Grow The A Nut Stabinding GRS Ratio dygnet by Banding died by Stable Funding The Law APSA NE P210 dom 1 2018 Marian Oraingan AD. as rowego nikdo dag by wym Group Cowgate.com LCR by Ne, ne day AS CR hele www wife na may whe Pore Gondo 17 Werpac Group Acer Risk appetite and risk types Westpac's appetite for risk is informed by our strategic objectives and business plans, regulatory rules and ratios, and the potential for adverse outcomes that result in material impacts on our customers, our staff, our reputation, our regulatory relationships and/or our financial position including the potential for capital and liquidity ratios to fall below target levels in stressed scenarios. Refer to the Strategic Review section of the Westpac 2020 Annual Report for a discussion on the current risk management issues facing Westpac. Westpac distinguishes between different types of risk and takes an integrated approach toward identifying assessing and managing risks. The annual review of Westpac's Risk Management Framework, which includes the Risk Management Strategy and Risk Appetite Statement, together with the establishment and monitoring of key controls through supporting frameworks and policies all play vital roles. Overview of key risk types risk culture - the risk that our culture does not promote and reinforce behavioural expectations or structures to identify, understand, discuss and act on risks. This leads to ineffective risk management, poor risk awareness, risk-taking outside of risk appetite that is tolerated and a culture where key learnings are not integrated into Group-wide and customer outcomes, impeding continuous Improvement: strategic risk - the risk that Westpac makes incomplete strategic choices, does not implement its strategies successfully, or does not respond effectively to changes in the operating environment capital adequacy risk - the risk that Westpac has an inadequate level or composition of capital to support its normal business activities and to meet its regulatory capital requirements under normal operating environments or stressed conditions: funding and liquidity risk - the risk that Westpac cannot meet its payment obligations or that it does not have the appropriate amount, tenor and composition of funding and liquidity to support its assets; credit risk - the risk of financial loss where a customer or counterparty fails to meet their financial obligations to Westpac; market risk - the risk of an adverse impact on earnings resulting from changes in the value of Westpac's positions as a result of a change in financial market factors, such as foreign exchange rates, interest rates, commodity prices and equity prices. This includes interest rate risk in the banking book - the risk to interest income from a mismatch between the duration of assets and liabilities that arises in the normal course of business activities; operational risk - the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. This definition excludes strategic risk. While legal risk and regulatory risk arise through inadequate or failed processes, people and systems or from external events, these are reflected primarily in conduct and compliance risk; cyber risk - the risk that Westpac or its third parties data or technology are inappropriately accessed, manipulated or damaged from cybersecurity threats or vulnerabilities; conduct and compliance risk - the risk of failing to abide by compliance obligations required of us or otherwise failing to have behaviours and practices that deliver suitable, fair and clear outcomes for our customers and that support market integrity; reputational and sustainability risk - the risk that an action, inaction, transaction, investment or event will reduce trust in Westpac's integrity and competence by clients, counterparties, investors regulators, employees or the public; and financial crime risk - the risk that Westpac fails to prevent financial crime and comply with applicable global financial crime regulatory obligations Pillar 3 report Controlling and managing risk We have adopted and continue to embed a Three Lines of Defence model to aid in end-to-end management of risk, within which all employees play an active role. We have put in place a risk management framework that seeks to: deliver suitable, fair and clear outcomes for our customers that support market integrity; protect Westpac's depositors, policyholders and investors by maintaining a balance sheet with sound credit quality and buffers over regulatory minimums; and meet our regulatory and statutory obligations. The Board is responsible for approving Westpac's overall Risk Management Framework for managing financial and non-financial risk, including the Westpac Group Risk Management Strategy and the Westpac Group Risk Appetite Statement and for monitoring the effectiveness of risk management by Westpac. The Board has delegated to the Board Risk Committee responsibility to establish a view of the Group's current and future risk position relative to its risk appetite and capital strength; review and approve frameworks and policies for managing risk; and review and, where appropriate, approve risks beyond the approval discretion provided to management. In June 2020, the Board Legal, Regulatory & Compliance Committee was established as a sub-committee of the Board Risk Committee to assist with overseeing financial crime risk, material litigation and regulatory Investigations, customer remediation activities and customer complaints, compliance and conduct risk and material legal and regulatory change relevant to the Group. 6.4 Liquidity risk Risk Class Owner Head of Liquidity Risk Risk Management Liquidity Risk Management Framework Framework Our approach to liquidity risk aims to manage cash flows so at all times we seek to be able to fund assets and meet obligations as they become due, and The Group maintains a stable, sustainable and diversified funding base measured through limits and targets on wholesale funding and Risk Appetite Statement deposits and holds a portfolio of liquid assets to provide a very high degree of resilience against market disruption. We have no appetite to fall below: a Net Stable Funding Ratio of 100%; or a Liquidity Coverage Ratio of 100% Group Risk Appetite Dashboard measures: Coverage Current Menure Description Amber Status Rationale for inclusion in GRAD Rationale for Risk Level Group Appetite limit Level 2 Group (Sep 18) Level 3 entity Net Stable Funding The NSFR calculated as Available Stable Regulatory Requirement by APRA Ratio (NSFR) Funding divided by Required to Funding ASP210) to be mplemented from 1 The cogatory minimum Lovef 2 Group is 100% APRANSFR groenter to reduce the Jary 2018 unang nk of an AD over a one your time hormon tyregring an ito land is activities with sucony stati sources of funding in order to magte the risk of the funding stress Masurement Sportland of Month Group Liquidity The LCR measures a bank's ability to meet its Regulatory Rogoment by APRA The regulatory minimum Coverage Ratio (LCRdiy needs under an acuto liquidity stress CASP210) 1sted in the scenario, mesured over a 30 day time frame Groups Appetito The objective of the LCR is to promote Statement Mensurement Spot total at end of Month resence of a bank's ligudly nisk protio The fore shown by ensuring that is sufficient high quality (OLAD I SUV the BROCved sigricant stresscon (n combined wwwly after the diosyncratic and market wide shock) consideration of liquidity risk force as a key qually measure Management notification trigoriset with immediate notification to the Group CRO and CFO Liquidity coverage ratio Liquidity Coverage Ratio Westpac's LCR as at 30 September 2020 was 150%! (30 June 2020: 140%) and the average LCR for the quarter was 151% (30 June 2020: 146%). Liquid assets included in the LCR comprise High Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA), the Committed Liquidity Facility (CLF) offered by the Reserve Bank of Australia and additional qualifying Reserve Bank of New Zealand securities. LCR liquid assets also includes Westpac's Additional Allowance of the Term Funding Facility (TFF). Westpac's portfolio of HQLA averaged $116.7 billion over the quarter. Funding is sourced from retail, small business, corporate and institutional customer deposits and wholesale funding. Westpac seeks to minimise the outflows associated with this funding by targeting customer deposits with lower LCR outflow rates and actively manages the maturity profile of its wholesale funding portfolio Westpac maintains a buffer over the regulatory minimum of 100% 30 September 2020 30 June 2020 Total unweighted Total weighted Total unweighted Total weighted $m value (average value (average)value (average)" value (average) Liquid assets, of which: 1 High-quality liquid assets (HQLA) 116,687 112,215 2 Alternative liquid assets (ALA) 64,641 3 Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) securities 8,283 8,524 56,804 270.996 23,802 260,515 23,415 135,453 135,543 6.773 17,029 127,633 132,882 6,382 17.033 158,397 71,549 74,305 17,809 163,325 65,410 78,824 16,277 76.666 10.182 46,314 10.182 86,445 11.470 51,077 11.470 Cash Outflows 4 Retail deposits and deposits from small business customers, of which: 5 Stable deposits 6 Less stable deposits 7 Unsecured wholesale funding, of which 8 Operational deposits (all counterparties) and deposits in networks for cooperative banks 9 Non-operational deposits (all counterparties) 10 Unsecured debt 11 Secured wholesale funding 12 Additional requirements, of which: 13 Outflows related to derivatives exposures and other collateral requirements 14 Outflows related to loss of funding on debt products 15 Credit and liquidity facilities 16 Other contractual funding obligations 17 Other contingent funding obligations 18 Total cash outflows Cash inflows 19 Secured lending (e.g. reverse repos) 20 Inflows from fully performing exposures 21 Other cash inflows 22 Total cash inflows 196 312 11.275 26,567 11,275 197854 15,071 30,143 15,071 516 184,521 516 14,776 546 182,237 546 14,526 185 39,767 185 3,379 324 38,670 324 3,331 128,238 136,037 9.270 8.831 2604 20,705 5,304 2.604 7,908 5,906 10.458 2,791 19,155 6,216 2.791 9,007 23 Total liquid assets 24 Total net cash outflows 25 Liquidity Coverage Ratio (%) Number of data points used 181,774 120,330 151% 66 185,380 127,030 146% 63 Roskape and risk typce Westpecsaporite for risk is informed by our legitives and business plan. regulatory and and the potential for adverse outcomes that result in material impacts on our customers. Our wat our reputation below target levels in stressed scenarios out regulatorytellinis andior our financial position including the potential for and quidity rates Refer to the State Redes tection of the Web 2000 Annual Report for den on the curent management facing Westec Westpac distinguished between different types of risk and is an integrated aproach toward certifying assessing and managing risks. The review of West's Risk Management Framework, which includes the Risk Management Strategy and Risk Apple Statement together wih he establishment and monitoring of key control rough supporting frews and is la ville Overview of key risk types .nak culture the risk that our outure does not promote and reinforce behavious cation or structures identify understand discuss and confi. This leads to ineffective risk management pour les Group wide and customer outcomes moeding continuous Improvement y aming went integrated into Strategic nik-The risk That Westmoncomite statek choices to not permettre successfully, or does not respond electively to changes in the cerute ennet capital adequacy - the risk the Westpac has an inadequate level or composition of capital to supports nome business active and to meet regulatory capital requiremere under som sperate environments or stressed conditions . Anding and liquidity is the risk that Weste carne mets payment obligation that does not have the appropriate amount, men and composition of tanding and liquidity to support team rederik -Thenak of financial low where a customer or counterparty tails to meet their finance calation to Wester . manat risk - the risk of an adverse impact on camins resulting from charge the value of West position as a result of a change in financial market factors, such as foreign exchanges, terest commodity prices and equity prices. This includes interest rate risk in the banking book them to interest Income from mich between the duration of best in the role of business actives: operational risk the risk of los resulting from date or failed internare, people and systems fomedereverits. This definition excludes strategick Wielewi and regulatory for through inadequate tuled process people and perfromsdal events. These are the primary conduct and compliances your risk the rok that Westpac or is third parties data or technology oly. manipulated or damaged from cybercules or weiter conduct and compliance is the risk of falling to abide by compliance obligation med dus or there kuing to have behavioun and practices that deliver stor for and deutcomes for our customers that support marketing ty . reputational and sustainability risk - the risk that an action inaction, transaction Investment or events reduce bust Westes integrity and competence by clients parties, investors atos, employees or the public and . fnancial criment - the risk that Westpac ale to provenancial rend comply with probe nancial crime registory obligation WS2000 spc Pillar 3 report Controlling and managing ik We have adopted and continue to embed a The Lines of Defence model to aid in and to end management of nak wthin which all employees play an diverse Wewe put in placerisk management framework that deliver subrand de outcomes for our customers the apportare protect Western depositon, policyholders and investors by martineng balance sheet with sound credit quality and buffers over ropullory and meet our regulatory and try obligations The Board is responsible for approving Wespais overall Risk Management Framework for managing francia And non financial risk, including the Westpac Group Risk Management Stathe West Group Risk Appelle Statement and for monitoring the effectiveness of the management by Vespa The Board hot dringuted to the lord sk Committee mponsibility to wish a view of the Group's coment and future risposition rive to trokette and capital stringh: review and frames and policies for managing risk and review and there appropriate, aproveries beyond the prove discretion provided to management In June 2020, the Board Legal Regulatory & Compliance Committee was established a sub-comme of the Board Risk Commits with over franciscrimes munition and registry Investigatiom customer remediation advies and customer complaints compliance and condud risk and material legal and regulatory charge to the Grove WBC 120.001 0436 6.4 Liquidity risk Risk Clms Owner Head of Liquidity Risk Risk Management Liquidity Risk Management Framework Framework Our approach to quity risk is to manage shows so at all times we seek to be able to find assets and meet obligations as they become dus and The Group maintains a sustainable and diverse finding to measured Trough me and targeon whose funding and Risk Appetite Statement posts and holds a portfolo ofiad assets to provide a wry high degree of reforce against market diruption. We have no aspetto to below aNet Stable Funding Ratio of 100.0 aligidity Coverage Rule of 100% Group Risk Appetite Dashboard measures C Coverage Menu Rosie te sien IGRAD Referito Grow The A Nut Stabinding GRS Ratio dygnet by Banding died by Stable Funding The Law APSA NE P210 dom 1 2018 Marian Oraingan AD. as rowego nikdo dag by wym Group Cowgate.com LCR by Ne, ne day AS CR hele www wife na may whe Pore Gondo 17 Werpac Group Acer Risk appetite and risk types Westpac's appetite for risk is informed by our strategic objectives and business plans, regulatory rules and ratios, and the potential for adverse outcomes that result in material impacts on our customers, our staff, our reputation, our regulatory relationships and/or our financial position including the potential for capital and liquidity ratios to fall below target levels in stressed scenarios. Refer to the Strategic Review section of the Westpac 2020 Annual Report for a discussion on the current risk management issues facing Westpac. Westpac distinguishes between different types of risk and takes an integrated approach toward identifying assessing and managing risks. The annual review of Westpac's Risk Management Framework, which includes the Risk Management Strategy and Risk Appetite Statement, together with the establishment and monitoring of key controls through supporting frameworks and policies all play vital roles. Overview of key risk types risk culture - the risk that our culture does not promote and reinforce behavioural expectations or structures to identify, understand, discuss and act on risks. This leads to ineffective risk management, poor risk awareness, risk-taking outside of risk appetite that is tolerated and a culture where key learnings are not integrated into Group-wide and customer outcomes, impeding continuous Improvement: strategic risk - the risk that Westpac makes incomplete strategic choices, does not implement its strategies successfully, or does not respond effectively to changes in the operating environment capital adequacy risk - the risk that Westpac has an inadequate level or composition of capital to support its normal business activities and to meet its regulatory capital requirements under normal operating environments or stressed conditions: funding and liquidity risk - the risk that Westpac cannot meet its payment obligations or that it does not have the appropriate amount, tenor and composition of funding and liquidity to support its assets; credit risk - the risk of financial loss where a customer or counterparty fails to meet their financial obligations to Westpac; market risk - the risk of an adverse impact on earnings resulting from changes in the value of Westpac's positions as a result of a change in financial market factors, such as foreign exchange rates, interest rates, commodity prices and equity prices. This includes interest rate risk in the banking book - the risk to interest income from a mismatch between the duration of assets and liabilities that arises in the normal course of business activities; operational risk - the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. This definition excludes strategic risk. While legal risk and regulatory risk arise through inadequate or failed processes, people and systems or from external events, these are reflected primarily in conduct and compliance risk; cyber risk - the risk that Westpac or its third parties data or technology are inappropriately accessed, manipulated or damaged from cybersecurity threats or vulnerabilities; conduct and compliance risk - the risk of failing to abide by compliance obligations required of us or otherwise failing to have behaviours and practices that deliver suitable, fair and clear outcomes for our customers and that support market integrity; reputational and sustainability risk - the risk that an action, inaction, transaction, investment or event will reduce trust in Westpac's integrity and competence by clients, counterparties, investors regulators, employees or the public; and financial crime risk - the risk that Westpac fails to prevent financial crime and comply with applicable global financial crime regulatory obligations Pillar 3 report Controlling and managing risk We have adopted and continue to embed a Three Lines of Defence model to aid in end-to-end management of risk, within which all employees play an active role. We have put in place a risk management framework that seeks to: deliver suitable, fair and clear outcomes for our customers that support market integrity; protect Westpac's depositors, policyholders and investors by maintaining a balance sheet with sound credit quality and buffers over regulatory minimums; and meet our regulatory and statutory obligations. The Board is responsible for approving Westpac's overall Risk Management Framework for managing financial and non-financial risk, including the Westpac Group Risk Management Strategy and the Westpac Group Risk Appetite Statement and for monitoring the effectiveness of risk management by Westpac. The Board has delegated to the Board Risk Committee responsibility to establish a view of the Group's current and future risk position relative to its risk appetite and capital strength; review and approve frameworks and policies for managing risk; and review and, where appropriate, approve risks beyond the approval discretion provided to management. In June 2020, the Board Legal, Regulatory & Compliance Committee was established as a sub-committee of the Board Risk Committee to assist with overseeing financial crime risk, material litigation and regulatory Investigations, customer remediation activities and customer complaints, compliance and conduct risk and material legal and regulatory change relevant to the Group. 6.4 Liquidity risk Risk Class Owner Head of Liquidity Risk Risk Management Liquidity Risk Management Framework Framework Our approach to liquidity risk aims to manage cash flows so at all times we seek to be able to fund assets and meet obligations as they become due, and The Group maintains a stable, sustainable and diversified funding base measured through limits and targets on wholesale funding and Risk Appetite Statement deposits and holds a portfolio of liquid assets to provide a very high degree of resilience against market disruption. We have no appetite to fall below: a Net Stable Funding Ratio of 100%; or a Liquidity Coverage Ratio of 100% Group Risk Appetite Dashboard measures: Coverage Current Menure Description Amber Status Rationale for inclusion in GRAD Rationale for Risk Level Group Appetite limit Level 2 Group (Sep 18) Level 3 entity Net Stable Funding The NSFR calculated as Available Stable Regulatory Requirement by APRA Ratio (NSFR) Funding divided by Required to Funding ASP210) to be mplemented from 1 The cogatory minimum Lovef 2 Group is 100% APRANSFR groenter to reduce the Jary 2018 unang nk of an AD over a one your time hormon tyregring an ito land is activities with sucony stati sources of funding in order to magte the risk of the funding stress Masurement Sportland of Month Group Liquidity The LCR measures a bank's ability to meet its Regulatory Rogoment by APRA The regulatory minimum Coverage Ratio (LCRdiy needs under an acuto liquidity stress CASP210) 1sted in the scenario, mesured over a 30 day time frame Groups Appetito The objective of the LCR is to promote Statement Mensurement Spot total at end of Month resence of a bank's ligudly nisk protio The fore shown by ensuring that is sufficient high quality (OLAD I SUV the BROCved sigricant stresscon (n combined wwwly after the diosyncratic and market wide shock) consideration of liquidity risk force as a key qually measure Management notification trigoriset with immediate notification to the Group CRO and CFO Liquidity coverage ratio Liquidity Coverage Ratio Westpac's LCR as at 30 September 2020 was 150%! (30 June 2020: 140%) and the average LCR for the quarter was 151% (30 June 2020: 146%). Liquid assets included in the LCR comprise High Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA), the Committed Liquidity Facility (CLF) offered by the Reserve Bank of Australia and additional qualifying Reserve Bank of New Zealand securities. LCR liquid assets also includes Westpac's Additional Allowance of the Term Funding Facility (TFF). Westpac's portfolio of HQLA averaged $116.7 billion over the quarter. Funding is sourced from retail, small business, corporate and institutional customer deposits and wholesale funding. Westpac seeks to minimise the outflows associated with this funding by targeting customer deposits with lower LCR outflow rates and actively manages the maturity profile of its wholesale funding portfolio Westpac maintains a buffer over the regulatory minimum of 100% 30 September 2020 30 June 2020 Total unweighted Total weighted Total unweighted Total weighted $m value (average value (average)value (average)" value (average) Liquid assets, of which: 1 High-quality liquid assets (HQLA) 116,687 112,215 2 Alternative liquid assets (ALA) 64,641 3 Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) securities 8,283 8,524 56,804 270.996 23,802 260,515 23,415 135,453 135,543 6.773 17,029 127,633 132,882 6,382 17.033 158,397 71,549 74,305 17,809 163,325 65,410 78,824 16,277 76.666 10.182 46,314 10.182 86,445 11.470 51,077 11.470 Cash Outflows 4 Retail deposits and deposits from small business customers, of which: 5 Stable deposits 6 Less stable deposits 7 Unsecured wholesale funding, of which 8 Operational deposits (all counterparties) and deposits in networks for cooperative banks 9 Non-operational deposits (all counterparties) 10 Unsecured debt 11 Secured wholesale funding 12 Additional requirements, of which: 13 Outflows related to derivatives exposures and other collateral requirements 14 Outflows related to loss of funding on debt products 15 Credit and liquidity facilities 16 Other contractual funding obligations 17 Other contingent funding obligations 18 Total cash outflows Cash inflows 19 Secured lending (e.g. reverse repos) 20 Inflows from fully performing exposures 21 Other cash inflows 22 Total cash inflows 196 312 11.275 26,567 11,275 197854 15,071 30,143 15,071 516 184,521 516 14,776 546 182,237 546 14,526 185 39,767 185 3,379 324 38,670 324 3,331 128,238 136,037 9.270 8.831 2604 20,705 5,304 2.604 7,908 5,906 10.458 2,791 19,155 6,216 2.791 9,007 23 Total liquid assets 24 Total net cash outflows 25 Liquidity Coverage Ratio (%) Number of data points used 181,774 120,330 151% 66 185,380 127,030 146% 63