Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(ALL of the drop-down options are either INCREASES, DECREASES, or NO CHANGE) The effect of transactions on ratios (ALL of the drop-down options are either
(ALL of the drop-down options are either INCREASES, DECREASES, or NO CHANGE)
The effect of transactions on ratios
(ALL of the drop-down options are either INCREASES, DECREASES, or NO CHANGE)
(ALL of the drop-down options are either INCREASES, DECREASES, or NO CHANGE)
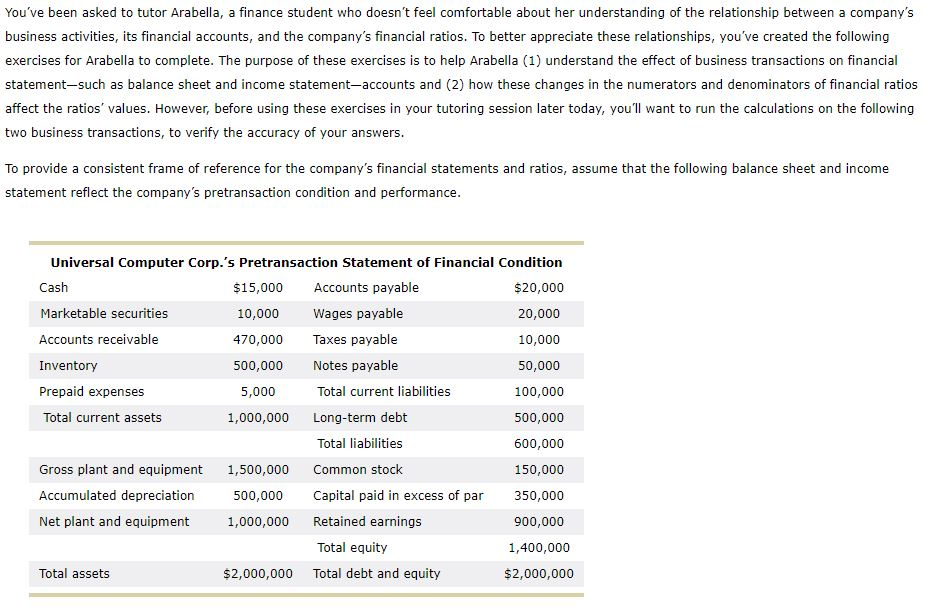
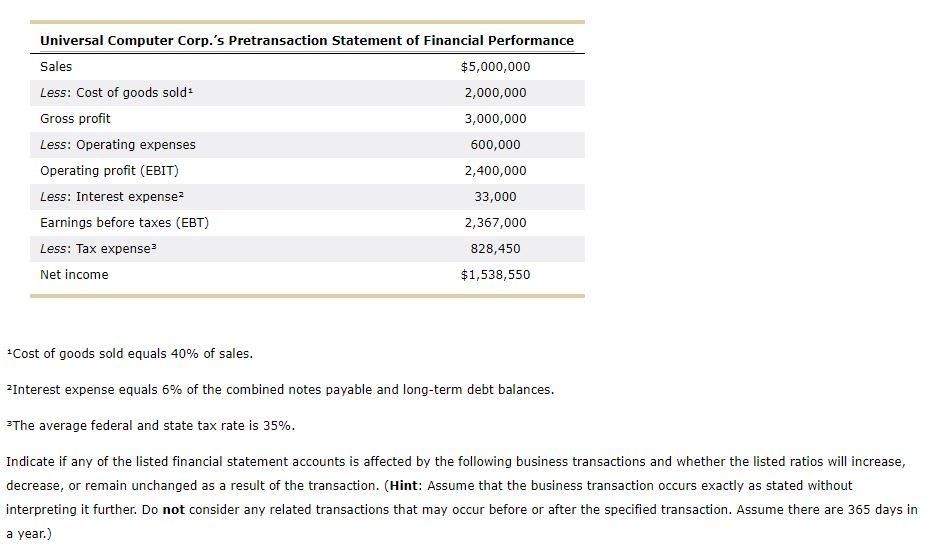
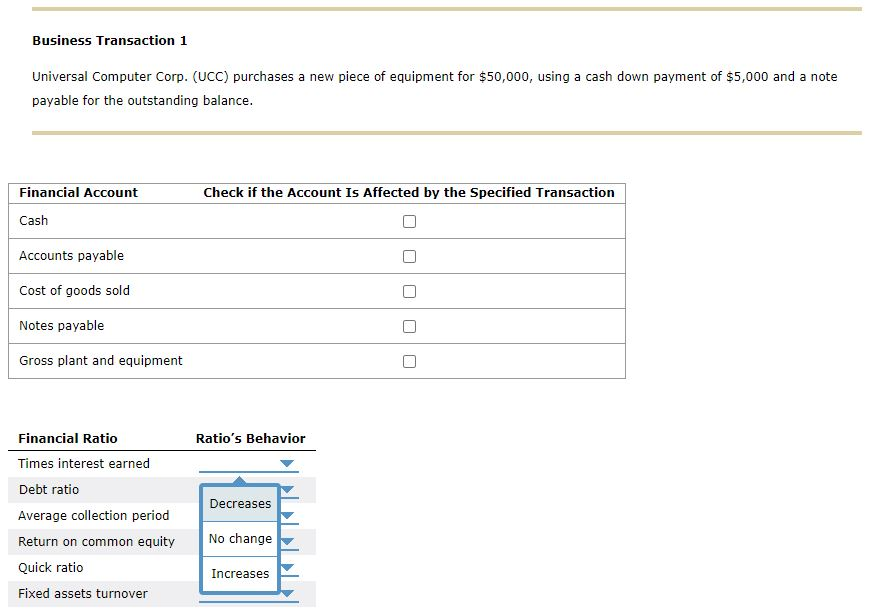
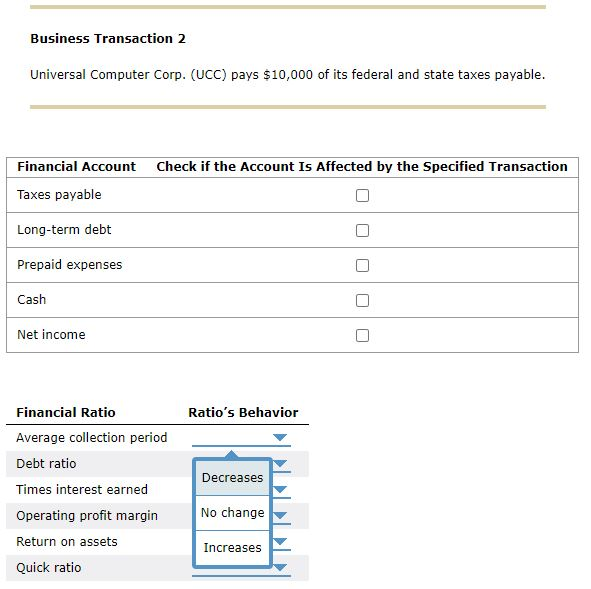
You've been asked to tutor Arabella, a finance student who doesn't feel comfortable about her understanding of the relationship between a company's business activities, its financial accounts, and the company's financial ratios. To better appreciate these relationships, you've created the following exercises for Arabella to complete. The purpose of these exercises is to help Arabella (1) understand the effect of business transactions on financial statement-such as balance sheet and income statement-accounts and (2) how these changes in the numerators and denominators of financial ratios affect the ratios' values. However, before using these exercises in your tutoring session later today, you'll want to run the calculations on the following two business transactions, to verify the accuracy of your answers. To provide a consistent frame of reference for the company's financial statements and ratios, assume that the following balance sheet and income statement reflect the company's pretransaction condition and performance. Universal Computer Corp.'s Pretransaction Statement of Financial Condition Cash $15,000 Accounts payable $20,000 Marketable securities 10,000 Wages payable 20,000 Accounts receivable 470,000 Taxes payable 10,000 Inventory 500,000 Notes payable 50,000 Prepaid expenses 5,000 Total current liabilities 100,000 Total current assets 1,000,000 Long-term debt 500,000 Total liabilities 600,000 Gross plant and equipment 1,500,000 Common stock 150,000 Accumulated depreciation 500,000 Capital paid in excess of par 350,000 Net plant and equipment 1,000,000 Retained earnings 900,000 Total equity 1,400,000 Total assets $2,000,000 Total debt and equity $2,000,000 Universal Computer Corp.'s Pretransaction Statement of Financial Performance Sales $5,000,000 Less: Cost of goods sold 2,000,000 Gross profit 3,000,000 Less: Operating expenses 600,000 Operating profit (EBIT) 2,400,000 Less: Interest expensez 33,000 Earnings before taxes (EBT) 2,367,000 Less: Tax expense? 828,450 Net income $1,538,550 - Cost of goods sold equals 40% of sales. 2 Interest expense equals 6% of the combined notes payable and long-term debt balances. The average federal and state tax rate is 35%. Indicate if any of the listed financial statement accounts is affected by the following business transactions and whether the listed ratios will increase, decrease, or remain unchanged as a result of the transaction. (Hint: Assume that the business transaction occurs exactly as stated without interpreting it further. Do not consider any related transactions that may occur before or after the specified transaction. Assume there are 365 days in a year.) Business Transaction 1 Universal Computer Corp. (UCC) purchases a new piece of equipment for $50,000, using a cash down payment of $5,000 and a note payable for the outstanding balance. Check if the Account Is Affected by the Specified Transaction Financial Account Cash Accounts payable Cost of goods sold Notes payable Gross plant and equipment Ratio's Behavior Financial Ratio Times interest earned Debt ratio Average collection period Return on common equity Quick ratio Decreases No change Increases Fixed assets turnover Business Transaction 2 Universal Computer Corp. (UCC) pays $10,000 of its federal and state taxes payable. Financial Account Check if the Account Is Affected by the Specified Transaction Taxes payable Long-term debt Prepaid expenses Cash Net income Ratio's Behavior Decreases Financial Ratio Average collection period Debt ratio Times interest earned Operating profit margin Return on assets Quick ratio No change IncreasesStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


