Question
All business decision problems have certain common characteristics. These four items below constitute a formal description of the problem and provide the structure necessary for
All business decision problems have certain common characteristics.
These four items below constitute a formal description of the problem and provide the structure necessary for a solution:
1. A decision-maker
2. Choices or alternative courses of action (strategies)
3. Events or states of nature
4. Consequences or payoffs.
Suppose you are the inventory manager of T-Shirts R Us. Your company is an online store that sells T-shirts and nothing else. You have to decide how many men's T-shirts to order for the summer season.
You buy the T-shirts from an offshore manufacturer who imposes a condition on you; you have to order in batches of 100. If only 100 T-shirts are ordered, the cost is $10 per shirt, if 200 or more are ordered, the cost is $9 per shirt; and if 300 or more shirts are ordered the cost is $8.50 per shirt.
The results of market survey provide you with information that the selling price will be $12 per shirt and that the possible sales levels are 100, 150, or 200 units; but you cannot assign any probability estimate to the alternative levels of demand or sales.
If any T- shirt remains unsold during summer, it can be disposed off at half the price ($6) in winter. The marketing manager also feels that there is a goodwill loss of $.50 for each T-shirt that consumers want to purchase from your shop but cannot because of stock-outs.
It is not possible for you to wait for some time to study the nature (or determine the level) of demand, nor can you place more than one order. Thus, complete uncertainty prevails.
As the inventory manager, you must decide how many T- shirts to order in the face of uncertain demand.
The three alternative strategies are to order 100 shirts (A1), 200 shirts (A2) or 300 shirts (A3).
The states of nature are three levels of demand: 100 (D1), 150 (D2), or 200 (D3). You are forced to make this decision in the face of uncertainty because you don't know what the demand level will be.
Consequences are measures of the net benefit or payoff (reward) association with each of the levels of demand. The specific consequence or outcome depends not only on the decision (A1, A2, or A3) that is made but also on the event (D1, D2, or D3) that occurs.
There is a consequence or outcome associated with each combination of decision or action and event. These consequences are generally summarized in a payoff matrix.
The Payoff Matrix:
A payoff matrix is an essential tool of decision-making. It is a nice way of summarizing the interactions of various alternative action and events. Thus we can say that a payoff matrix provides the decision-maker with quantitative measures of the payoff for each possible consequence and for each alternative under consideration.
Please I need to know the ANSWERS OF BELOW IMAGES :
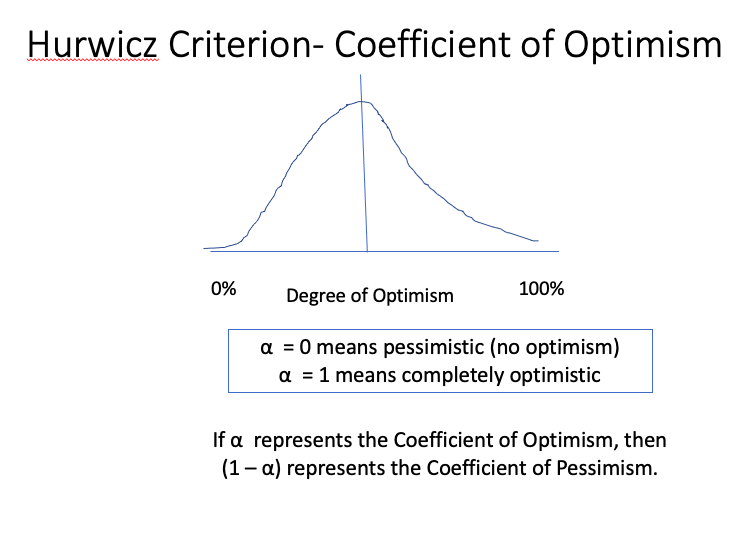
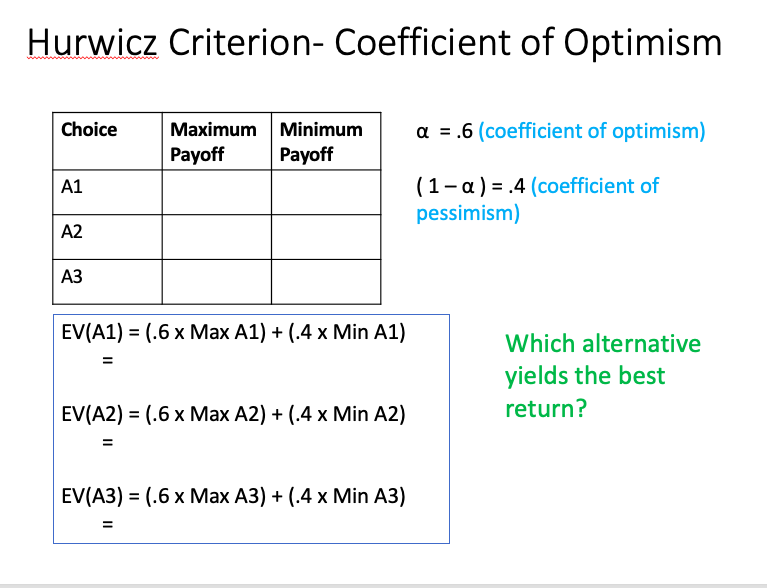
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


