Question
all the DFAs and NFAs in this homework use = {0, 1} as the alphabet. 1. (50 point) For i=1,2 and 3, design NFAs Ni,
all the DFAs and NFAs in this homework use = {0, 1} as the alphabet.
1.
(50 point) For i=1,2 and 3, design NFAs Ni, such that L(Ni) = B5, where:
(a) B1 = {w | w has an even number of 0 s, or, contains exactly two 1 s}. (b) B2 = {w | every odd position of w is 1}. (c) B3 = {w | all strings except the empty string and the string 11}. (d) B4 = {0} with two states.
(e) B5 = 011+ with three states.
Your answer should provide, for each NFA, a finite state diagram where all the states, the starting state, all of the accepting states and all the transitions (with the corresponding labels) are dis- played/drawn clearly. Show intermediate step(s) when applicable.
2.

3.
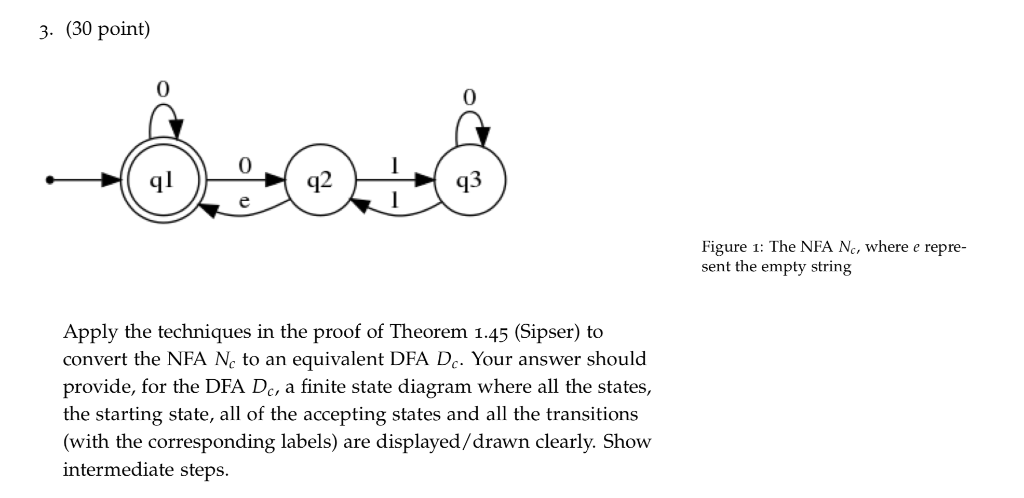
2. (20 point) By using the NFAs you have constructed in the first question, apply the standard methods as desribed in in Sipser (Figure 1.46, 1.48 and 1.50) to design NFA Na and a NFA N, such that Your answer should provide, for each DFA, a finite state diagram where all the states, the starting state, all of the accepting states and all the transitions (with the corresponding labels) are dis played/drawn clearly. Show intermediate steps. 3. (30 point) 0 0 0 q2 q3 Figure 1: The NFA Nc, where e repre- sent the empty string Apply the techniques in the proof of Theorem 1.45 (Sipser) to convert the NFA Nc to an equivalent DFA Dc. Your answer should provide, for the DFA D, a finite state diagram where all the states, the starting state, all of the accepting states and all the transitions (with the corresponding labels) are displayed/drawn clearly. Show intermediate steps
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


