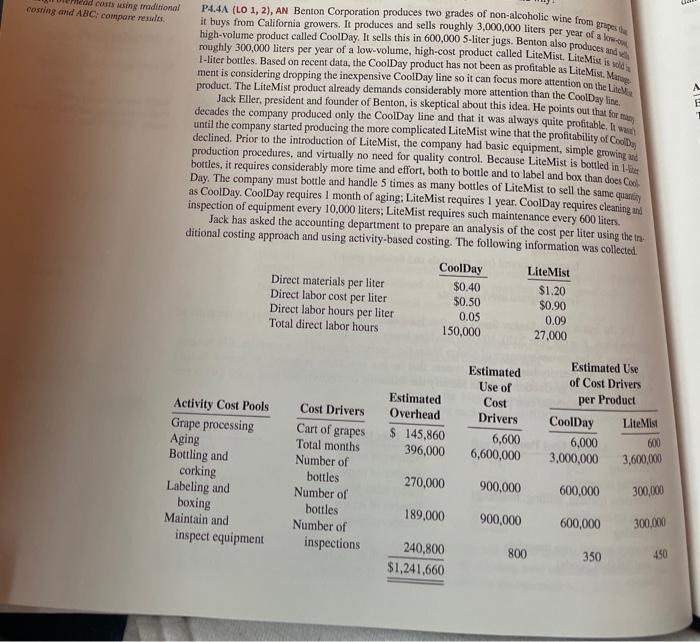
an Wed costs using traditional costing and ABC compare rendes it buys from California growers. It produces and sells roughly 3,000,000 liters per year of a low- P4.4A (LO 1, 2), AN Benton Corporation produces two grades of non-alcoholic wine from grupos high-volume product called CoolDay. It sells this in 600,000 5-liter jugs, Benton also produces and roughly 300,000 liters per year of a low-volume, high-cost product called Lite Mist. Lite Mist is I-liter bottles. Based on recent data, the CoolDay product has not been as profitable as Lite Mist. Mata m17 ment is considering dropping the inexpensive CoolDay line so it can focus more attention on the Lite product. The Lite Mist product already demands considerably more attention than the CoolDayline Jack Eller, president and founder of Benton, is skeptical about this idea. He points out that for meg decades the company produced only the CoolDay line and that it was always quite profitable. It was until the company started producing the more complicated Lite Mist wine that the profitability of Code declined. Prior to the introduction of Lite Mist, the company had basic equipment, simple growing and production procedures, and virtually no need for quality control. Because Lite Mist is bottled in 1-lite bottles, it requires considerably more time and effort, both to bottle and to label and box than does Col Day. The company must bottle and handle 5 times as many bottles of Lite Mist to sell the same quantity as CoolDay. CoolDay requires 1 month of aging: Lite Mist requires 1 year. CoolDay requires cleaning and inspection of equipment every 10,000 liters, LiteMist requires such maintenance every 600 liters. Jack has asked the accounting department to prepare an analysis of the cost per liter using the tra ditional costing approach and using activity-based costing. The following information was collected CoolDay Lite Mist Direct materials per liter $0.40 $1.20 Direct labor cost per liter $0.50 $0.90 Direct labor hours per liter 0.05 0.09 Total direct labor hours 150,000 27.000 Cost Drivers Estimated Use of Cost Drivers 6,600 6,600,000 Estimated Overhead $ 145,860 396,000 Estimated Use of Cost Drivers per Product CoolDay Lite Mist 6,000 600 3,000,000 3,600,000 Cart of grapes Activity Cost Pools Grape processing Aging Bottling and corking Labeling and boxing Maintain and inspect equipment 270,000 900,000 Total months Number of bottles Number of bottles Number of inspections 600,000 300,000 189,000 900,000 600,000 300,000 240,800 $1,241,660 800 350 450 Cartoons Instructions Answer each of the following questions. (Round all calculations to three decimal places.) 2. Under traditional product costing using direct labor hours, compute the total manufacturing cost b. Under ABC, prepare a schedule showing the computation of the activity-based overhead rates c Prepare a schedule assigning cach activity's overhead cost pool to each product, based on the use of liter of both products. 2.C (per cost driver) Co-CD , Include a computation of overhead cost per liter. d. Compute the total manufacturing cost per liter for both products under ABC, c. Write a memo to Jack Eller discussing the implications of your analysis for the company's plans. In this memo, provide a brief description of ABC as well as an explanation of how the traditional approach can result in distortions