Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
An Inventory Game to Introduce Variable Demand - The new flying broomstick Nimbus 2020 has just come out! Quidditch fans and broomstick retail stores
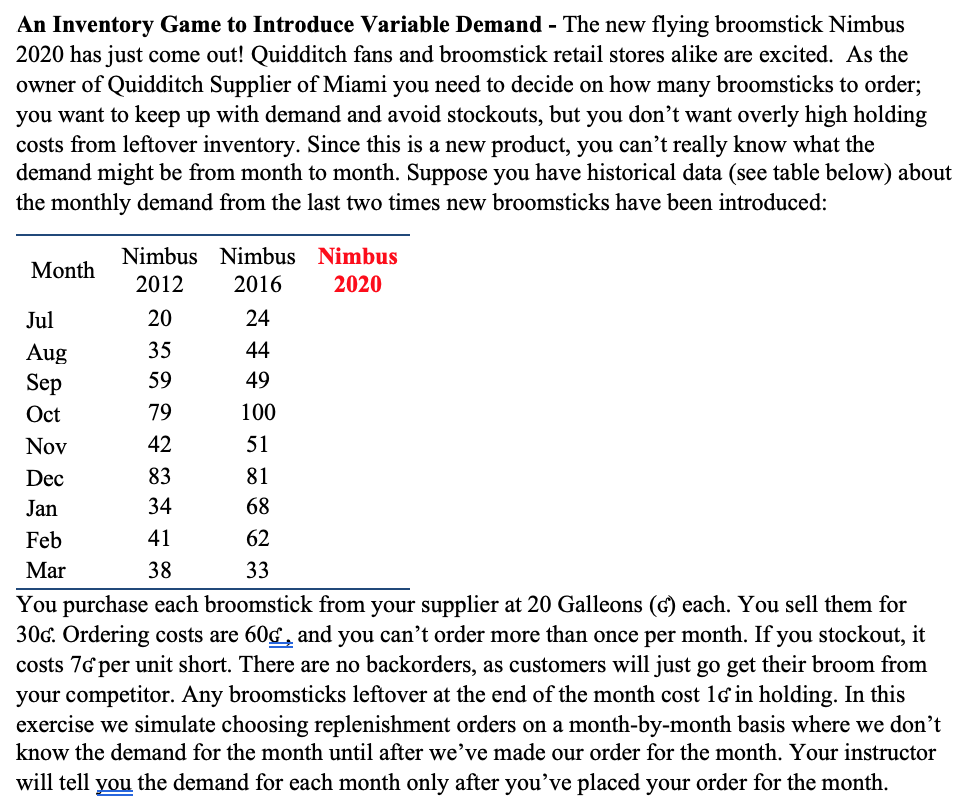
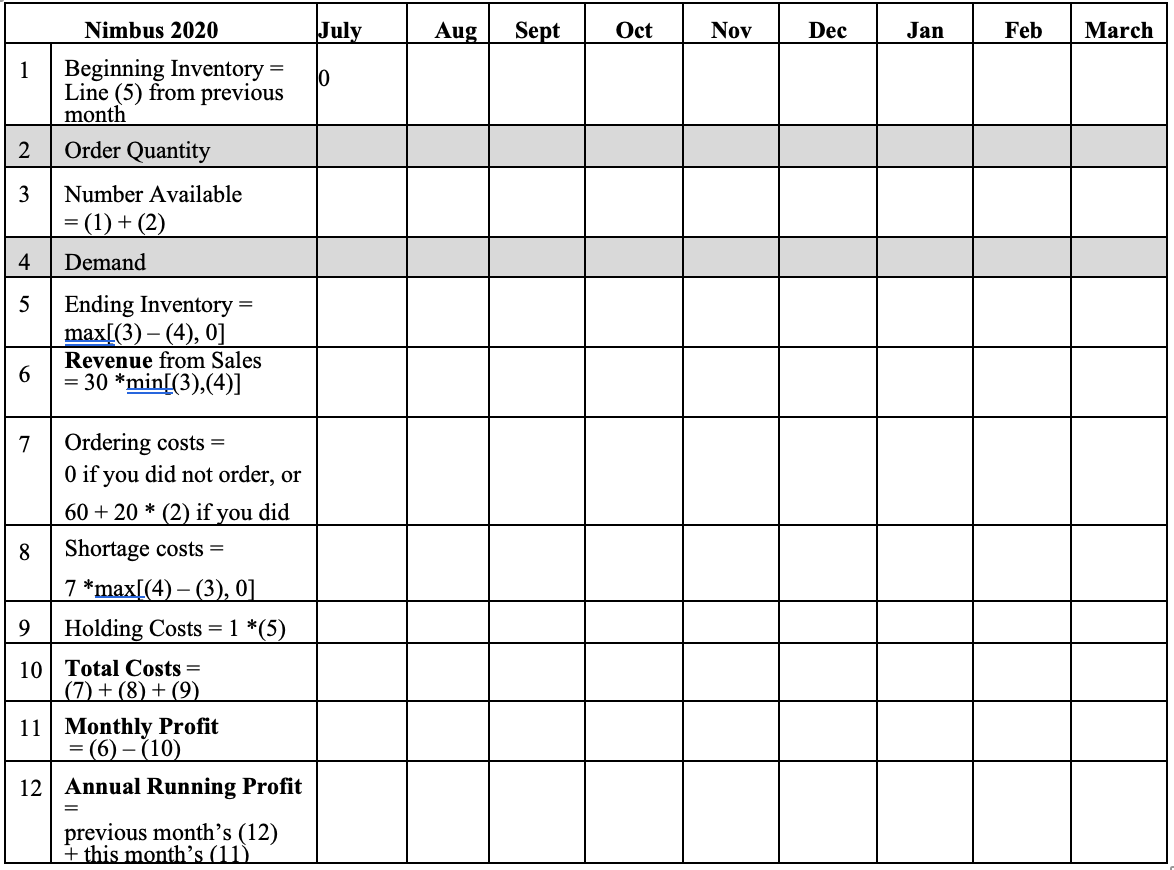
An Inventory Game to Introduce Variable Demand - The new flying broomstick Nimbus 2020 has just come out! Quidditch fans and broomstick retail stores alike are excited. As the owner of Quidditch Supplier of Miami you need to decide on how many broomsticks to order; you want to keep up with demand and avoid stockouts, but you don't want overly high holding costs from leftover inventory. Since this is a new product, you can't really know what the demand might be from month to month. Suppose you have historical data (see table below) about the monthly demand from the last two times new broomsticks have been introduced: Nimbus Nimbus Nimbus Month 2012 2016 2020 Jul 20 24 Aug 35 44 Sep 59 49 Oct 79 100 Nov 42 51 Dec 83 81 Jan 34 68 Feb 41 62 38 Mar 33 You purchase each broomstick from your supplier at 20 Galleons (G) each. You sell them for 30G. Ordering costs are 60G, and you can't order more than once per month. If you stockout, it costs 76 per unit short. There are no backorders, as customers will just go get their broom from your competitor. Any broomsticks leftover at the end of the month cost 16 in holding. In this exercise we simulate choosing replenishment orders on a month-by-month basis where we don't know the demand for the month until after we've made our order for the month. Your instructor will tell you the demand for each month only after you've placed your order for the month. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Nimbus 2020 Beginning Inventory = Line (5) from previous month Order Quantity Number Available = (1)+(2) Demand Ending Inventory = max[(3) (4), 0] Revenue from Sales = 30*min[(3),(4)] Ordering costs = 0 if you did not order, or 6020 (2) if you did Shortage costs = 7 *max[(4)(3), 0] 9 Holding Costs = 1 *(5) 10 Total Costs = (7)+(8)+(9) 11 Monthly Profit = (6) (10) 12 Annual Running Profit previous month's (12) + this month's (11) July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


