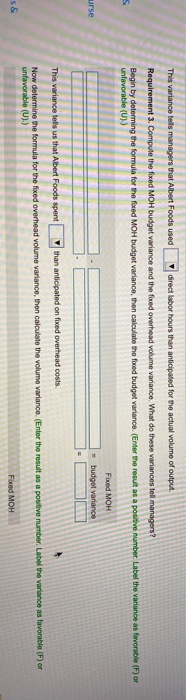
Albert Foods processes bags of organic frozen fruits sold at specialty grocery stores. (Click the loon to view additional information) Read the requirements Requirement 1. How much variable overhead would have been allocated to production? How much fixed overhead would have been allocated to production? The variable overhead allocated to production is $ Now determine the fixed overhead allocated to production The fixed overhead allocated to production is $ Requirement 2. Compute the variable MOH rate variance and the variable MOH efficiency variance. What do these variances toll managers? Begin by determing the formula for the variable MOH rate variance, then calculate the variable overhead rate variance. (Enter the result as a positive number. Enter rates to two decimal places. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Variable overhead rate variance This variance tells managers that Albert Foods actually incurred on variable manufacturing overhead than they would have expected given the actual hours used. Now determine the formula for the variable MOH officiency variance, then calculate the efficiency variance. (Enter the result as a positive number. Enter any rates to two decimal places Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Variable overhead efficiency variance x This variance tels managers that Albert Foods used direct labor hours than anticipated for the actual volume of output Requirement 3. Compute the fixed MOH budget variance and the foued overhead volume variance. What do these variances tell managers? Begin by determing the formula for the fixed MOH budget variance, then calculate the fixed budget variance. (Enter the result as a positive number. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) 5 Forced MOH urse - budget variance This variance tells us that Albert Foods spent than anticipated on fixed overhead costs Now determine the formula for the fixed overhead volume variance, then calculate the volume variance. (Enter the result as a positive number. Label the variance as favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Faced MOH s & Forced MOH = budget variance This variance tells us that Albert Foods spent than anticipated on fixed overhead costs Now determine the formula for the fixed overhead volumo variance, then calculate the volume varianos. (Enter the result as a positive number. Label the variance as tuvorable (F) or unfavorable (U).) Fixed MOH = volume variance This variance tells managers that Albert Foods produced cases of frozen organic fruits than originally expected. The company allocates manufacturing overhead based on direct labor hours. Albert has budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead for the year to be $624,000. The predetermined fixed manufacturing overhead rate is $15.80 per direct labor hour, while the standard variable manufacturing overhead rate is $0.90 per direct labor hour. The direct labor standard for each case is one - quarter (0.25) of an hour. nt erhe The company actually processed 168,000 cases of frozen organic fruits during the year and incurred $694,200 of manufacturing overhead. Of this amount, $652,000 was fixed. The company also incurred a total of 42,200 direct labor hours. ood 1. How much variable overhead would have been allocated to production? How much fixed overhead would have been allocated to production? 2. Compute the variable MOH rate variance and the variable MOH efficiency variance. What do these variances tell managers? 3. Compute the fixed MOH budget variance and the fixed overhead volume variance. What do these variances tell managers? fixe he